Do you know the differences between workstation and desktop? If you are considering whether to buy a workstation or a desktop, you can read this post, in which MiniTool lists 7 differences of workstation vs desktop.
Some people may wonder what the difference is between workstation and desktop. To put it bluntly, the workstation is also a type of desktop computer, but it is different from the ordinary computer.
In terms of appearance, you cannot distinguish them and the workstation’s appearance is basically the same as the ordinary desktop computers’. Then, what makes the workstation different from the ordinary desktop computer? Now, follow me to learn about workstation vs desktop.
1. CPU
A workstation computer requires a processing power for compute-intensive applications. Therefore, it’s usually configured with multiple processor cores. More processor cores mean more processing abilities, which make the workstation respond more quickly, and multiple applications can be run simultaneously without performance loss.
Ordinary desktops usually install a CPU ranging from Intel Core i3 to Intel Core i7, while a workstation usually installs a CPU starts with an Intel Core i7 and includes at least one or two Intel Xeon processors.
8 Useful Solutions to Fix Your CPU 100% in Windows 10
2. Memory
An entry-level work-station is typically configured with about twice the memory of a desktop PC (or with the same amount of memory using smaller, lower cost DIMMs), so that it is capable of large tasks.
Besides, all Intel Xeon processor-based workstations support Error Correcting Code Memory (ECC Memory), which automatically detects and corrects up to 99.9998 percent of memory errors to improve data integrity and system uptime.
3. Hard Drive
Ordinary desktop computers usually include an HDD or a SATA SSD. Some high-end computers may include PCI-E SSD. However, workstation may consider RAID or use PCI-E SSD directly.
4. GPU
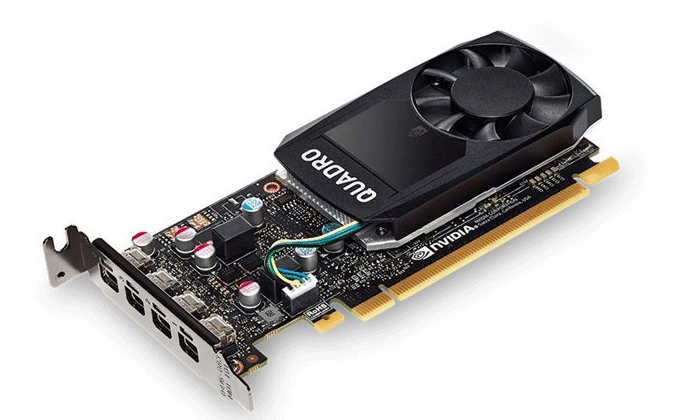
Desktop computers usually use ordinary graphics cards like Nvidia geforce, which focuses on optimizing DirectX and a few games that use OpenGL. However, workstations generally use professional graphics cards like Nvidia quadro or firepro, which can display complex 3D models with high precision, fully support the OpenGL standard and SLI architecture.
In this way, workstations can support more multi-head output and higher screen resolution, meeting modeling design, finance and other users’ needs for large screen display.
5. Performance and Reliability
In terms of performance, a desktop has enough power to do most tasks such as email, web surfing, word processing, and gaming. But workstation components can produce several times the power of consumer-level hardware (depending on the configuration).
Workstations can handle CAD, animation, data analysis, and photorealistic renderings, as well as video and audio creation and editing.
As for reliability, many components in a workstation are held to a higher standard than what’s found in a typical desktop PC, using better quality capacitors and other components. Workstations are designed to keep your productivity high and downtime and desk-side visits to a minimum.
6. OS and ISV Certification
For desktops, maybe Windows 10 Home is enough. But for workstations, Windows 10 Professional or Windows 7 Professional is suitable because the latter version comes with business features. Some people may also use other OS like Linux, etc.
Workstations have the most extensive ISV certification in the industry. If a workstation passes through the cooperative certification test with independent software developers such as Adobe, Autodesk, Ansys, and Avid, it means that the performance of professional software on workstation platforms is more stable.
Therefore, in the face of huge 3D rendering and computing work, the workstation can still run in a long time and high load operation, effectively avoiding work delays caused by downtime.
7. Price
Due to the above advantages, workstations are more expensive than desktops. Most business PCs cost as low as $500 and go as high as $1,000, whereas a workstation can start at $1,500 and go as high as $3,000 for a high-end machine.
After learning about desktop vs workstation, you should choose the right PC according to your needs.

![Windows 10 High Memory Usage [Causes and Solutions]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/06/windows-10-high-memory-usage-thumbnail.jpg)
![11 Methods to Make Games Run Faster on Computer [Work Fast]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/08/how-to-make-games-run-faster-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :