When you run Systemd commands, you may receive error "System has not been booted with systemd as init system (PID 1). Can't operate." In this post, MiniTool Partition Wizard tells you why you will get this error and how to solve it.
System Has Not Been Booted With Systemd as Init System
Many people report that they have received error “System has not been booted with systemd as init system (PID 1). Can’t operate.” This error usually occurs when they run a systemd command under Linux systems.
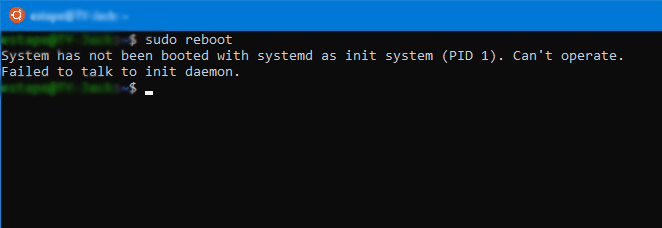
The reason why this error occurs is that the Linux system is not using systemd as the init system. As we all know, the boot process of the Linux system is as follows:
- Power on PC and it will activate the BIOS.
- The BIOS will read MBR to find the boot loader.
- The boot loader will load the system kernel, which will manage the computer’s hardware resources and act as an interface between software and hardware.
- The kernel will then activate an init process (its process ID is 1) which is the first process of the system. It is responsible for spawning all other user processes. The init process is very unique and can complete tasks that other processes cannot.
Then, what is an init system? The Init system can define, manage and control the behavior of the init process. And it is responsible for organizing and running many independent or related initialization tasks, so that the computer system can enter a certain user-subscribed operating mode smoothly.
Linux systems have many init systems, such as System III, System V, Upstart, etc. But since 2015, most Linux distributions have adopted the systemd to replace those traditional init systems. In addition, the systemd is backward compatible with System V.
However, in the following two cases, systemd will not be enabled by default:
- You are using Linux systems in WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux).
- You have skipped the init process (/sbin/init).
How to Solve This Issue
To solve the “System has not been booted with systemd as init system” error, I gathered 3 ways. If you are facing the same issue, you can try them one by one.
Way 1. Use Equivalent Sysvinit Command
If you run Linux systems via WSL, the Linux system will use System V init system, instead of systemd. In this case, you can’t run systemd commands, but you can run equivalent Sysvinit commands.
This table may help you.
| Systemd command | Sysvinit command |
| systemctl start service_name | service service_name start |
| systemctl stop service_name | service service_name stop |
| systemctl restart service_name | service service_name restart |
| systemctl status service_name | service service_name status |
| systemctl enable service_name | chkconfig service_name on |
| systemctl disable service_name | chkconfig service_name off |
Way 2. Add /sbin/init in the Command
Modern Linux systems allow users to skip the init process. For example, if you execute command “init=/bin/bash” in bootloader environment, the system will start a single-user root shell environment and no user password is required.
In this environment, all commands are executed with the default path /bin/bash. In this case, you should use /sbin/init to replace /bin/bash.
Way 3. Enable SystemD Using Scripts
To always enable systemd on WSL2, you can apply the scripts from diddledani. Click the link and it will show you how to complete that job step by step. Some people report that it works for them.

![What Is Linux Boot Process? [A Detailed Introduction]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2021/03/linux-boot-process-thumbnail.png)


User Comments :