You may find the difference between size and size on disk. Do you know why? How to narrow the size vs size on disk huge difference? If you are also searching for the answers, this post of MiniTool is your best choice.
Most of the time, the values between size and size on disk are very close. However, a great many people still notice there is a big difference between size and size on disk when opening the properties of a file or folder.
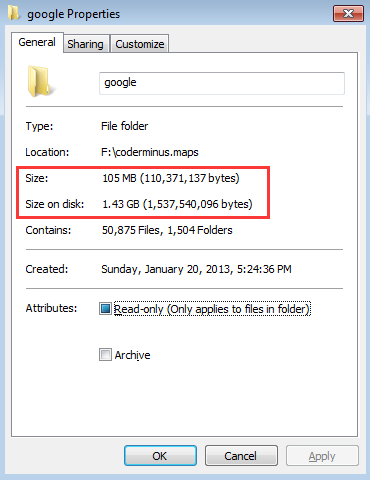
Some people reported this question on forums or communities. They want to know why there is such a huge difference between size and size on disk. For example, a user from SuperUser reported that size on disk is always lager than size.
I was looking on properties of a file and saw two little bit confusing things that make me confused. What does mean “Size” and “Size on disk” for a file? I’ve read a post just like this that has been solved but I didn’t get my answer. Please clarify me.
Size VS Size on Disk
To figure out the size vs size on disk huge difference, you need to understand their own concept. So, this section will explain the definition of size and size on disk separately.
What Does File Size Mean?
When opening the properties of a file, folder, or drive, you will find the values of the size and bytes. The values indicate the actual size and the actual number of bytes in the file. The file size measures how much data a file contains on the storage device. It is presented in the form of the byte. Have a look at the screenshot below. The numbers inside the red box are the actual file size.
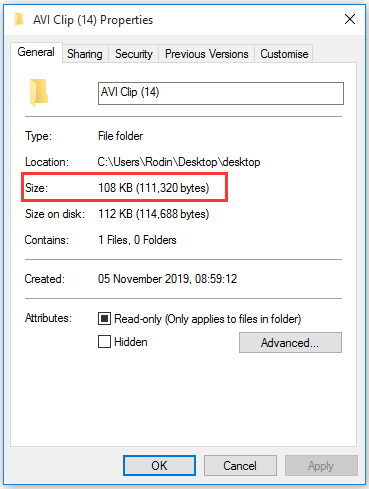
What Does File Size on Disk Mean?
The size on disk indicates the number of bytes that the file actually takes up on the hard disk drive. When a file is written to the file system of a modern storage device, it may take up slightly more disk space than the actual file size. That is why you find there is a difference between size and size on disk.
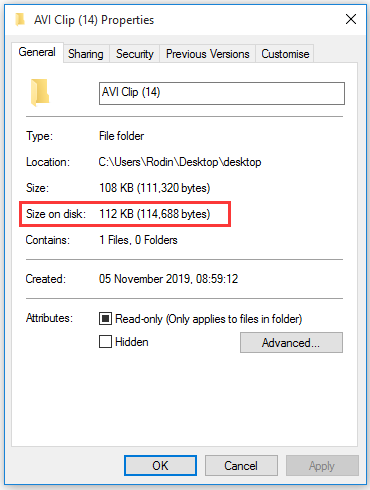
What Affects the File Size on Disk
So, what affects the file size on disk? In fact, it depends on the way that your file system stores the file on the hard drive. To reduce the number of addresses that are being used by the files, the file system will treat a number of bytes as a single cluster.
The maximum file size that a file system can support is not only decided by the capacity of the file system, but also by the number of bits reserved for the file size information. For example, the maximum file size that FAT32 file system supports is 4,294,967,295 bytes.
Usually, common cluster sizes can range from 512 Bytes to 64 KB (NTFS file system). No matter how small each actual file size, the file that is written to the hard drive will occupy a discrete number of clusters. For instance, if you save a 1 KB file in a file system with 2 KB clusters, the size on disk will take up 2 KB.
If you save the 1 KB file in a file system with 32KB clusters, the file will take up 32 KB disk space. The amount of wasted space for each file will not surpass the cluster size that you set for a file system.
Now, you may have known why the size on disk is always slightly bigger than the actual size of a file. Well, you may encounter some exceptions as well. The size on disk can be the same as or smaller than the actual size. It may occur when you use the automatic file compression feature provided by your operating system. Since the file is compressed, the size on disk would often be smaller substantially.
Generally speaking, there is no big difference between the size on disk vs size. However, many users reported that there is a huge difference between size and size on disk. What happened here? Please keep reading on the following part.
Why There Is Big Difference Between Size VS Size on Disk
As you might know, a hard disk is made up of the Tracks and Sectors. When using a Windows PC, the operating system will allocate disk space for each file in clusters or allocation units. The file system of your drive can set different cluster size, which affects the size on disk.
When it comes to the size on disk vs size huge difference, you can check if there are lots of small files inside the folder and the cluster size is relatively large. If it is, the discrepancy will be much bigger because every single file will waste drive space. When the wasted drive space adds up to a certain level, it is very likely that the size on disk is greatly larger than the actual size.
So, this situation often occurs when there are a large number of small files. Besides, the size on disk also depends on the cluster size of your file system. Here we take the 32 KB cluster size (FAT 32 file system) for example. Assuming that there are 50000 files inside your disk. You can calculate the following result:
The files will take about 1.6 GB disk space (the minimum space: 50000*32). Then the disk space that every single file takes is always a multiple of the allocation unit size. If each file size is 2 KB on average, you would get about 100 MB total. But the disk size will also waste 15 times (30 KB per file) of actual file size on average because of the allocation size, which can consume much larger size on disk than actual size.
Generally speaking, the larger the allocation unit size (cluster size) you set for disk, the more disk space will be wasted especially if you have a large number of small files. Usually, 4 KB is a common cluster size of a drive today. Well, you can choose 32 or 64 KB cluster size that is widely used for large files like games, 3D movies, etc.
Right now, you may have a deep understanding of size vs. size on disk. More importantly, what should you do to narrow the size vs size on disk huge difference? Please keep reading the following text.
How to Narrow the Size VS Size on Disk Huge Difference
To make full use of your storage devices, you need to manage the cluster size effectively. Changing the cluster size of the disk can help you narrow the huge difference between size on disk vs size.
Here you can utilize the Windows built-in tools Disk Management and Diskpart to change the allocation unit size. Both of the 2 tools require you to format the specific partition. Well, you can choose MiniTool Partition Wizard that can help you change cluster size without data loss.
Method 1. Use Disk Management
When it comes to changing cluster size, Disk Management is a commonly used tool. You can follow this full guide to change the cluster size.
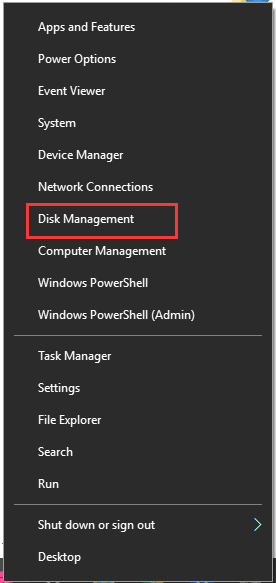
Step 1. Right-click the Start button and select Disk Management from the context menu.
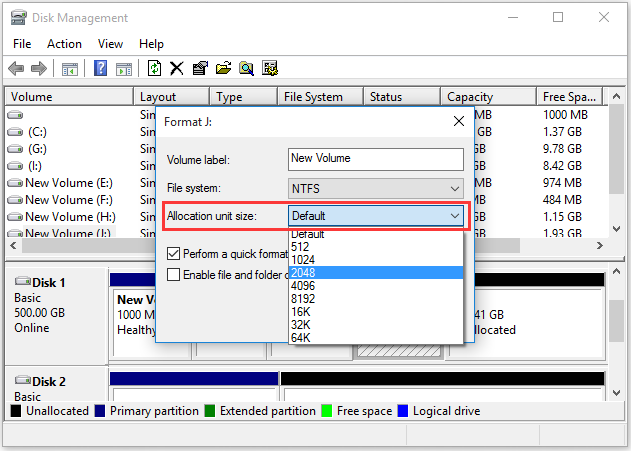
Step 2. Right-click the partition that you encounter the size vs size on disk huge difference issue and select Format.
Step 3. In the pop-up window, select the allocation unit size from the drop-down menu based on your demands and click OK to continue.
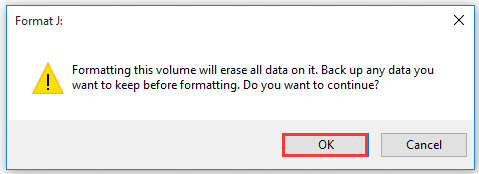
Step 4. Then, you will receive a warning message stating that all the data on the partition will be deleted. If there are important data on the drive, please back up them. Click on the OK button to confirm.
Method 2. Use Diskpart
You can run Diskpart to change the cluster size of your drive. This operation also requires you to format the partition, so please make a backup in advance. Now, follow the steps below.
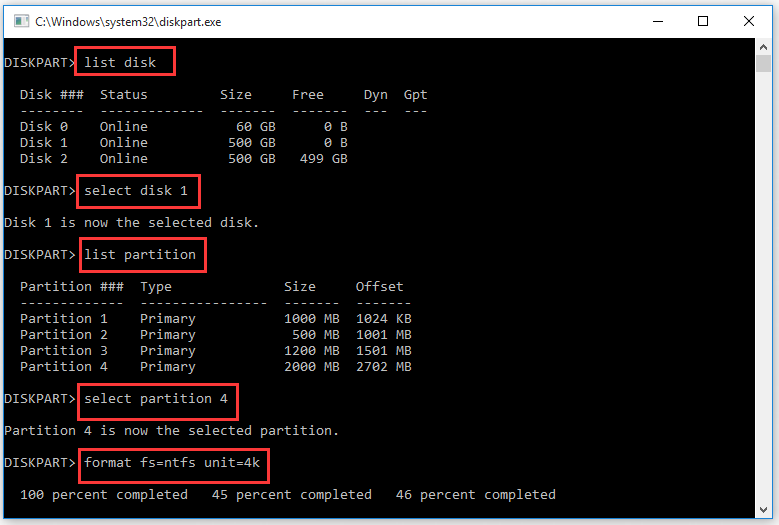
Step 1. Press Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type diskpart in the box and hit Enter.
Step 2. In the pop-up window, type the following commands and hit Enter after each.
- list disk
- select disk * (replace * with the number of the target disk or partition that you want to change cluster size)
- list partition
- select partition *
- format fs=ntfs unit=4k
Now, you will find the cluster size has been changed successfully. In addition to the 2 tools, any better choice to change cluster size without data loss? Yes, there is! Please keep reading.
Method 3. Use MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro Ultimate Edition can help you change cluster size without data loss. It is a powerful partition management tool that boasts many other practical features such as convert MBR to GPT without data loss, upgrade hard drive, resize partition, etc.
It is very simple to operate with just a few clicks.
Step 1. Install this program to your computer and launch it to get the main interface.
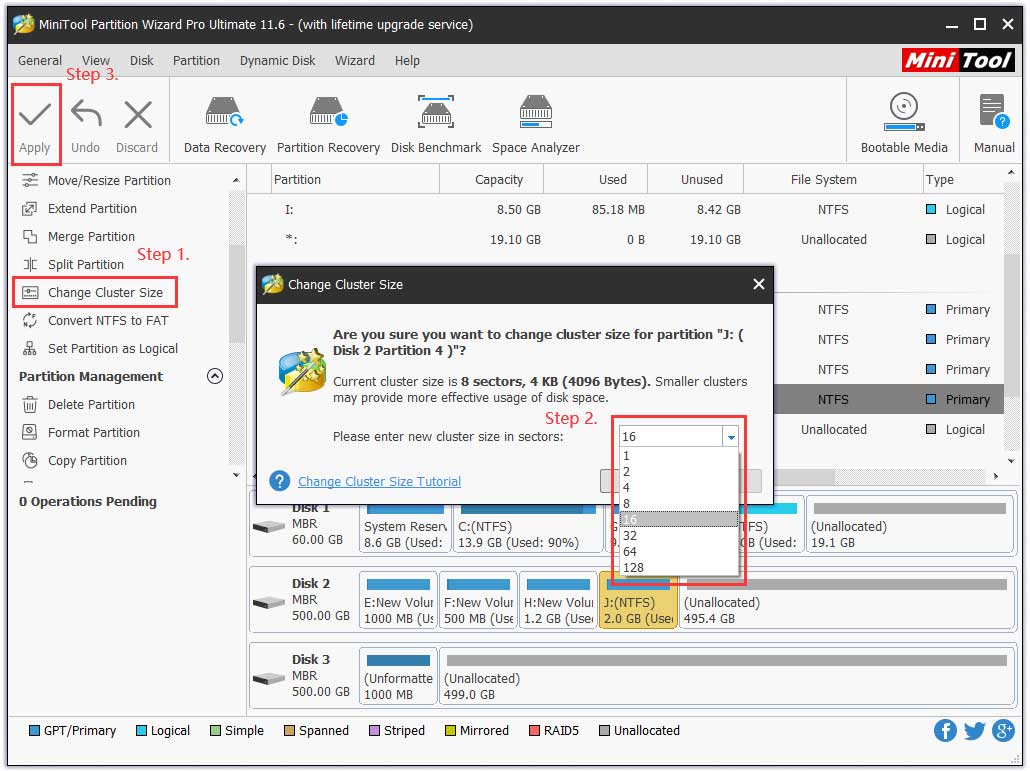
Step 2. Select the partition that comes with the issue and click on the Change Cluster Size feature from the left pane.
Step 3. Select a suitable cluster size from the drop-down menu and click on the Yes button to back the main interface.
Step 4. Click on Apply to execute this operation.
Have A Try Now!
Size vs. size on disk what’s the difference between them? Why there is so big difference between size and size on disk? Have you figured these questions out? If you have any questions, please send us an e-mail via [email protected]We also appreciate any ideas left in the comment area.
Size VS Size on Disk FAQ
- Right-click the Start button and select Disk Management from the context menu.
- Right-click the volume that you want to reduce the size and select Shrink Volume.
- Enter the amount of disk space in the box and click on Shrink.
- Press Win + E keys to open the File Explorer and click on This PC from the left pane.
- Right-click the drive that you want to check and select Format.
- In the Format window, you can check the allocation unit size of your disk.
- Connect the USB to your computer and then open the Disk Management
- Right-click your USB drive and select Format from the context menu.
- Select FAT32 from the drop-down menu of the file system and click on OK. If your USB drive holds more than 32GB capacity, you can use a professional tool like MiniTool Partition Wizard to format a large USB drive.

User Comments :