If you are using the cloud storage, you might have heard about the private and public cloud. What are them and what’s the difference between them? If you are seeking for the answers as well, this article is written for you. Here, MiniTool Partition Wizard provides brief introduction to the private and public cloud.
The cloud is a collection of purpose-built servers, and it also contains the software and databases that run on those servers. These servers can perform one or more services like storage, compute, database, email, and so on. The cloud works the same way with the common cloud storage providers like Dropbox and Google Drive.
The cloud allows users to access the data center over the Internet anytime, anywhere, and from almost any device. Thanks to the cloud, users and companies don’t need to speed too many resources to manage, update, or maintain physical servers by themselves. And this technology brings great convenience to our daily lives as well.
Is the server in a private cloud or a public cloud? Should I use private cloud or public cloud? These are common questions about the cloud asked by users. The private cloud and public cloud are two types of cloud deployments. Just keep reading to get further information about them.
Related article: What Is Cloud Computing Security and Why Is It Important?
What Is Private Cloud?
A private cloud is a server, data center, or distributed network dedicated to only one user or organization. It can be set at the on-site data center of the organization or hosted by a third-party service provider. An organization and its private have a one-to-one relationship.
If an organization is using a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are maintained and deployed on a private network, and the hardware and software work only for this organization. Commonly, the data and applications that are not available to the public run on a private cloud and they can be accessed only by members of the special entity.
Simply put, by using a private cloud, you can enjoy the benefits of the cloud without sharing resources with other organizations.
What Is Public Cloud?
Different from the private cloud, the public cloud is off-premises and may include servers in one or more data centers. It can be used by multiple users or organizations – not limited to a specific user/organization. It is the most common type of cloud computing deployment.
In a public cloud, the resources are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and delivered over the public internet. If you are using a public cloud, you share the same hardware, storage, and devices with other users or organizations, and you just need to pay for the resources you use. Amazon web service is a typical example of a public cloud.
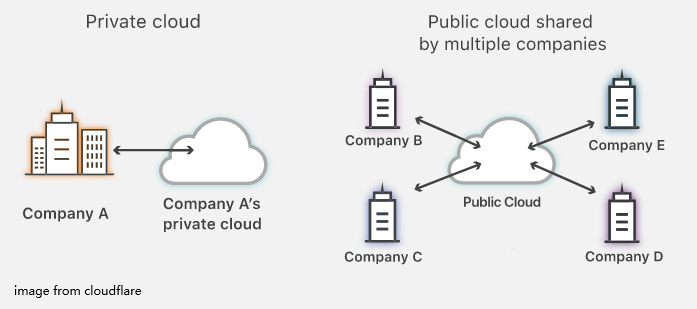
Private Cloud vs Public Cloud
After learning about what private cloud and public cloud are respectively, let’s have a closer look at the differences between these two types of cloud computing. When you decide which cloud to use, you had better figure out their features and choose one according to your needs and budgets.
The private cloud is managed and used by a single client, while the public cloud serves multiple clients. They differ from each other in the following main aspects:
- Customization: The private cloud can provide specific hardware and services as per the needs of its client organization. As different clients may have different demands, the public cloud provides all the possible services and hardware, and the customization is limited.
- Capital cost: To set up and maintain a private cloud, certain capital cost is required. But there’s no capital cost if you use a public cloud, because it is managed by the service provider. So, the public cloud is commonly cheaper than the private cloud.
- Security: The private cloud provides high security and control. There might be the risk of data leakage in a public cloud, and the security largely depends on service provider.
- Reliability: Compared with private cloud, the public cloud offers high reliability as its vast network of servers can ensure against failure.
To get more information about the differences, you can have a look at this page from Microsoft.

User Comments :