How to protect your files from being accessed by other users? Normally, you don’t need to worry about it because Windows has already solved it for you. When you build up a computer, you get your own profile and a set of permissions, which stops others from accessing your files or folders.
If you’re using NTFS file system, you can configure the NTFS permissions on your files or folders to keep your local or shared data away from others. Besides, you can set the share permissions for the folders shared between PCs/tablets to avoid privacy leakage, and they work for the folders both in NTFS and FAT32 file system.
In the following contents, you can learn about the basic information about file permissions as well as the differences between share and NTFS permissions.
NTFS and Its Security
Before learning about what NTFS permissions are, let’s talk about NTFS first.
NTFS stands for New Technology File System, which is used to store and retrieve files on a storage device running the Windows NT operation system.
It is used to replace FAT (File Allocation Table) and HPFS (High Performance File System) file system. Compared with these two file systems, NTFS is better in performance, reliability, disk space usage and security. Click to know more about the differences between NTFS and FAT.
Why is NTFS securer than the other file systems?
In NTFS, each file/folder is given a security descriptor. This descriptor defines the owner of the file or folder, and it contains two access control lists (ACLs) of users or groups that have access to a certain object (an object can be a file or folder).
One is discretionary access control list (DACL). It decides the type of interactions (such as reading, writing, executing and deleting) that are allowed or forbidden by which user or group. For example, all users may be able to read and execute the files in C:Program Files folder. However, only administrative user can modify them.
The other one is system access control list (SACL). It defines which interactions with the file or folder need to be audited before modifying. This ACL is usually used when there is something to do with sensitive files of a company.
With these ACLs, NTFS has a high security which FAT and HPFS lack.
About NTFS Permissions
NTFS permissions are used to manage access to data stored in the partition with NTFS file system. NTFS permissions determine who have access to certain files or folders and they can be assigned to individual user or group.
There are different types of NTFS permissions for files and folders that Windows allows you to assign:
- Full control: It specifies whether a user or group has all available permissions for a file or folder, including adding, modifying, moving and deleting files or folders. In addition, you can change permissions settings for all files and subdirectories.
- Modify: It specifies whether a user or group can modify a file or the contents in a folder. It’s more restrictive than full control.
- Read & execute: It allows a user or group to view and run executable files in a folder.
- List Folder Contents: This is a NTFS folder permission which specifies whether a user or group can list the content of a folder.
- Read: It determines whether a user or group can read the data in a file or folder. You are unable to read an executable file or open the folder where it’s stored if only this permission is assigned for it.
- Write: It decides whether a user or group is able to change the content in a file, create files and folders, or write data and attributes for a folder.
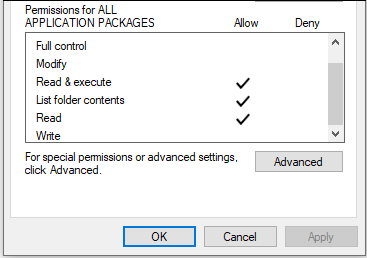
About Share Permissions
Share permissions control the access to folders shared over a network. Different from NTFS permissions, share permissions can be used for the folder with both NTFS and FAT file system.
There are three types of share permissions, and you can set each of them to Allow or Deny according to your needs.
- Read: It allows a user or group to view file and subfolder in the target folder. You can read the contents and run programs with this permission. By default, “Everyone” group is granted with this permission.
- Change: Besides everything allowed by the read permission, users with this permission can modify data, delete and add files and subfolders to the folder.
- Full control: Users with this permission will get all available permissions, including read and change permission. By default, full control permission is granted to “Administrators” group.
NTFS vs. Share Permissions
NTFS and share permissions are both popular among Microsoft Windows users. Although they’re the same in the purpose: to avoid unauthorized access to files and folders, there are some differences between share and NTFS permissions.
- Types: There are more types of NTFS permissions than those of share permissions. So, share permissions are easier to apply and manage, while NTFS permissions makes you control your shared folders and files more precisely.
- File System: NTFS permissions can be used only for the files and folders in NTFS file system. However, you can set share permissions for folders in both FAT and NTFS file systems.
- Users: Share permissions apply to network users, but NTFS permissions affect access both locally and remotely.
After knowing the differences between share and NTFS permissions, you can choose to use NTFS or share permissions according to your needs. In the following contents, you will learn about how to change share and NTFS permissions.
How to Change Share and NTFS Permissions
As it is mentioned, you can restrict file or folder permissions to protect your information by changing share or NTFS permission. But before you make any changes, here are some rules you need to know:
- If you grant a user full control permission to a folder, the user will be able to take ownership of the folder, unless he is restricted in some other way. So, you need to be careful in granting full control.
- You can restrict a folder by NTFS permission and share permission at the same time, but the final access permission is decided by the more restrictive permission.
- You can grant permissions to any user, group or computer. You’d better assign permissions to groups, because system performance can be improved while verifying access to an object.
How to Check NTFS Permissions and Change Them
If you’re using NTFS file system, you’d better use NTFS permissions to restrict file or folder permissions. You just need to specify the level of access for users and groups. For example, you can allow a user to read the contents in the file, enable another user to make changes to the file, and prevent some users from accessing the file.
How to check NTFS permissions and change it? You can figure it out in the following step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Right-click the file or folder.
Step 2: Select Properties.
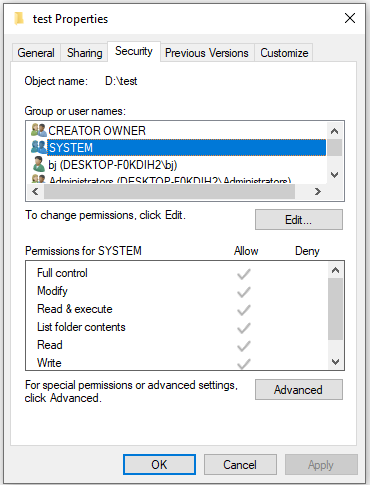
Step 3: Switch to Security tab to check NTFS permissions. As the picture shows, Object name, Group or user names and permissions types are displayed here, and you can click each user or group to check which NTFS permissions they have to access this file or folder.
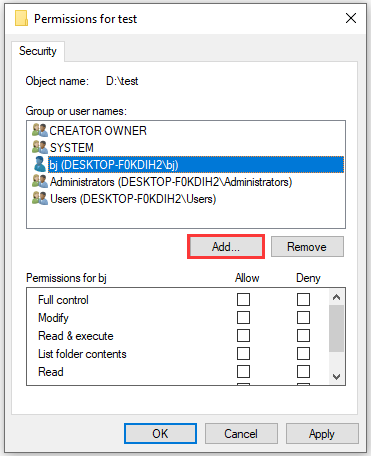
Step 4: If you need to change NTFS permissions, click Edit. Then in the pop-up window, select a group or user, or click Add to add more users or groups.
Step 5: Check the permissions you want to assign to the group or user. Then click Apply and OK to save the changes you have made.
How to Check Share Permissions
To manage the shared folder in FAT32 file system, you can use share permissions. Here is how to check the share permissions settings.
Step 1: Right-click the shared folder and choose Properties.
Step 2: In the Properties window, switch to Sharing tab and click Advanced Sharing.
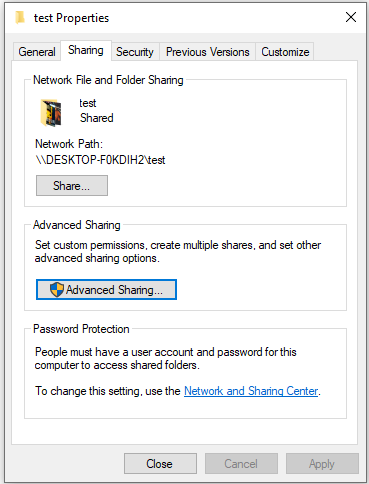
Step 3: In the pop-up window, select Permissions. Then you can see share permissions for groups or users.
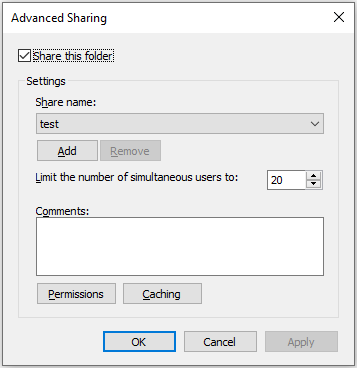
The method of changing share permissions is similar to that of changing NTFS permissions. If you want to make any changes, you can refer to the steps in the former part.
Convert FAT32 to NTFS
As NTFS permissions for files and folders are not available if you’re using FAT32 file system, you can convert FAT32 to NTFS to solve the problem. Here are two options for you: using Command Prompt and using MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Option 1: Using Command Prompt
This may be a little complicated and dangerous if you don’t use Command Prompt often. Before the operation, you need to check the drive letter of the drive on which your shared file or folder is stored. Then you can follow the steps below to convert FAT32 to NTFS.
Step 1: Press Win + R to invoke Run window. Then input cmd and press Shift + Ctrl + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
Step 2: In Command Prompt window, type convert * /fs:ntfs (* represents the drive where the shared file or folder is stored) and press Enter to execute the command.
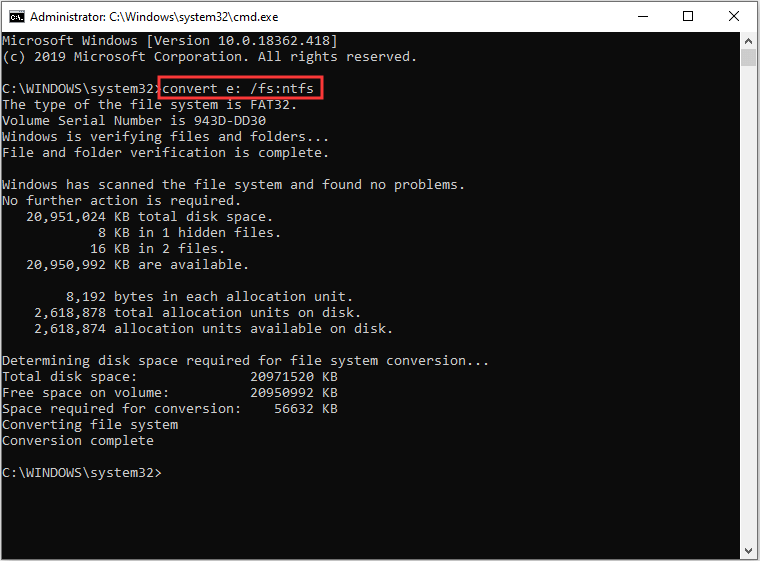
Then you just need to wait until the process is complete.
Option 2: Using MiniTool Partition Wizard
If you’re not professional in computer technology, I recommend you using MiniTool Partition Wizard, a great partition manager. It helps you convert FAT32 to NTFS within a few clicks.
Step 1: Download and install this manager from the following button.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2: Launch it. Then right-click the target partition for which you need to change the file system and select Convert FAT to NTFS.
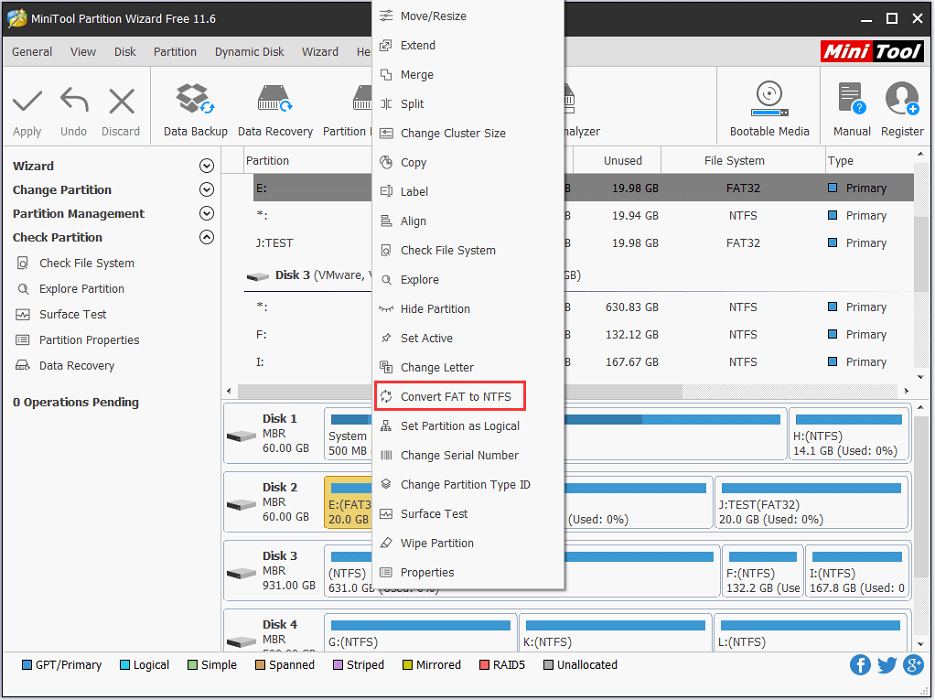
Step 3: In the following window, click Start to begin the operation.
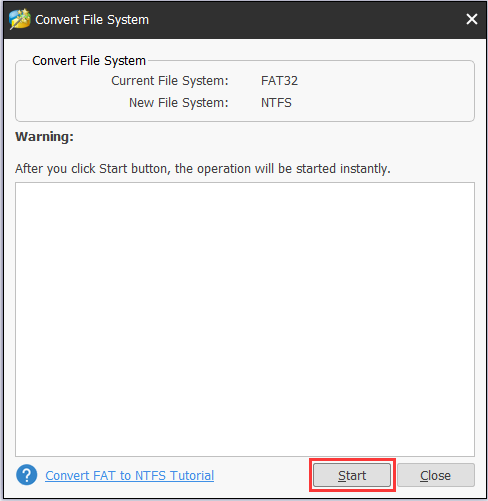
Step 4: When the conversion is completed, click Close button.
Then you can exit MiniTool Partition Wizard and check if NTFS permissions are available.
Bottom Line
NTFS permissions and share permissions help you protect the shared files or folders. After learning about the differences between them, you can better manage the permissions settings. Besides, if you want to make any changes to them, you can follow the instructions above.
For any questions, you can post them in the comment section below. If you encounter any problems while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please don’t hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
NTFS Permissions FAQ
- Read
- Write
- Execute
- Delete
- Change permission
- Take ownership

User Comments :