Information about Not in a Hypervisor Partition Error
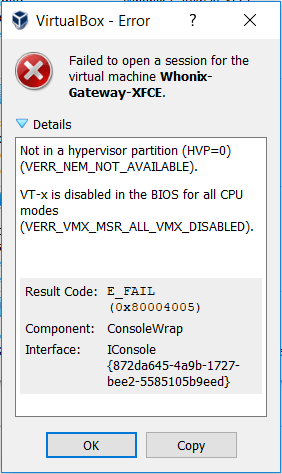
When you try to run a virtual system in VirtualBox, you may get an error message: Not in a hypervisor partition (HVP=0) (VERR_NEM_NOT_AVAILABLE). Under this message, the detailed reasons will be listed. The reasons are as follows:
- VT-x is disabled in the BIOS for all CPU modes (VERR_VMX_MSR_ALL_VMX_DISABLED).
- AMD-V is disabled in the BIOS (or by the host OS) (VERR_SVM_DISABLED).
Then, what is VT-x/AMD-V? Both they are virtualization technologies.
1. VT-x
VT-x is the virtualization technology developed by Intel (abbreviated as Intel-VT or IVT). With this technology, a set of hardware devices can be virtualized through the virtual machine viewer (VMM, Virtual Machine Monitor) for the operating system of the virtual machine.
These technologies have been implemented by software on VMware and Virtual PC in the past, but the hardware support with VT enabled can accelerate the progress of such software.
The 32-bit/64-bit VT extension is called “VT-x”; the VT of the IA-64 processor is called VT-i; of course, there are other virtualization technologies called VT-c (Intel network card) and VT-d (Virtualization for Directed I/O).
In Linux, Intel processors that support virtualization will have a flag named “vmx” in a special file /proc/cpuinfo.
2. AMD-V
AMD-V, short for AMD Virtualization, is the name of the virtualization extension provided by AMD for the 64-bit x86 architecture. In some BIOS versions, AMD-V is also called AMD SVM. In Linux, AMD processors that support virtualization will have a flag named “svm” in a special file /proc/cpuinfo.
Fix Not in a Hypervisor Partition Error
Virtualization technology not only needs the support from processors, but also needs the support from chipsets and BIOS. When the error “not in a hypervisor partition (hvp=0) (verr_nem_not_available)” appears, it means that your computer has the virtualization disabled at the BIOS level and you need to enable this technology to set up a new virtual machine.
Here is the tutorial on how to enable virtualization technology (VT-x or AMD-V) in BIOS:
Step 1: Restart your laptop/desktop. Then, on the boot screen, press the BIOS key to enter into BIOS mode. (The BIOS key may vary depending on computer models. But you can follow the on-screen instructions or search it online)
Step 2: In the BIOS interface, use arrow keys to skip to Configuration tab. In most cases, the virtualization item is under Configuration, System Configuration, Advanced Configuration, or something like those.
Step 3: After finding the virtualization item (IVT, AMD-V, or something related to virtualization), press Enter key to make sure it is enabled.
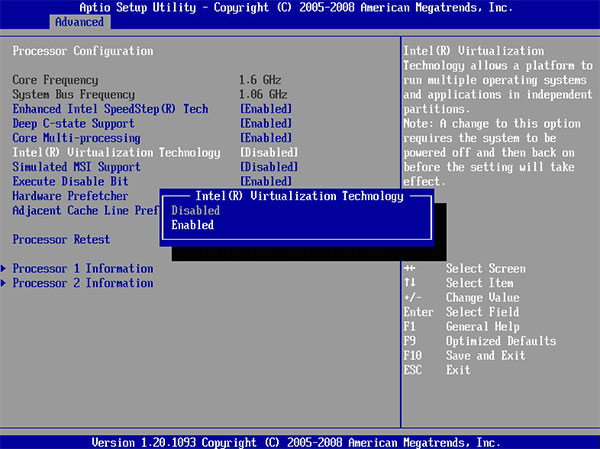
Step 4: Press F10 to save the changes and then exit from BIOS.
After enabling Virtualization in BIOS, you should then restart your computer to run the virtual machine in VirtualBox again. This time, you will open this VM smoothly.



User Comments :