How to Access MSConfig
Where is MSConfig in Windows 10? Many users may wonder this problem. In this part, I will show you how to access MSConfig through 2 ways.
Method 1. Access MSConfig Through Windows Search Box
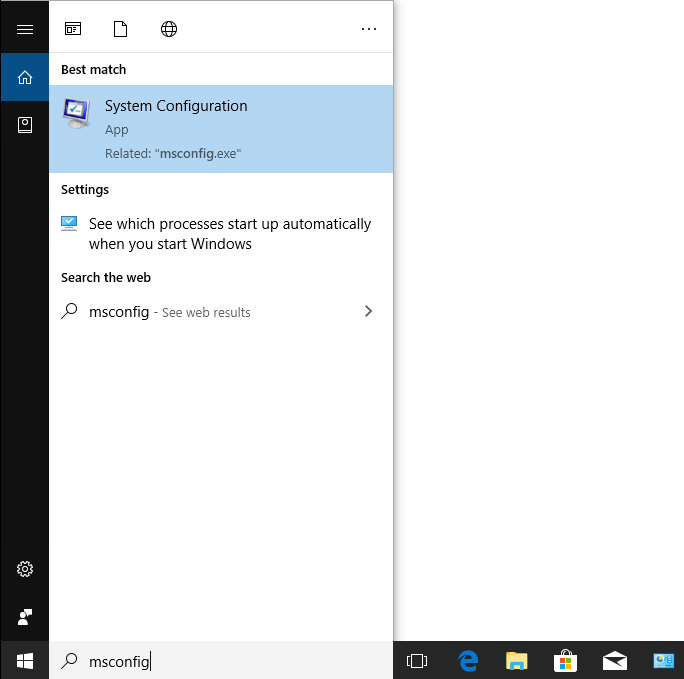
Click inside the Windows search box on the taskbar and type “msconfig” into it. Then click the best-matched search result: System Configuration.
Method 2. Access MSConfig Through Run Dialog
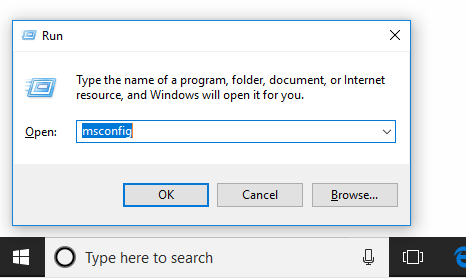
Step 1: Press “Windows + R” keys simultaneously to call out Run dialog.
Step 2: Type “msconfig” in the Run box and then press Enter key to open System Configuration.
How to Use MSConfig
Once you open System Configuration, you will see a window shown like the following picture:
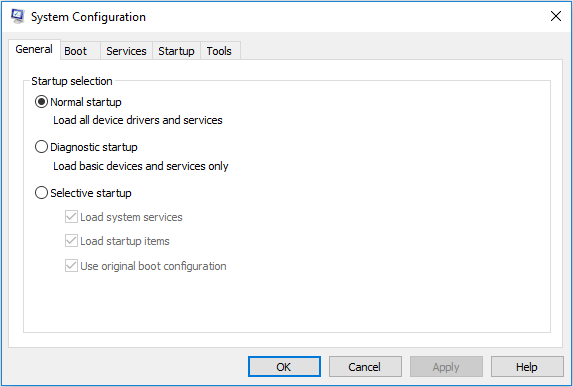
The System Configuration window consists of 5 different tabs: General, Boot, Services, Startup, and Tools. These tabs and various options under them are very useful for managing your computer. Let’s learn their functions.
1. General Tab
When you open System Configuration, the General tab will be displayed by default. It provides you with 3 Startup selections: Normal startup, Diagnostic startup, and Selective startup.
- Normal startup: This mode will boot up Windows as is, with all the installed startup items, drivers, and services. In this mode, there is almost no restriction on what ads to the boot process.
- Diagnostic startup: Similar to booting into safe mode, this mode only runs Windows services and drivers. It can help you rule out Windows files and services as being the source of possible system stability problems.
- Selective startup: This mode runs basic Windows services and drivers and allows you to select other services and startup items you want to run, from the Services and Startup tabs. In this way, you can slowly determine what is causing the problem in your boot process.
2. Boot Tab
The Boot tab is shown like the following picture:
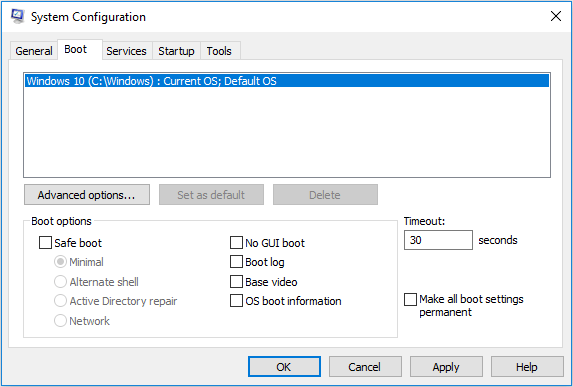
In the top area, a white box lists operating systems installed on the current machine. Under the white box, there are other important functions like Advanced options and Boot options.
- Advanced options: This feature enables you to configure such things as the number of processors, the amount of memory, and Global Debug settings.
- Boot options: This feature allows you to trigger your Windows into different booting modes by checking different options.
- Safe Boot Minimal: Boots to the Windows GUI only running critical services running and disabling networking.
- Safe Boot Alternate Shell: Boots to a command prompt running critical services running and disabling networking and the GUI.
- Safe Boot Active Directory Repair: Boots to the Windows GUI running critical services and Active Directory.
- Safe Boot Network: Boots to the Windows GUI running critical services and networking.
- No GUI Boot: Does not display the Windows Vista splash screen when you are booting.
- Boot Log: Stores information from the boot process in a log located in %systemroot% called ntbtlog.txt.
- Base Video: Loads the system with standard VGA drivers instead of those that specifically relate to your hardware.
- OS Boot Information: Shows all the drivers during the boot process as they load up.
3. Services Tab
When the operating system boots up, only services that are checked here can run at startup. If you don’t want some services to run at startup, uncheck them here.
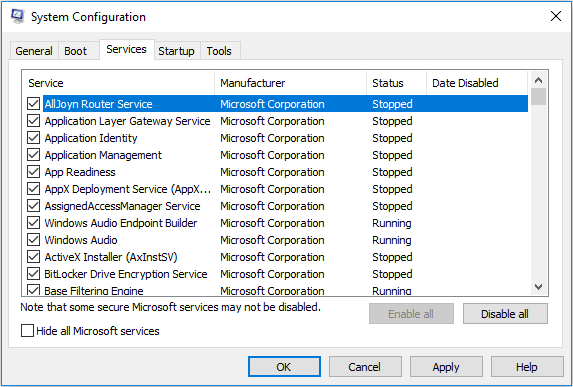
If you believe that any of the Windows Services is causing an issue, then this section lets you deselect, and help you figure. However, be careful when you decide to disable a service because you might cause other problems.
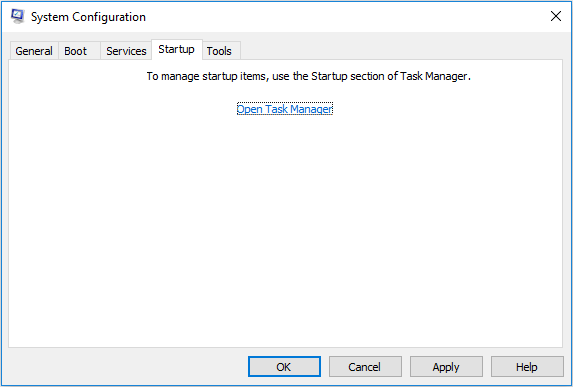
4. Startup Tab
In this tab, there is only one option: Open Task Manager. As the name suggests, it will help you open Task Manager. In Task Manager, you can monitor processes and hardware performances, disable startup items, end tasks, etc.
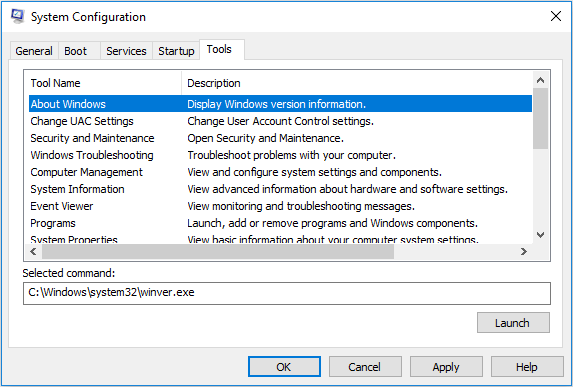
5. Tools Tab
Tools tab lists some Windows administrative tools. To use these tools, you just need to select the one you want and then click Launch button.




User Comments :