Have you encountered lsass.exe high CPU issue? If so, MiniTool offers you 4 possible solutions to solve it. Read on to learn what lsass.exe is and get these solutions.
LSASS.exe, also called Local Security Authority Subsystem Service, is a valuable Windows operating system process that is responsible for enforcing the security policy on the computer. When a user logs into the Windows Server, it is responsible for handling the password changes and creating the access tokens while updating the security log.
However, it may cause high CPU usage issue. Users reported that issue on forums like the following one:
I have a Windows Server 2016 Datacenter virtual machine running on AWS. My server experienced a sudden increase in CPU usage from lsass.exe, rendering the server unusable. Note that this server is a workgroup machine and has no active-directory oriented functionality…Anyone able to offer any sort of insight as to what is causing lsass to burn CPU? forums.iis.net
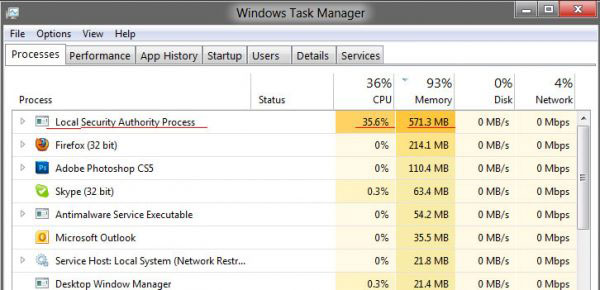
Then, how to solve the lsass.exe high CPU/memory problem? Please keep reading to get solutions.
Fix 1. Run Antivirus Program
LSASS.exe file is often targeted and mimicked by malware. If C drive is your system partition, this file’s original location is C:WindowsSystem32.
Therefore, if the Task Manager shows a process with a similar name is eating a lot of CPU, but its location is different when you right-click on it and choose Properties to see its detailed information, you may be aware that this process is a malware.
If so, you should run a full system scan by using a reliable antivirus software.
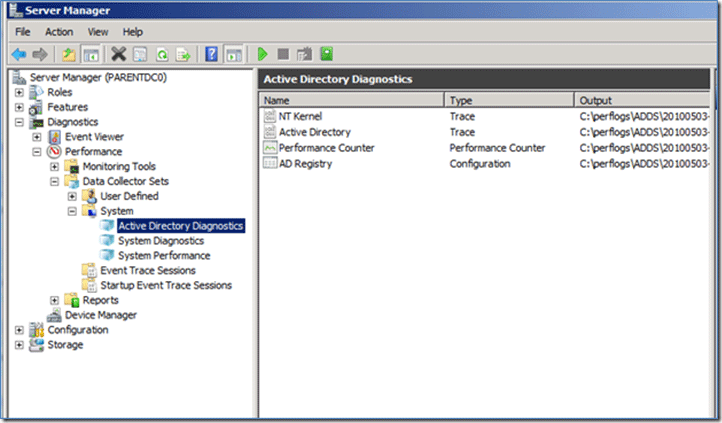
Fix 2. Run Active Directory Data Collector
If you are running Windows Server 2008 or later version, you can use Performance Monitor’s Active Directory Data Collector Set to determine what the problem cause is. Please refer to the following steps:
Step 1: Open Server Manager on Windows Server, or go to Start > Run > Perfmon.msc and then press enter.
Step 2: Expand Diagnostics > Reliability and Performance > Data Collector Sets > System.
Step 3: Right-click on Active Directory Diagnostics and then click Start in the menu which appears. Then, it will start to gather data and compile the report.
Step 4: Once the report has compiled, navigate to Diagnostics > Reliability and Performance > Reports > System > Active Directory Diagnostics to view the report or reports which have been completed.
Fix 3. Check Certificate
One user reported that his lsass.exe high CPU issue is caused by having unknowingly replaced a 2048 SSL certificate with a 4096 certificate, which left behind lower server head room. If so, you just need to switch back to the original certificate.
Fix 4. Delete a User File
Some users reported that deleting “C:Users<username>appdataroamingmicrosoftprotect<guid>” may work. Please note that if you have multiple local accounts, it needs to be done under every account.
Of course, there are also some users reporting that this method doesn’t work for them. Every time, this file reappears within 20 seconds after it is deleted. There are also some users warning that this move will corrupt the user profile. Please refer to this discussion.
If this method also doesn’t work for you, you can try System File Checker to replace the potentially damaged lsass.exe file or update the OS or the virtual machine to the latest version.
Final Words
Do you have any problem with this above solutions? Do you have other solutions to solve this problem? Please leave a comment below.


User Comments :