USB is a familiar word in today’s life. But lots of people are still confused about it and come up with the question “what does USB stand for”. To dispel the doubt, MiniTool tailors this post in which USB port and USB devices are detailed introduced.
What Does USB Stand For?
What comes to your mind when I mention USB? USB Type-C, USB 3.0, or USB flash drive?
USB is the abbreviation of Universal Serial Bus that is a technical specification of input and output interfaces. Showing up in 1996, USB port is a standard cable connection interface for personal computers and consumers’ electronics devices.
Before 1994, there was a multitude of connectors at the back of PCs. Facing this issue, a group of seven companies began to design and develop a new technology that was USB in 1994.
This decision was to address the usability issue of existing interfaces, simplify software configuration of all devices connected to USB, and permit greater data rates for external devices. In simple words, making the external devices be connected to PCs fundamentally easier is the fundamental purpose.
The technology has been widely used in electronic products, including computers, phones, cameras, digital televisions, game consoles (Xbox One X and PS4 Pro), and so on. It could be said that USB is ubiquitous in today’s life.
However, the ubiquitous technology still makes lots of people confused. To figure out “what does USB stand for”, the following content will expound USB meaning from different points, including USB connectors, USB speed standards, and USB devices.
USB Connectors
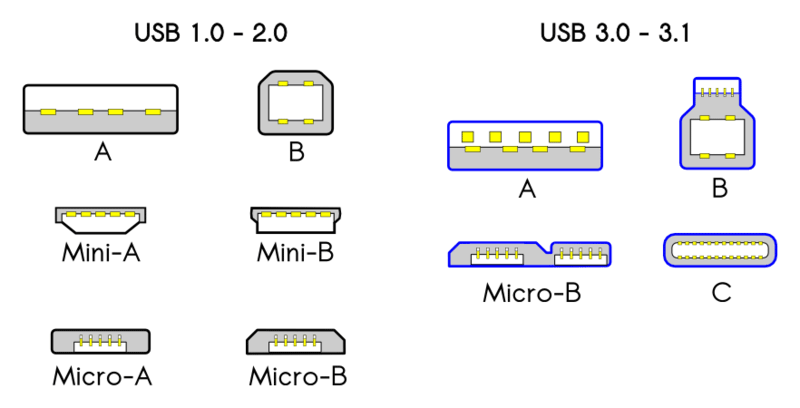
To charge a phone, we always plug cables into the USB port on the phone. The end of the cable is the USB connector. Nowadays, USB connectors come in different shapes and sizes. The most common USB connectors include USB-A, USB-B, USB-C, Mini USB, and Micro USB.
USB-A
USB-A, a traditional USB host port design, is a flat and rectangular interface. You can find the A-style connectors on virtually desktop computers, laptops, TVs, game consoles, media players, and other devices.

This connector holds the connection in place by friction, which is the reason that you can connect and disconnect the device very easily via this connector.
You may have ever seen the A-A cable. Please note it is not wise to use an A-A cable for data transfer between two computers, as this may cause irreparable damage to your computers and may even cause a fire hazard.
USB-B
The USB-B connector can be found when you plug in a printer cable or an external hard drive cable to a computer. The B-style connector is almost square and has slightly beveled corners on the top ends of the connector.
Similar to the USB-A, USB-B also takes advantage of the friction of the connector to stay in place.

Mini-USB
Mini-USB is also known as Mini-B. This connector is used with some cameras and MP3 players. But for the newer devices, you can find that Mini-USB has given a way to the Micro-USB and USB-C.
As the name suggests, this connector is smaller than a regular USB port as the following image shows.

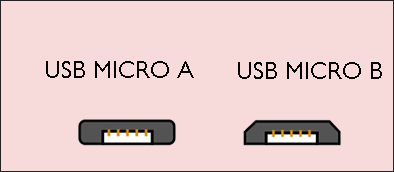
Micro-USB
Announced in 2007, Micro-USB has two formats, namely Micro-A and Micro-B. This connector is used to connect computer peripherals and charge smartphones.
USB-C
USB-C or USB Type-C is the newest USB connector on the market. It has become the standard for many new laptops, tablets, and phones.
Unlike other types of USB connectors, this connector is reversible, meaning that you can plug it into any USB-C device whether its side is “up” or “down”. It is a very user-friendly design.
Furthermore, this connector boasts higher speeds of data transfer.

USB Speed Standards
Each USB connector has a standard of speed. Until now, the USB speed standards have undergone 4 generations, namely USB 1.x, USB 2.0, USB 3.x, and USB 4. Let’s learn about them one by one.
USB 1.x
USB 1.0 appears in 1996 with the data transfer rate of 1.5Mb/s. Two years later, USB 1.0 was upgraded to USB 1.1 that features the data transfer rate of 12Mb/s.
The 1.5Mb/s Low Speed was intended for the low data rate devices, like keyboards, mice and joysticks; the 12Mb/s Full Speed was designed for the higher-speed devices, like printers and floppy disk drivers.
USB 2.0
In 2000, USB 2.0 was released. This generation evolved from USB 1.0 with the data transfer rate of 60Mb/s. The high data transfer rate is enough to meet the speed requirements of most peripherals.
Apart from the high data transfer rate, USB 2.0 also features the Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI), which makes all devices that support USB 1.1 be recognized by the computer via USB 2.0.
USB 3.x
2008 witnessed that the USB 3.0 specification was released. This USB protocol specification was designed to increase the data transfer data up to 5 Gbit/s, decrease power consumption, and increase power output.
UBS 3.0 is also called SuperSpeed as this generation includes a new, higher speed bus called SuperSpeed in parallel with the USB 2.0 bus. As for compatibility, USB 3.0 is also compatible with USB 2.0.
In 2013, USB 3.1 was launched with the data transfer rate of 10 Gbit/s. A year later, USB 3.2 came out with the data transfer rate of 20Gbit/s.
USB 4
Have you ever heard USB 4 in 2019? The USB Implements Forum published the official USB 4 protocol specification in this year. The new USB port generation features the data transfer rate up to 40 Gbit/s and it is backward-compatible with USB 2.0 and USB 3.x. To learn more about the new spec, please read The USB 4 Standard Is Announced: It’s A Big Upgrade.
Differences Among USB 1.0, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0
Apart from the different data transfer rates and compatibility, USB 1.0, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 are distinct from each other in the following aspects.
Color:
You can tell the three USB ports generations from each other by looking at the color of the plastic inside the device. The USB 1.0 features a white plastic color; USB 2.0 is black; USB 3.0 is blue.
Data transfer direction:
USB 2.0 and the older models only support the data process in a single direction at a time. But thing comes to be different in USB 3.0 and the later models. This generation allows for data transfer in both directions.
The reason for this difference is that USB 2.0 and the older models adopt the half-duplex data transmission method, while USB 3.0 and the later models use the full-duplex data transmission method.
Power level:
USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 operate at 5V, 1.8 A, whereas USB 3.1 operates at 20V, 5A to help users to power up larger devices.
The number of connector wires:
USB 2.0 has a total of 4 connector wires, while USB 3.0 has a total of 9. The increased connector wires also attribute to the two-way communications at one time.
Further reading:
Some users may confuse USB connectors and USB speed standards. Here I would take USB Type-C USB 2.0 for example.
USB Type-C is a USB connector specification. The specification defines the mechanical and electrical parameters of connectors. However, USB 2.0 is a USB protocol specification. This specification defines the physical layer of communication, signaling standard, decoding and encoding scheme, data transfer rate, etc.
USB Devices
In this part, I would like to show you why USB devices become so popular, what the main USB devices are, what you should do before using a USB external drive to store data.
Why Are USB Devices So Popular?
USB devices are widely used in today’s life, which may be attributed by the following merits of USB devices.
- USB devices support hot plug. This means you can hot plug a USB device to your computer without restarting system.
- Some USB devices (like USB flash drive) are easy to take.
- Various USB devices can be connected to the computer via the same specification, like USB mouse, and USB printer.
What Are the Main USB Devices?
You may have noticed that there are many devices connected to your computer via USB ports. The common USB devices include:
- Keyboard;
- Mouse (read the tutorial to make your mouse cursor easier to see) ;
- Digital camera;
- Printer;
- Scanner;
- Smartphone;
- External drive;
- …
Here I would like to focus on the 7th USB device and show you what you need to pay attention to when using them.
External drive or external storage includes USB flash drive, hard drive, tap drives and so on. When do we need to connect external storage to our computers? The most common situations are:
- The space of internal hard drive is running out and you need to add additional storage.
- Your computer cannot boot due to the blue screen errors and you use the USB flash drive as the bootable media.
- Back up the computer to keep data safe.
- Move files from one computer to another.
What You Should Do Before Using a USB External Drive to Store Data?
USB external device is useful! The running out space of the internal hard drive is really a headache. So, here I would like to show you how to use one USB external drive to get rid of the dilemma.
Before using a USB device to store data, you need to partition it and then format it. To complete that with ease, you can try MiniTool Partition Wizard. This program is adept in managing hard drive on Windows computer, as well as backing up computer and transferring data from one computer to another.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Move 1: Partition the USB drive
Step 1: Connect the USB external storage to a Windows computer.
Step 2: Download MiniTool Partition Wizard, install it and then launch it to get its main interface.
Step 3: Right-click the unallocated space of the drive and then select Create.
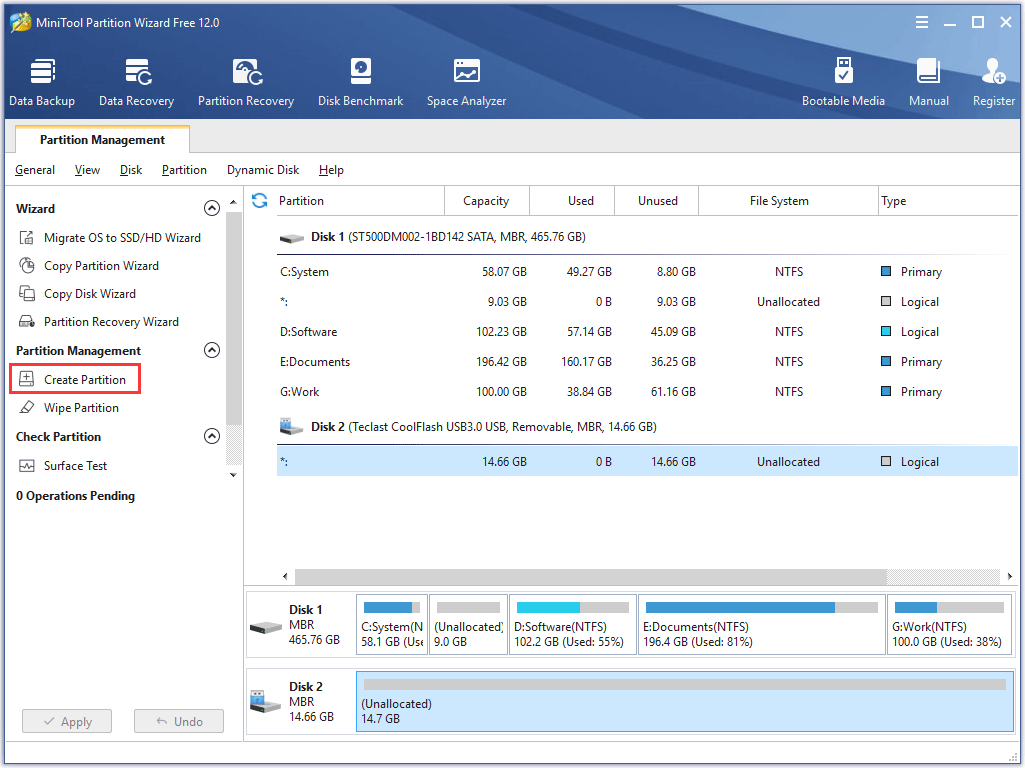
Step 4: On the new window, confirm the parameters, including Partition Type, File System, Drive Letter, Partition Volume, etc. Then click OK.
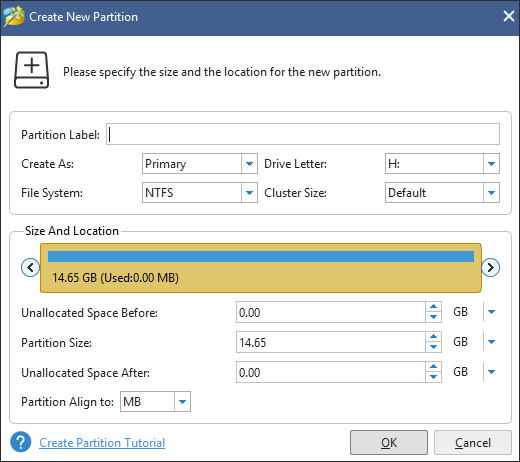
Step 5: Click Apply to execute the pending process.
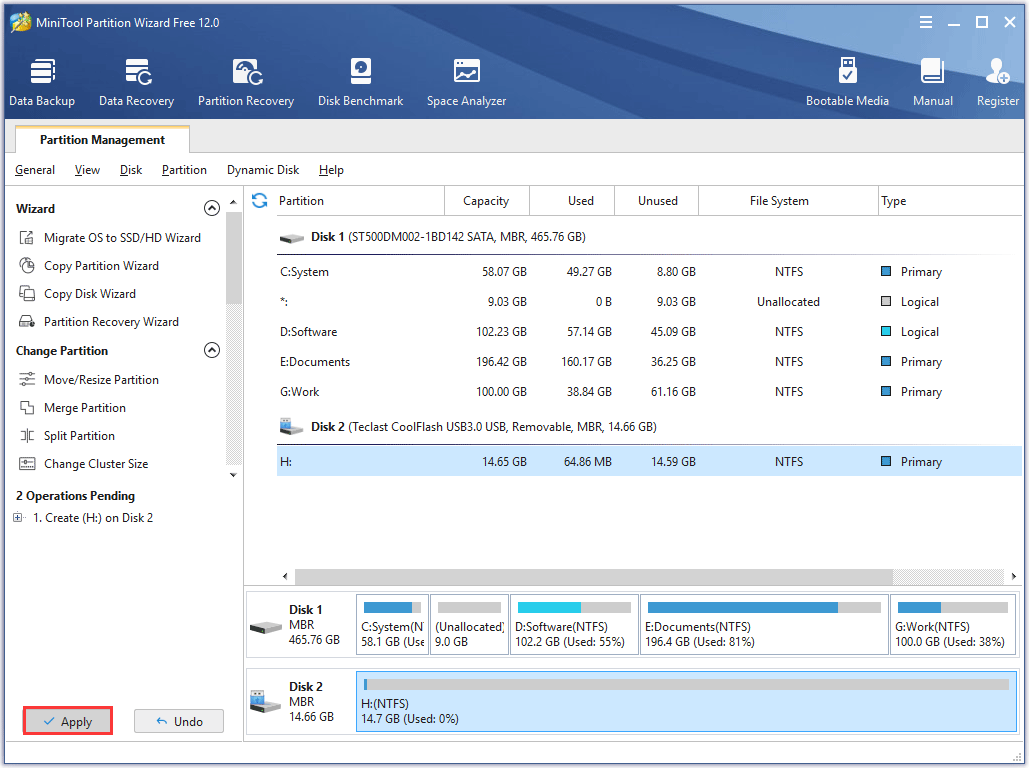
If you want to create more partitions, you should repeat the above steps.
Move 2: Format the USB drive
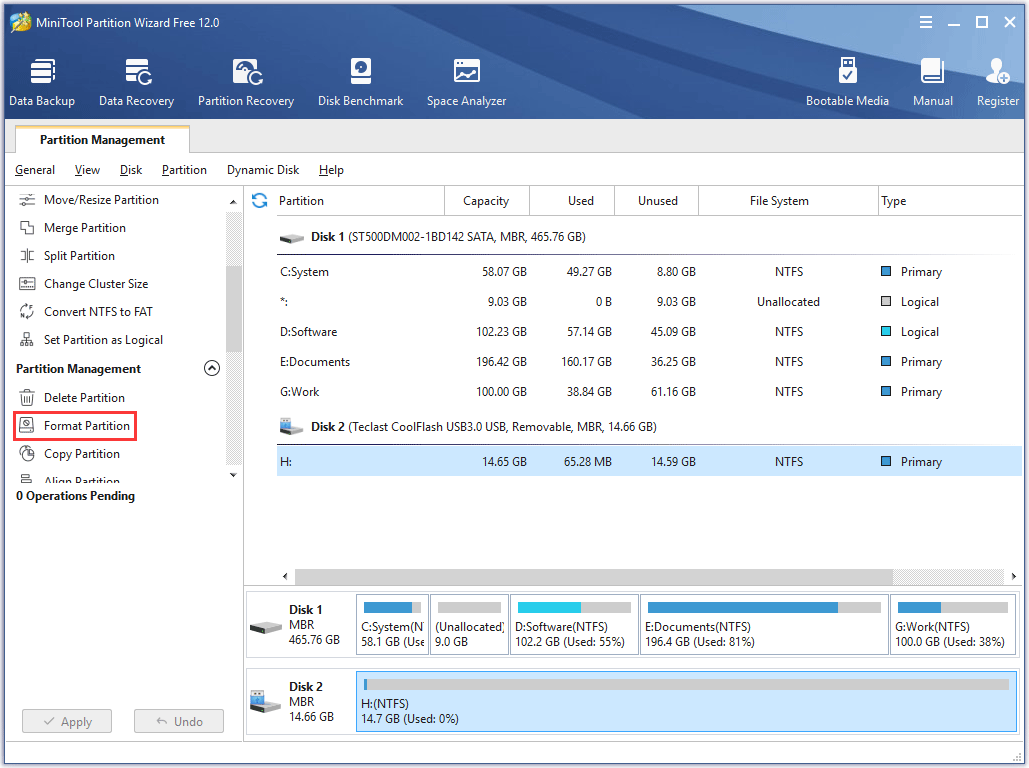
Step 1: Highlight the partition and then choose Format Partition from the left panel.
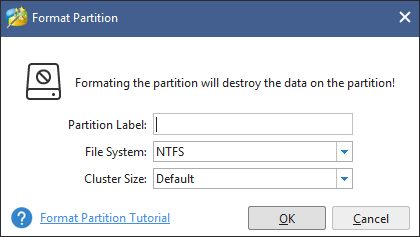
Step 2: Confirm the Partition Label, File System, and Cluster and then click OK.
Step 3: Click Apply to execute the changes.
Bottom Line
After reading, have you figured out the USB meaning? If you still have some doubts about USB, please leave them in the following comment zone. If you also have some difficulties in setting up the USB external drive via MiniTool Partition Wizard, please connect us via [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.
What Does USB Stand for FAQ
When USB refers to the USB connectors, you can use USB to transfer data between USB devices and charge the USB devices, like smartphone.
When USB refers to the USB devices, the use of USB is various. USB devices include printer, scanner, external drives, etc.


User Comments :