When selecting a file system for a USB drive, NTFS and FAT32 are most common options, each with its advantages and disadvantages. So, the best choice depends on your own needs. This post from MiniTool Partition Wizard discusses the advantages, disadvantages, and ideal usage scenarios to use NTFS or FAT32 for USB.
What Is NTFS?
NTFS (New Technology File System) was introduced by Microsoft in 1993 as part of the Windows NT 3.1 operating system. NTFS is the default file system for Windows operating systems, including Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server versions.
NTFS is a powerful and versatile file system designed to meet the needs of modern computing. It has many features, which you can explore in the following contents.
Key Features of NTFS:
- NTFS supports large files and volumes, making it suitable for modern storage needs.
- NTFS includes built-in security features that allow users to set permissions on files and folders. This enables fine-grained control over who can access or modify data.
- NTFS supports the Encrypting File System (EFS), which provides file-level encryption to protect sensitive data.
- NTFS uses a logging file system, which means that changes are tracked before data is written to help recover data in the event of a system failure.
- Files and directories can be compressed to save space on NTFS volumes. This compression is done transparently, so users do not need to decompress files manually.
- NTFS allows administrators to set disk quotas, limiting the amount of disk space that users can consume. This feature is particularly useful in multi-user environments to prevent any single user from monopolizing disk space.
- NTFS file system supports sparse files to increase disk space efficiency. When the sparse file feature is enabled, the system does not allocate hard drive space to a file unless it contains areas of non-zero data.
With these features, NTFS offers significant advantages in multiple aspects. For example:
The logging and transaction logging features make NTFS more reliable. It is more resistant to corruption and easier to recover from crashes. File and folder permissions and encryption provide strong security for NTFS, making it suitable for sensitive data.
Also, NTFS is scalable because it can handle very large files and volumes, making it suitable for modern storage needs. Finally, compression and sparse file features help save disk space and increase storage efficiency.
But NTFS is primarily supported by Windows operating systems. While macOS and Linux can read NTFS volumes, they may require additional software or drivers to write to them.
What Is FAT32?
FAT32, short for File Allocation Table 32, is a file system developed by Microsoft and introduced in 1996 with Windows 95 OSR2. FAT32 is an extension of the earlier FAT16 file system and is one of the most widely used file systems for USB drives, memory cards, and other portable storage devices.
Here are the main features and technical details about FAT32:
- FAT32 is supported by almost all operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and even older systems like DOS.
- The file allocation table is the core of FAT32, keeping track of which clusters (units of disk space) are used by which files. Each file is stored in a series of clusters, and the FAT maintains a linked list of these clusters for each file.
- The size of each cluster can vary, typically ranging from 512 bytes to 64 KB, depending on the size of the volume. Smaller cluster sizes reduce wasted space but can increase fragmentation. Larger cluster sizes can reduce file system overhead, but may waste storage space.
- FAT32 supports volumes up to 2 TB in size. Larger volumes are not supported due to the limitations of the 32-bit file allocation table. The maximum file size on a FAT32 volume is 4 GB. Files larger than this cannot be stored on a FAT32-formatted drive.
With the features of the FAT32 file system mentioned above, its advantages can be summarized into the following 2 points:
1. Cross-Platform Compatibility
FAT32 is readable and writable by almost all operating systems, making it the best choice for USB drives and other portable storage devices that need to work across multiple platforms.
2. Simplicity and Efficiency
FAT32 uses a simple file allocation table to keep track of files. This simplicity translates to faster read and write operations on smaller drives and devices with limited processing power.
Although FAT32 is known for its simplicity, compatibility, and efficiency, it also has some limitations.
- FAT32 is prone to fragmentation, which can slow down read and write operations over time as files become scattered across the drive.
- FAT32’s 4 GB file size limit and 2 TB volume size limit can be restrictive for modern storage needs. Users dealing with large files such as high-definition videos or large databases may find FAT32 inadequate.
- FAT32 file system lacks security features and advanced data recovery capabilities, making it more susceptible to data corruption and loss in the event of a crash or power failure.
Use NTFS or FAT32 for USB
After understanding the two file systems in detail, the discussion will continue with: which file system is better, should I use NTFS or FAT32 for USB?
When to Use NTFS for USB
While NTFS offers several advantages, it is not always the best choice for every situation. Here are the scenarios when using NTFS for USB is particularly beneficial:
- Use NTFS if your USB drive will be used primarily with Windows systems.
- Use NTFS if you need to store files larger than 4 GB.
- Use NTFS if your USB drive exceeds 2 TB in size.
- Use NTFS if you need to manage disk space usage.
- Use NTFS If you need to store encrypted data on your USB drive.
When to Use FAT32 for USB
Here’s the best performance experience you can get by formatting your USB to FAT32 format:
- Use FAT32 if your USB drive needs to span different operating systems and devices.
- Use FAT32 for smaller drives and files, typically less than 32 GB and 4 GB respectively.
- Use FAT32 if your USB does not require universal data transfer and sharing.
- Use FAT32 if your USB is older and does not support newer file systems.
- Use FAT32 if your USB drive stores non-critical data and does not require advanced security features.
How to Format USB Drives to NTFS or FAT32
With an understanding of the pros and cons of these two file systems and the scenarios they are best suited for USB flash drives, the following sections will provide you with a few ways to format your USB to NTFS or FAT32. Note that the formatting process will erase all data on the USB drive, so make sure you have backed up important files.
Method 1: Use Disk Management
Disk Management is a graphical tool that provides a user-friendly interface for managing disks and volumes. Here’s how to format USB flash drive using Disk Management:
Step 1: Right-click on the Start button or press Windows + X and select Disk Management from the menu.
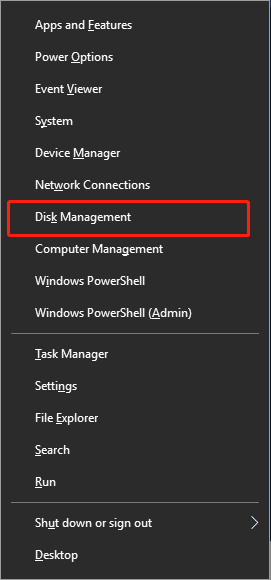
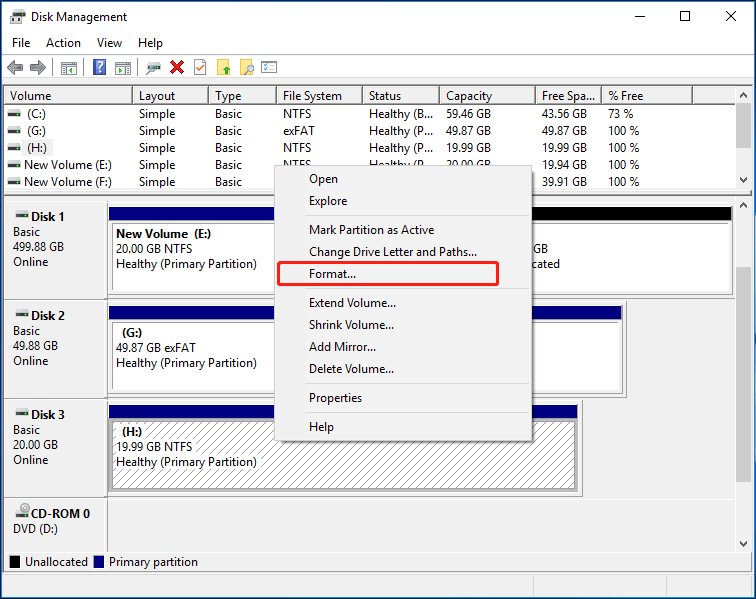
Step 2: In the Disk Management window, locate the USB drive you wish to format. Right-click on the drive and select Format.
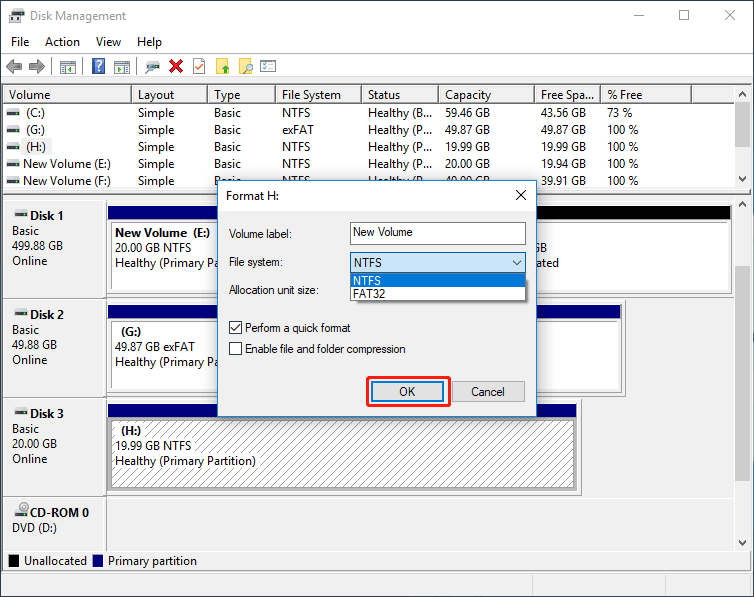
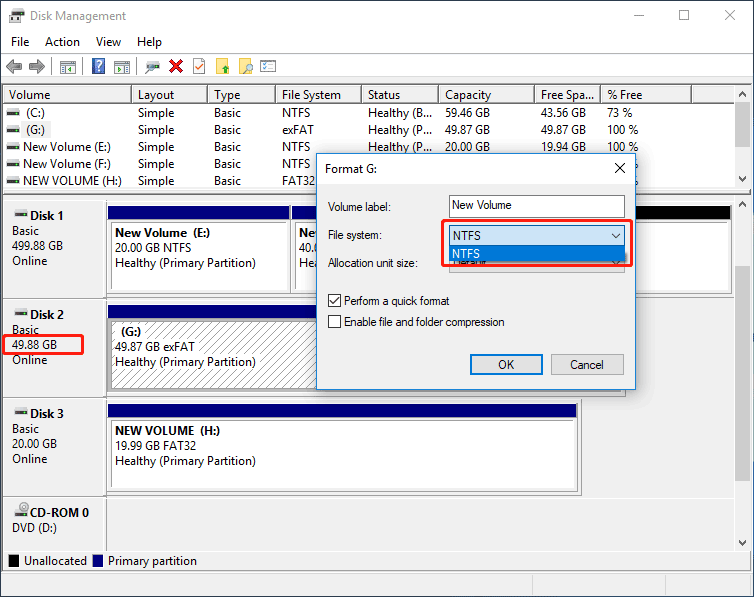
Step 3: In the disk formatting interface, specify volume label, file system (NTFS or FAT32) and allocation unit size. Perform a quick format is selected by default in Windows. Then, click OK to perform the formatting.
Method 2: Use Windows Explorer
In addition to the Disk Management, you can also format USB to NTFS or FAT32 via Windows File Explorer.
Step 1: Right-click the target USB drive you want to format in Windows Explorer, and then click Format.
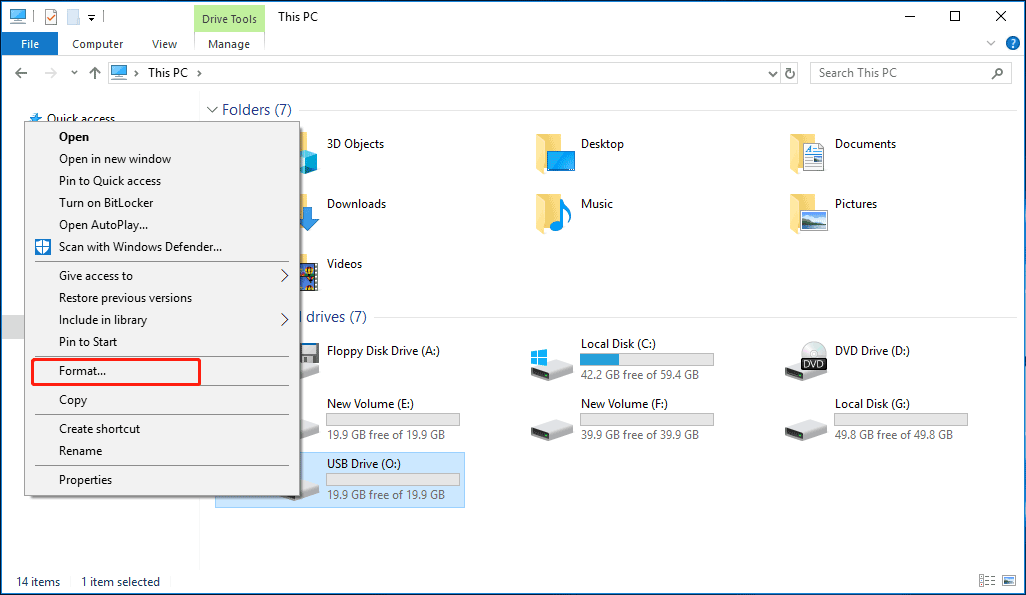
Step 2: Drop down the File System list, choose format USB to NTFS or FAT32, set the allocation unit size and volume label, choose Quick Format. Then, click Start to begin the format process.
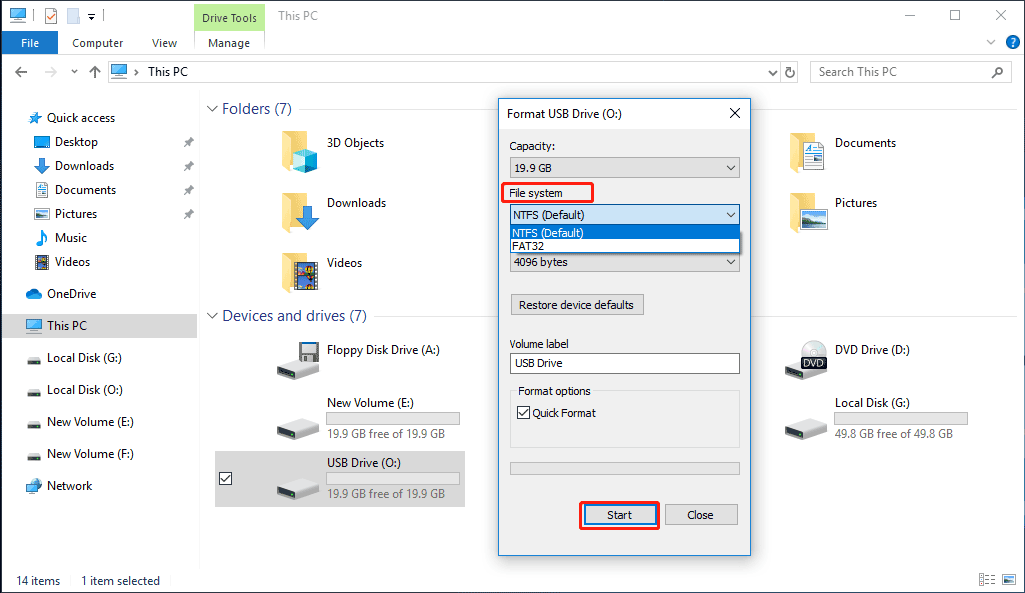
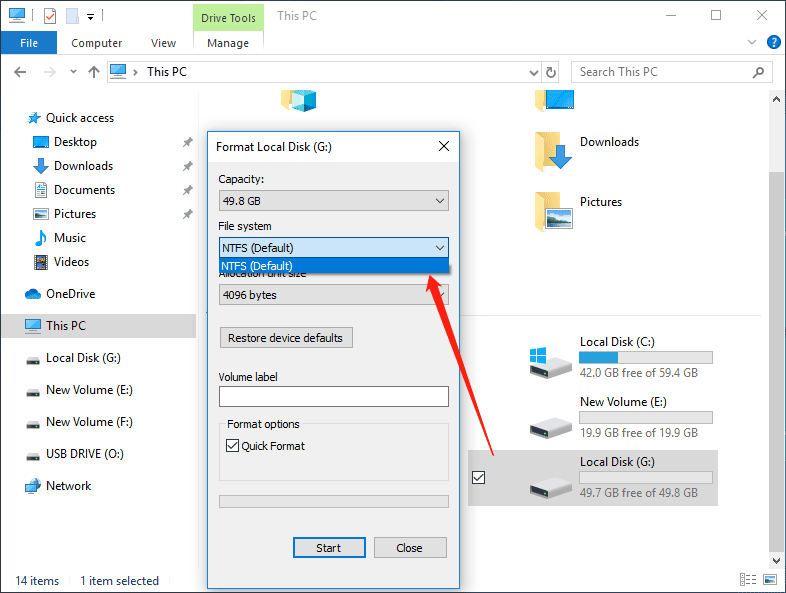
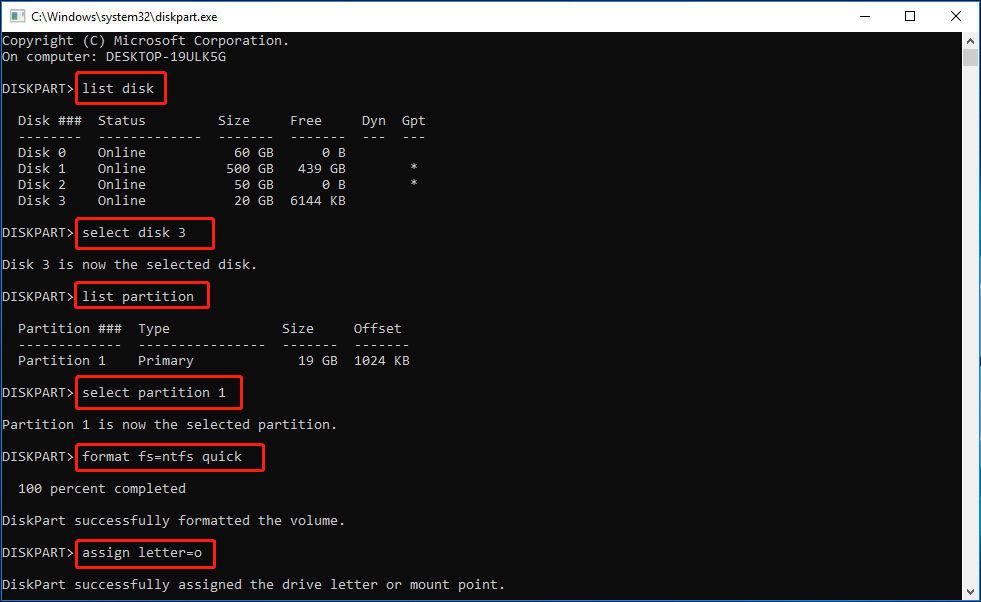
Method 3: Use DiskPart to Format USB Flash Drive
DiskPart is a command-line tool in Windows system that allows you to manage your disks and partitions. For administrators who prefer command-line tools, DiskPart provides a straightforward method to format USB drives.
Step 1: Press Windows + R, type diskpart, and press Enter to open the DiskPart tool.
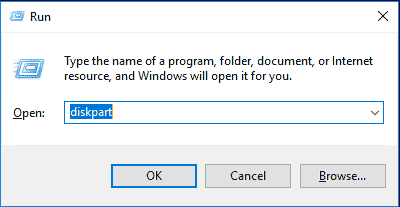
Step 2: Next, you can type the command lines below to format USB flash drive. Remember to press Enter after typing each command line.
- list disk (this command will list all available drives detected by the computer)
- select disk 1 (replace 1 with the exact USB drive number)
- list partition (this command will list all partitions on the selected disk)
- select partition X (replace X with the exact volume number of the target partition)
- format fs=ntfs quick (this command will format the USB flash drive to NTFS, you can add a quick flag after the command for a faster format.)
- assign letter=* (replace * with the preferred drive letter you want to assign to the USB drive)
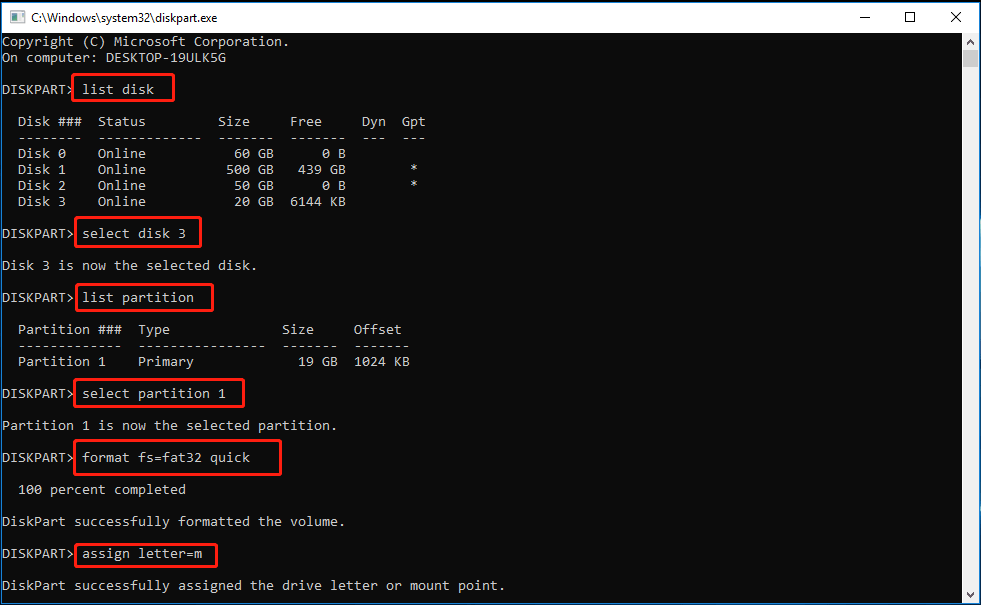
To format the USB flash drive to FAT32, just repeat the same steps but change NTFS to FAT32 in the fifth command line.
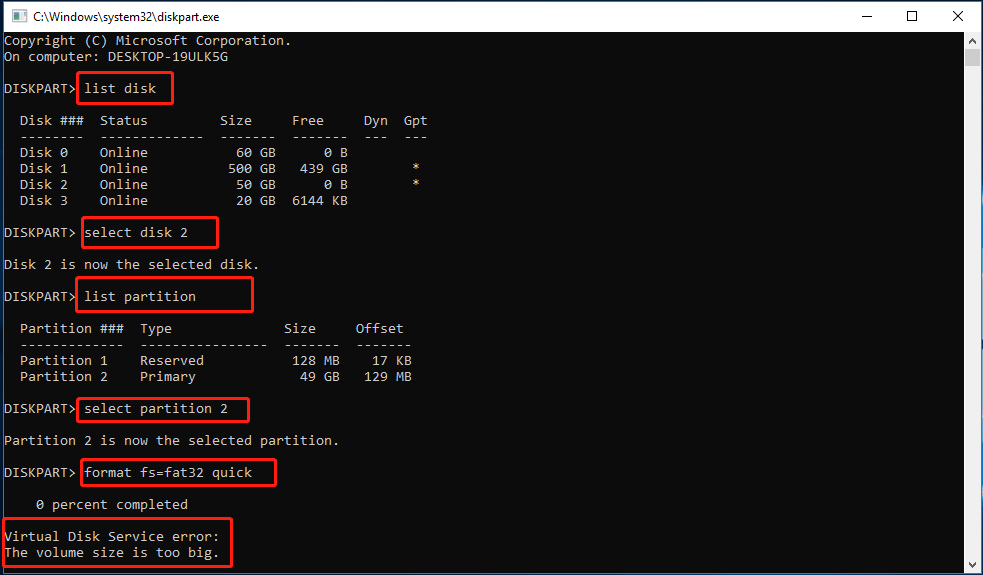
Method 4: Use MiniTool Partition Wizard to Quick Format USB
The above methods are very effective for formatting USB to NTFS. When formatting to FAT32, due to the size limitation of FAT32 file system (32 GB), Disk Management will not show FAT32 as an option; and in DiakPart, it will directly show an error message.
To solve this problem, here, I recommend you to use a third-party tool – MiniTool Partition Wizard. As a professional partition master for Windows computers, it can be used to convert MBR to GPT, rebuild MBR, clone hard drive, migrate OS to SSD/HDD, recover hard drive data, etc.
This professional partition management tool formats USB drives with no file size limitations and supports multiple file formats including: NTFS, FAT16, Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, exFAT and Linux Swap. And now, follow the guide below to format your USB device:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to the main interface. After selecting a partition of your USB flash drive, you will see the many features about partition management. Here, click Format Partition from the left panel.
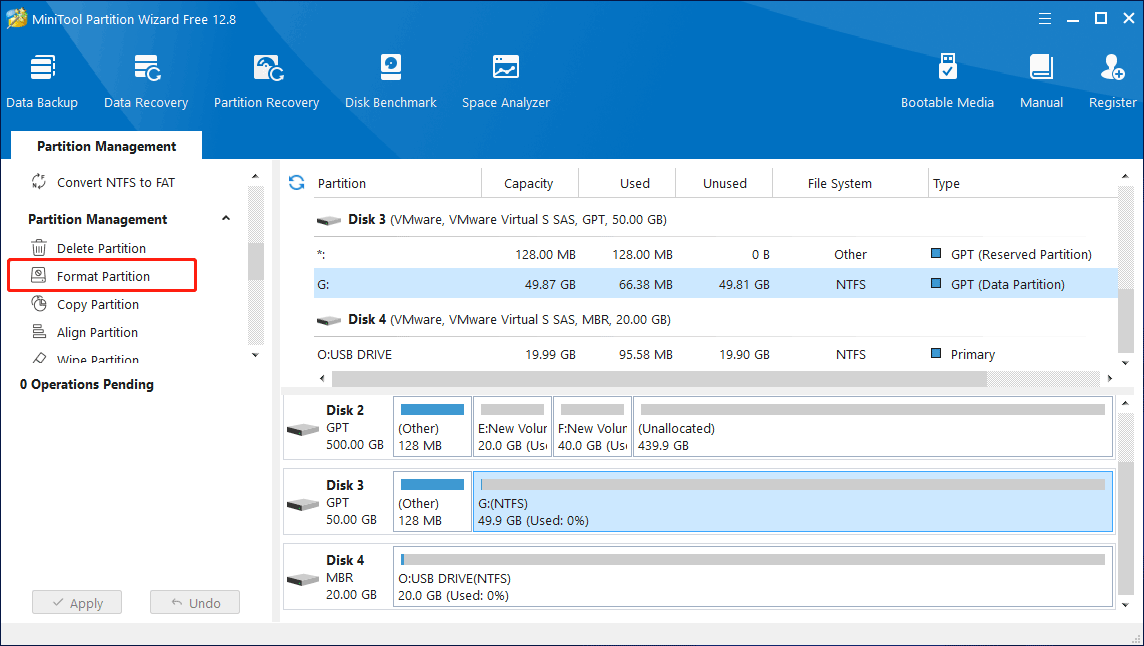
Step 2: In the pop-up Format Partition window, select NTFS or FAT32 and press OK button. Here, I will take formatting USB as FAT32 as an example.
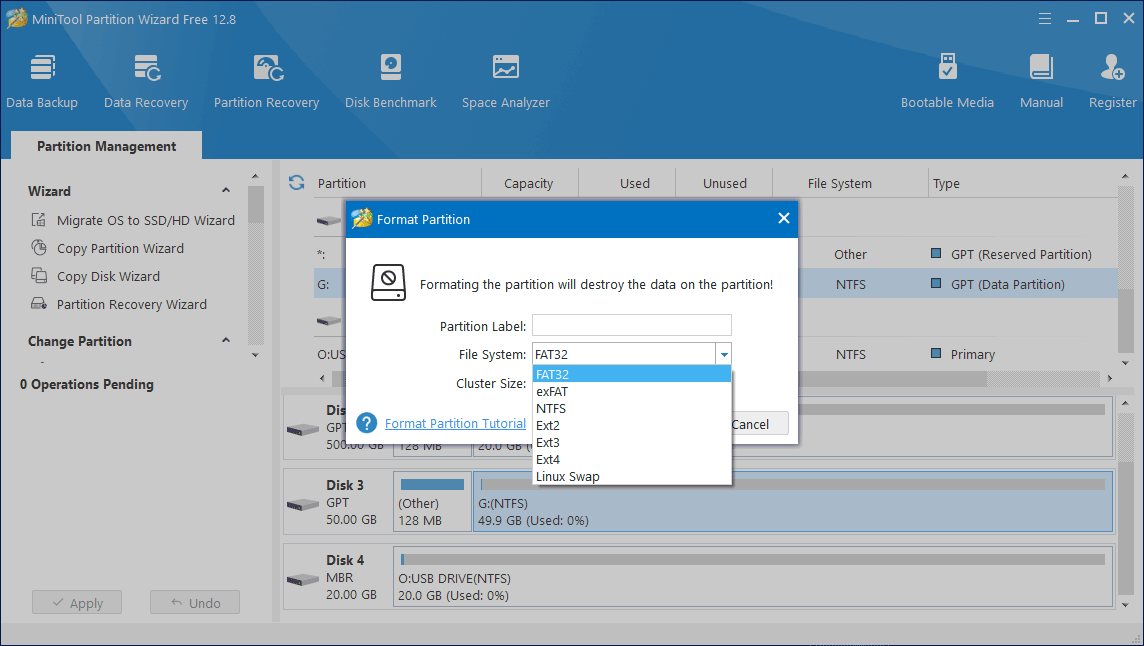
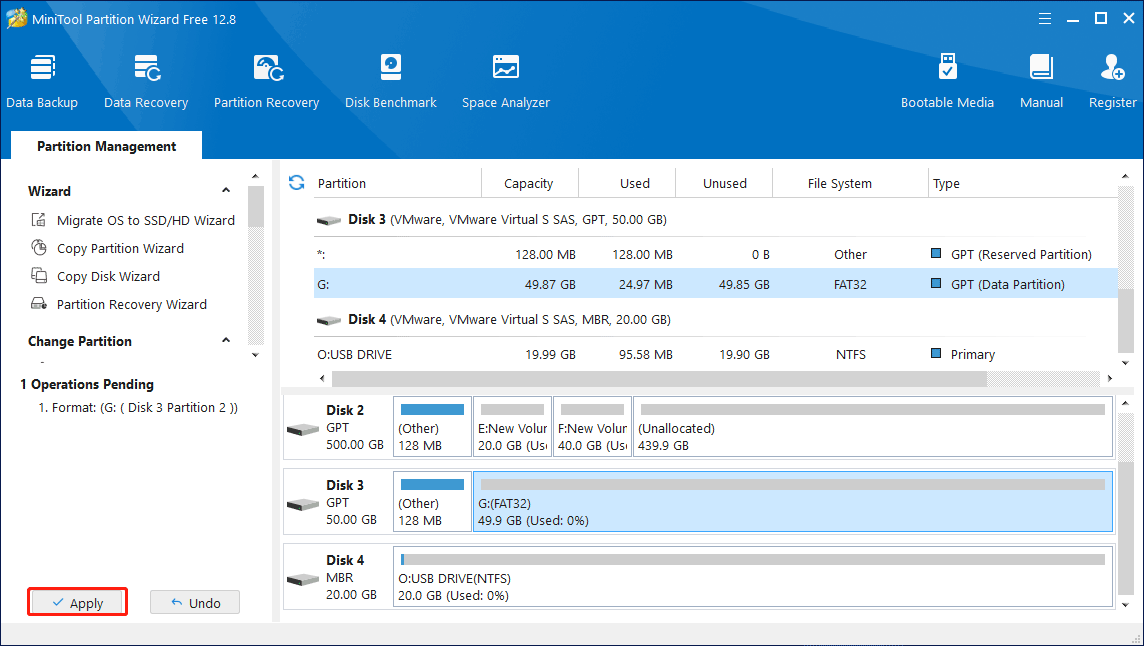
Step 3: Here you can see that MiniTool Partition Wizard successfully formatted a partition larger than 32GB to FAT32. Then, execute this change by clicking the Apply button.
Bottom Line
Considering NTFS or FAT32 for USB depend on your specific needs. By understanding the pros and cons of each file system mentioned in this post, you can make an informed decision. In addition, if you have any problems when using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can always contact us via the email [email protected].

![Quick Format VS Full Format [How to Choose For Data Security]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/06/quick-format-vs-full-format-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :