SD, short for Secure Digital, is a proprietary non-volatile memory card format. It is developed by the SD Association (SDA). This standard was released by SanDisk, Panasonic, and Toshiba in August 1999.
In the same year, they decided to develop and market the Secure Digital Memory Card. After that, multiple memory cards come into being.
Types of SD Cards – Capacity
Secure Digital contains five card families in three different sizes (standard, miniSD, microSD). The five families are the Standard-Capacity (SDSC), the High-Capacity (SDHC), the Extended-Capacity (SDXC), the Ultra-Capacity (SDUC), and the SDIO.
You may also like this: Learn Different Types of USB and the Method to Use It
SD or SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity)
The SD card is the first generation of the memory card, deriving from the MultiMediaCard (MMC) and including digital right management. A standard SD card’s dimension is 1.26 x 0.94 x 0.083 inches (32 x 24 x 2.1 – 1.4 mm).
The capacity of an SD card ranges from 128MB to 2GB. Its default file system is FAT16. It can work in all host devices that support SD, SDHC, and SDXC.
Mini SD
The miniSD was introduced by SanDisk Corporation on March 2003. It was adopted as a small form factor extension to the SD card standard in that year. A Mini SD card has a dimension of 0.85 x 0.79 x 0.055 inches (21.5 x 20 x 1.4 mm).

Also read: Thumb Drive VS Flash Drive: Compare Them and Make a Choice
Micro SD
The microSD portable miniaturized Secure Digital flash memory card was called T-Flash or TF (TransFlash) initially. Both the TransFlash and microSD cards function identically allowing either to work in devices made for the other.

MicroSD cards are the smaller-sized version of SD cards. The dimension of a microSD card is 0.56 x 0.43 x 0.039 inches (15 x 11 x 1 mm). The primary difference between SD cards and microSD cards is the form factor. MicroSD cards are more wide-in-use as they usually come with an SD adaptor allowing you to use microSD cards in hardware devices that only support SD cards.
Hardware devices are backward compatible with microSD cards too like they do for full-sized SD cards. MicroSD cards have the same standards of SD cards. The main microSD card types include microSDHC, microSDXC, and microSDUC. Their capacities are identical to their full-sized cards.
SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity)
The SDHC card is built based on the SDA 2.0 specification. Its capacity ranges from 4GB to 32GB. The default file system of SDHC card is FAT32. As SDHC works in a different way than standard SD card, it is not backward compatible with host devices that only take SD cards.

But the SDHC is compatible with most readers and host devices built after 2008. To ensure compatibility, you can check if there is an SDHC logo on cards and host devices like cameras, camcorders, etc.
SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity)
The SDXC card is a kind of memory card built based on the SDA 3.0 specification. Its default file system is exFAT, with a capacity ranging from 64GB to 2TB.
Since the file system and working manner of SDXC cards are different from that of standard SD cards, they are not compatible with host devices that only take SD or host devices only taking SDHC. However, the SDXC should be compatible with most host devices produced after 2010.

In summary, SDXC cards can only be used with SDXC host devices and won’t work with SD/SDHC host devices. SDXC host devices can support and use SD, SDHC, SDXC memory cards.
To ensure compatibility, check if your card and host devices have an SDXC logo. SDXC cards may not be supported by internal card readers on laptop up to the year 2008. These cards will work in SDHC compatible readers (not SD readers) if the PC OS supports exFAT.
Further reading:
Here, we list operating systems and the specific versions that support exFAT in the table below.
| Operating system | exFAT support | Patch download |
| Windows 10 | Supported natively | None |
| Windows 8 | Supported natively | None |
| Windows 7 | Supported natively | None |
| Windows Vista | You are required to update to Service Pack 1 or 2 | |
(Service Pack 2 or 3) | No longer supported by Microsoft | exFAT patch is no longer available for Windows XP systems |
| Mac OS X | Requires Mac OS X versions 10.6.6 and above | None |
SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity)
The SDUC format support cards up to 128TB and offers speeds up to 985MB/s in both the micro and full-size versions. It was announced in June 2018, described in the SD 7.0 specification.
Its interface type includes UHS-I, UHS-II, UHS-III, and SD Express. You should note that the SD Express interface can bed used in SDHC and SDXC cards too.
SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output)
The SDIO card, an extension of the SD specification, covers I/O functions. It can only work with host devices supporting their input-output functions. The SDIO family consists of low-speed and full-speed cards. Both the two SDIO cards support SPI and one-bit SD bus types.
SDIO cards can be structured as eight logical cards. At present, the SDIO card usually structures itself as one I/O card and one memory card. It supports most of the memory commands of SD cards.
Host devices manufactured for SDIO cards generally accept SD memory cards without I/O functions. As host devices need suitable drivers and applications to support the card’s I/O functions, the reverse is not true.
As shown in the above, there are various SD cards types. On the market, you can see different brands, sizes, quality SD cards. How to check if your SD card is fake and avoid buying such one again? Probably this post helps: Perform a Fake SD Card Test with Top 4 SD Card Checkers
SD Cards – Speed
The SDA defines three types of speed class ratings for SD cards. They are original speed class, UHS class, and video speed class. The content below will explain them one by one.
Original Speed Class
| Class | Minimum speed |
| 2 | 2MB/s |
| 4 | 4MB/s |
| 6 | 6MB/s |
| 8 | 8MB/s |
| 10 | 10MB/s |
UHS Speed Class
#1. Default
By default, an SD card reads and writes at the speed of 12.5MB/s.
#2. Hight Speed (HS)
High Speed Mode was brought in to support digital cameras with the 1.10 spec version.
The Ultra High Speed (UHS) bus is only available on some SDHC and SDXC cards.
#3. UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I)
UHS-I refers to Ultra High Speed Phase I designed for SDHC, which is added in SD spec 3.0. It can boost the performance of SDHC/SDXC cards. This standard defines two bus architecture options up to 50MB/s and 104MB/s data transfer rates.
Actually, USB is an improvement for the original SD interface specifications. When both the card and host device support UHS, host devices will get the maximum speed of the UHS. Otherwise, host devices will utilize the slower available SD maximum speed. You should note that there is no compatibility issue while using a UHS card with a non-UHS device.
#4. UHS-II (Ultra High Speed II)
UHS-II (Ultra High Speed II), designed for both SDHC and SDXC cards, is added in SD spec 4.0. It is an additional design enhancement with connector interface modifications that can improve the performance of cards. This standard defines bus architecture for options up to 156MB/s and 312MB/s. The 312MB/s option is implemented in memory cards by manufacturers.
Likewise, host devices will obtain the maximum UHS-II speed when the card and host devices support UHS-II. Otherwise, both the card and host device will use the fastest compatible UHS-I or SD bus speed. If you use a UHS-II card in a UHS-I or non-UHS device, you will not encounter compatibility problems.
#5. UHS-III (Ultra High Speed III)
UHS-III, released in February 2017, adds two new data rates to the standard. FD312 offers 312MB/s, while FD624 doubles that. The physical interface and pin-layout of UHS-III are identical to that of UHS-II. Besides, UHS-III retains backward compatibility.
Video Speed Class
Video Speed Class is defined to fulfill the need for high resolution and high-quality 4k and 8k video recording. It also includes a feature to support next-generation flash memory like 3D NAND. Moreover, this class covers the speed of HD video.
How to Manage an SD Card
If you want to put a new SD card into use, you need to perform some operations. Otherwise, you may encounter issues like SD card not showing up. According to actual conditions, you can format or partition the SD card.
MiniTool Partition Wizard helps you do that with ease. As a multifunctional partition manager, it allows you to create/format/delete/wipe/recover/extend/move/resize partitions within a few clicks. Importantly, it breaks the limit of Disk Management and CMD for partition creation.
To be specific, both Disk Management and CMD don’t allow you to create a FAT32 partition larger than 32GB, while MiniTool Partition Wizard allows. Here, we illustrate how to format and create an SD card through this partition program.
Step 1: Download and install MiniTool Partition Wizard by clicking the button below and following the on-screen instruction.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2: Connect your SD to your computer and then launch this program to go to its main interface.
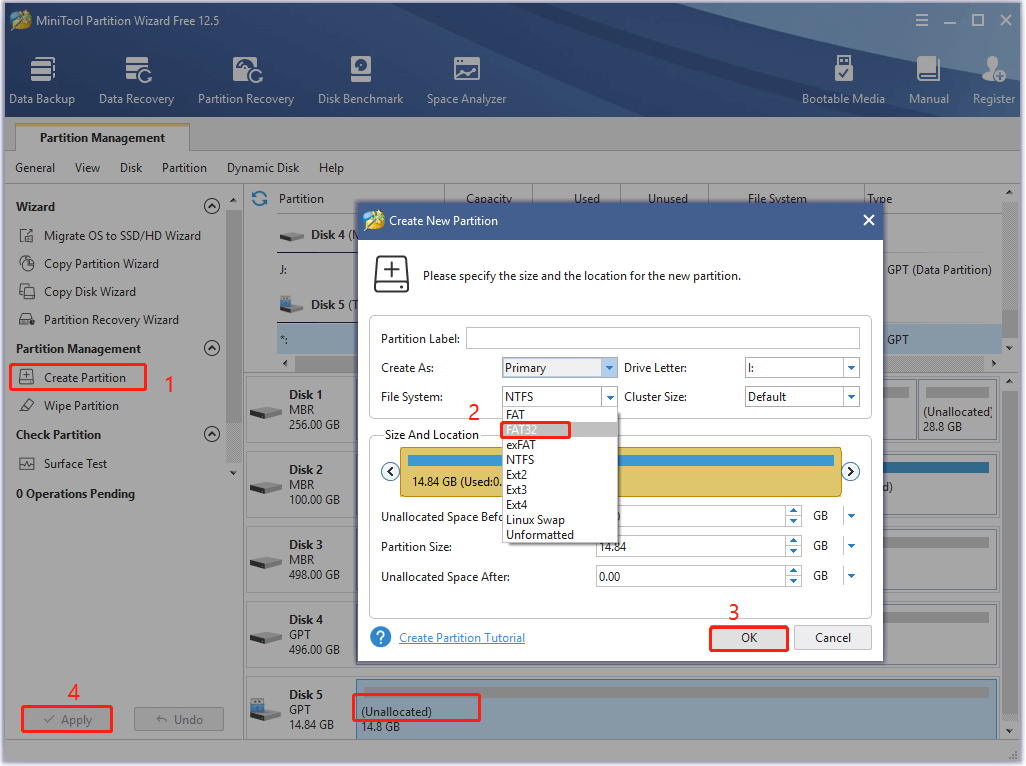
Step 3: Find the SD card from the disk map. If it doesn’t have a partition, create one. Otherwise, you can’t use the card.
- Click on the SD card and click the Create Partition option in the left pane.
- Choose a file system from the drop-down menu.
- Click OK and Apply to save and execute the changes you’ve made.
If the SD card is not formatted, you can format it manually by following the steps below.
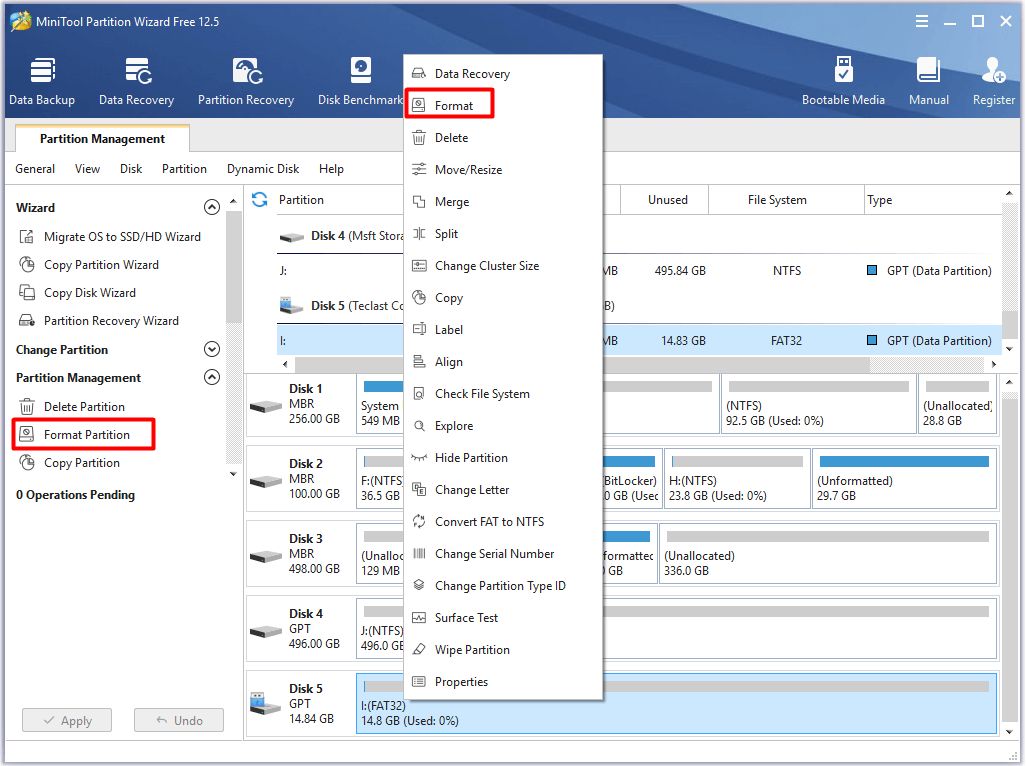
Step 1: After entering the main interface of MiniTool Partition Wizard, find and right-click on the connected SD card.
Step 2: Click on Format to continue. You can also highlight the SD card partition and click Format Partition in the action panel.
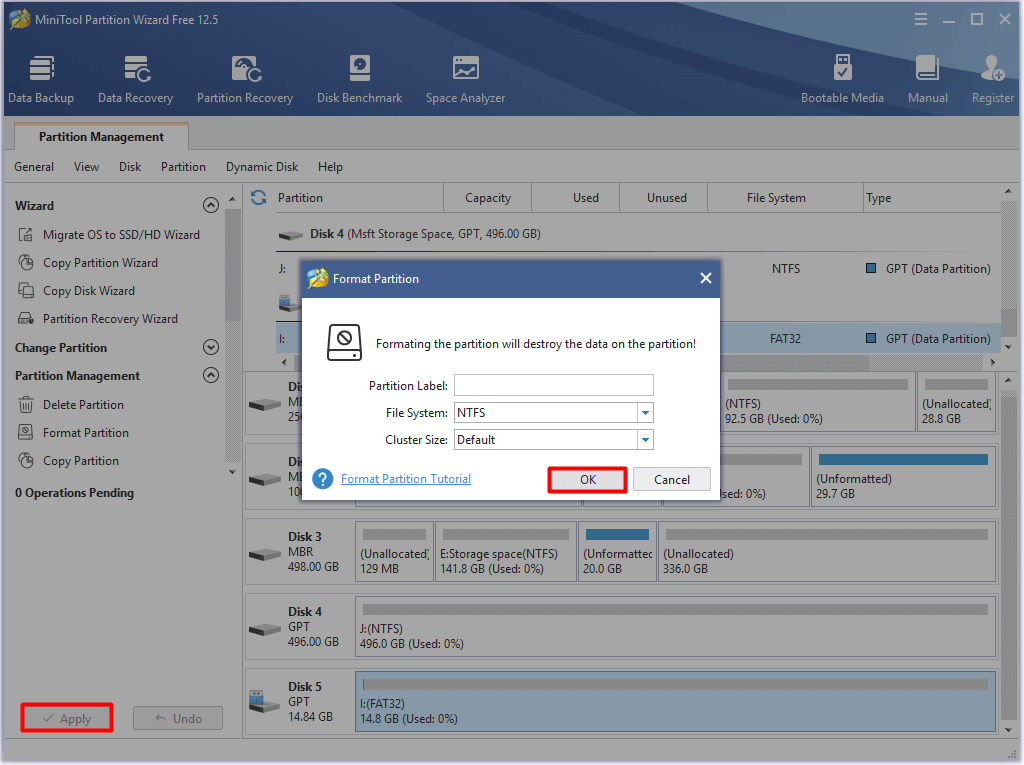
Step 3: In the Format Partition window, set partition label, file system, and cluster size according to your needs and click OK. If you don’t have special requirements, simply follow the default settings and click OK.
Step 4: Click Apply to execute the pending operation.
Also read: Ultimate Guide to Resolve Can’t Delete Files from SD Card Error
Bottom Line
To sum up, this post explains several SD card types and show you how to manage an SD card effectively. If you are unclear about these SD cards, this post is worth reading. More important, you can manage your SD card well with the given guides.
Do you have any questions about these types of SD cards? Well, you can write down your questions in the following comment area for sharing. For any issues occurring in the process of using MiniTool Partition Wizard, send us an email via [email protected]. We will back you as soon as possible.



User Comments :