This post tells you all things about SSD endurance, including its definition, importance, selection, test, and boost instructions. Besides, it also shows you how to perform an SSD health check via Partition Magic.
With many advantages, SSDs are preferred by plenty of users. Faced with various types of SSDs, you may get confused like many others. How to select a suitable SSD? If you are curious about it, pay attention to the following tips.
- Choose an SSD with the right form factor so that the drive can fit with your device. This guide shows you how to choose an SSD with the right form factor.
- The interface (SATA, SAS, or NVMe) of the SSD should be compatible with your device. This post collects the difference between SATA and NVMe.
- The read/write speed should meet your needs.
- The capacity should be large enough to hold all the items on your PC. For more information, please refer to this post: How Much Storage Should a Gaming PC Have? 500GB/1TB/2TB/3TB/4TB?
- The endurance, lifespan, and total number of terabytes written over time (TBW) should be far more than enough for your needs.
In this post, we mainly discuss SSD endurance, including its definition, importance, selection, test, and boost instructions. Explore the content now!
Also read: Here’s a Full Lenovo IdeaPad Gaming 3 SSD Upgrade Guide
About SSD Endurance
In this section, we will explain what SSD endurance is, how important SSD endurance is, and how to choose an SSD with the correct endurance.
What Is SSD Endurance
SSD endurance refers to the SSD’s capability to withstand sudden shocks and other environmental conditions, making it more resistant to failure over time. It also refers to the total data that an SSD can write under its warranty, often specified in “TBW” or “DWPD”.
TBW (Total Bytes Written) measures the total data that could be written to the SSD during its lifespan, while DWPD (Daily Writes Per Day) measures the number of times you can overwrite the whole SSD each day during its warranty time.
The P/E cycle is also called the program/erase cycle, which reflects the lifetime of an SSD because the number of P/E cycles that NAND can endure is finite. Once the number is reached, it’s impossible to write data on the SSD anymore. A cycle is each time a block is written and erased.
MTBF refers to the mean time between failures. It is calculated as the average time that an SSD can read/write data until it fails. The higher the MTBF, the more reliable the SSD is.
The Importance of SSD Endurance
SSD endurance is an essential factor that should be noticed while buying an SSD because it’s related to the lifespan and reliability of the drive. To be specific, you can choose an SSD that suits your needs and requirements best by SSD endurance.
Unlike HDD, there are no signs when an SSD is failing. After you learn the SSD endurance of your drive, you can back up the SSD via MiniTool ShadowMaker or other tools like that in time to avoid data loss.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Related articles:
- How long does data last on a USB/SD card
- Can the SSD lifespan be calculated
- Check if a hard drive is failing with SMART
Choose an SSD with Proper Endurance
Though a higher-endurance SSD offers better write performance than a lower-endurance SSD, it doesn’t mean choosing an SSD with too high endurance is good because this will increase the initial cost. However, buying an SSD with too low endurance increases the whole cost and troubles in the long run.
Since the total amount of written data exceeds warranty endurance, the possibility of losing data and SSD failing increases. Therefore, the cost of data recovery and SSD replacement increases. Given that fact, it is necessary to purchase an SSD with proper endurance.
What is a good SSD endurance? It varies greatly from what the SSD vendor specifies because of the dependency on the workloads. For example, there’s a distinction between client/consumer and data center/enterprise SSD endurance.
Different classes of drives have different endurance characteristics. In general, data center/enterprise SSDs have higher power, high performance, and higher endurance than consumer drives. They are rated for continuous workloads, while consumer SSDs often are tested when they are empty or “fresh out of the box” in the best conditions.
Consumer drives employ a cache to absorb the write. Besides, consumer NVMe SSDs also employ various low-power states to save battery life. As for enterprise/data center SSDs, they prioritize performance consistency, quality of service, and worse-case workload for measurement.
So, there’s a difference between client and enterprise SSD endurance. The SSD classes and requirements of clients and enterprise SSDs are summarized as follows.
| Application Class | Workload (JESD219) | Active Use (Power on) | Retention Use (Power off) | UBER |
| Client | Client | 40° C 8 hrs/day | 30° C, 1 year | ≤10-15 |
| Enterprise | Enterprise (10% 512B-4K, 67% 4K, 23% 8K-64K) | 55° C 24 hrs/day | 40° C, 3 months | ≤10-16 |
How to choose an SSD with the correct endurance? If you plan to keep an SSD for long-term (decades or centuries), you should buy an SSD with a high TBW rating (in the range of several hundred terabytes (TBs). What is a good SSD endurance? It depends on your situation.
Things will be easier if you know how much data your application will be writing. Determine the average amount of data written per day and then multiply it by the number of days a server is in service. Then use that number as a lower bound endurance limit. This average number is a lower bound because it’s prudent to add headroom for unexpected growth.
Perform an SSD Endurance Test
Manufacturers usually use DWPD and TBW to calculate how long an SSD lasts. For instance, if a 1TB drive is marked at 1 DWPD, you can write 1TB of data per data during the warranty period. So, SSD endurance can be measured and estimated by the following equations.
- DWPD to TBW: TBW = Capacity (TB) * DWPD * 365 * Warranty (Years)
- TBW to DWPD: DWPD = TBW / [365 * Warranty (Years) * Capacity (TB)]
To help you perform an SSD endurance test, the SNIA Solid State Drive Special Interest Group (SSD SIG) has developed a calculator and explanatory white paper. Click here to download the Endurance Calculator and then install it by following the prompted instructions. After that, launch the Endurance Calculator and conduct an SSD endurance test on your SSD.
How to Increase SSD Endurance
Learning from the above, SSD endurance is very important. Like others, you may wonder: Can I increase SSD endurance manually? The answer is for sure. Here are some available ways to increase SSD endurance.
For instance, you can try your best to avoid temperature extremes. Working on the SSD beyond its temperature specifications can result in performance drops and even premature failure. So, you should always keep temperatures within the manufacturer’s range of operation.
Besides, disable SSD defragmentation on your computer. By doing so, you can prolong the lifespan of your SSD. Setting up a maintenance schedule that includes periodic TRIM commands is also useful for improving SSD endurance. TRIM helps you maintain the performance of an SSD over time by optimizing its data storage capacity, which extends its lifespan in turn.
Perform an SSD Health Check
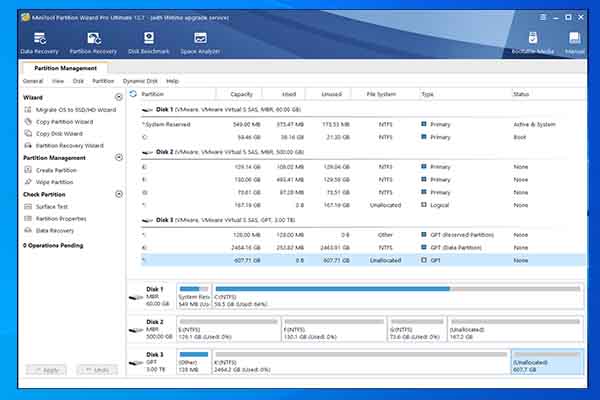
To know the health status of an SSD, you can perform an SSD health check manually. Here comes the need for MiniTool Partition Wizard – a comprehensive partition manager for Windows PCs. It can manage various storage devices, such as SSDs, HDDs, USB flash drives, SD cards, external hard drives, dynamic disks, etc.
For instance, it allows you to partition hard drive, format SD card FAT32, perform an SD card speed test, clone Samsung SSD to another SSD, convert MBR to GPT, recover data from external hard drive, and so on. As for disk error checking, both the Surface Test and Check File System features of MiniTool Partition Wizard work for you.
Install MiniTool Partition Wizard on your computer and then launch it to enter its main interface. After that, follow the steps below to scan your SSD for errors.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Right-click on a partition of the SSD and hit Check File System on the context menu.
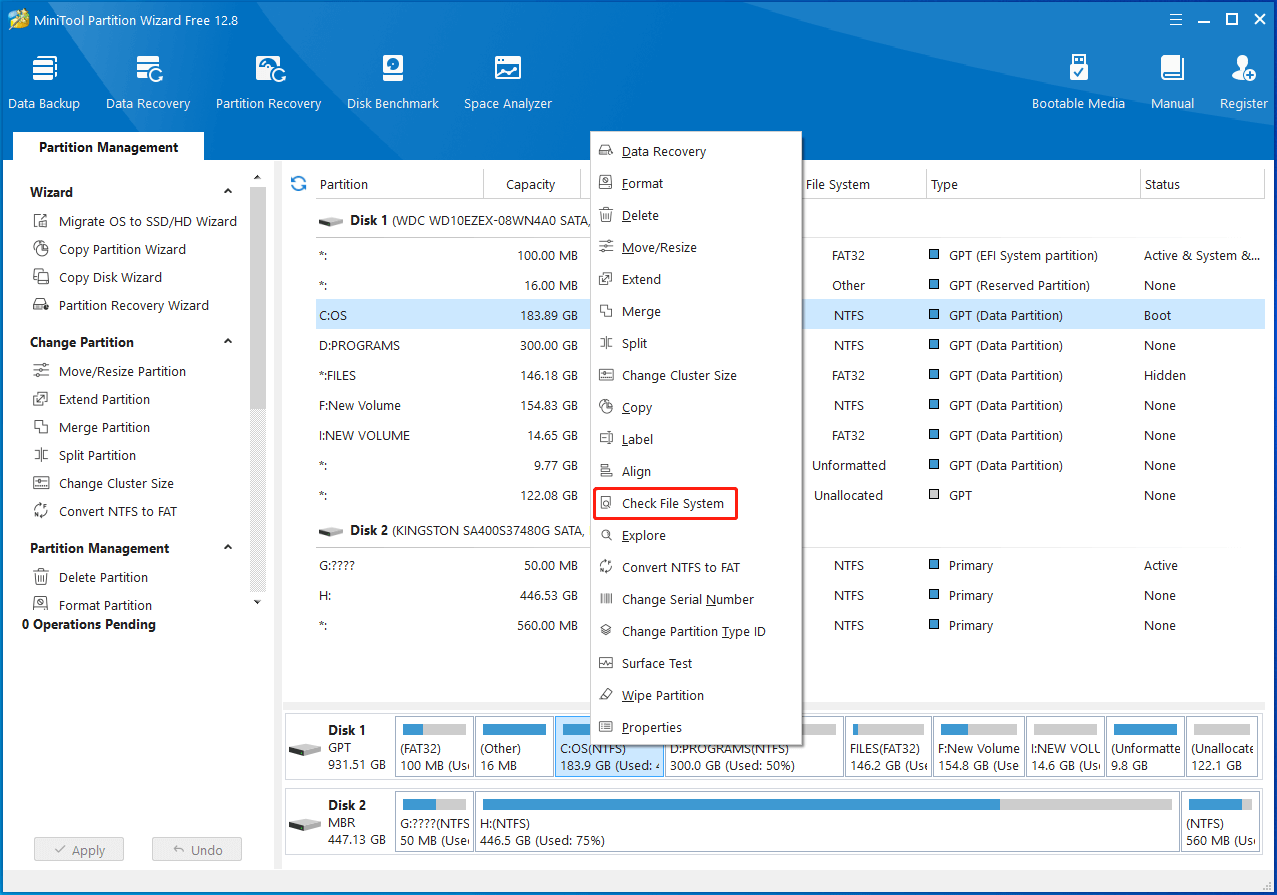
Step 2: In the prompted window, pick an option from the given options and click Start to begin the process. In this scenario, we select Check only. (Do not fix detected errors.). If any file system errors are found, run the Check File System feature again and tick the “Check & fix detected errors” option to solve them.
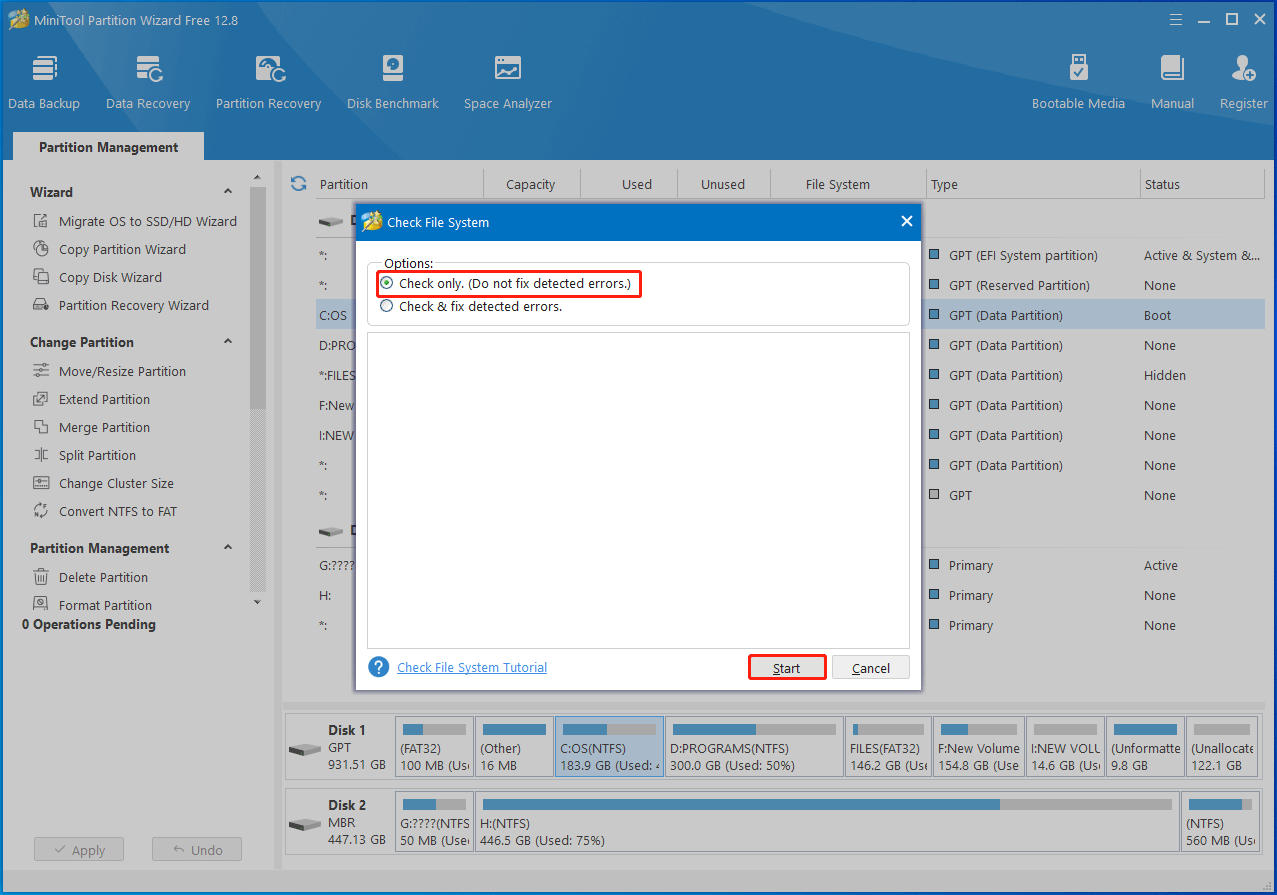
Step 3: Right-click on the SSD drive and choose Surface Test from the pop-up menu. Alternatively, highlight the SSD drive and click Surface Test under Check Disk in the left panel.
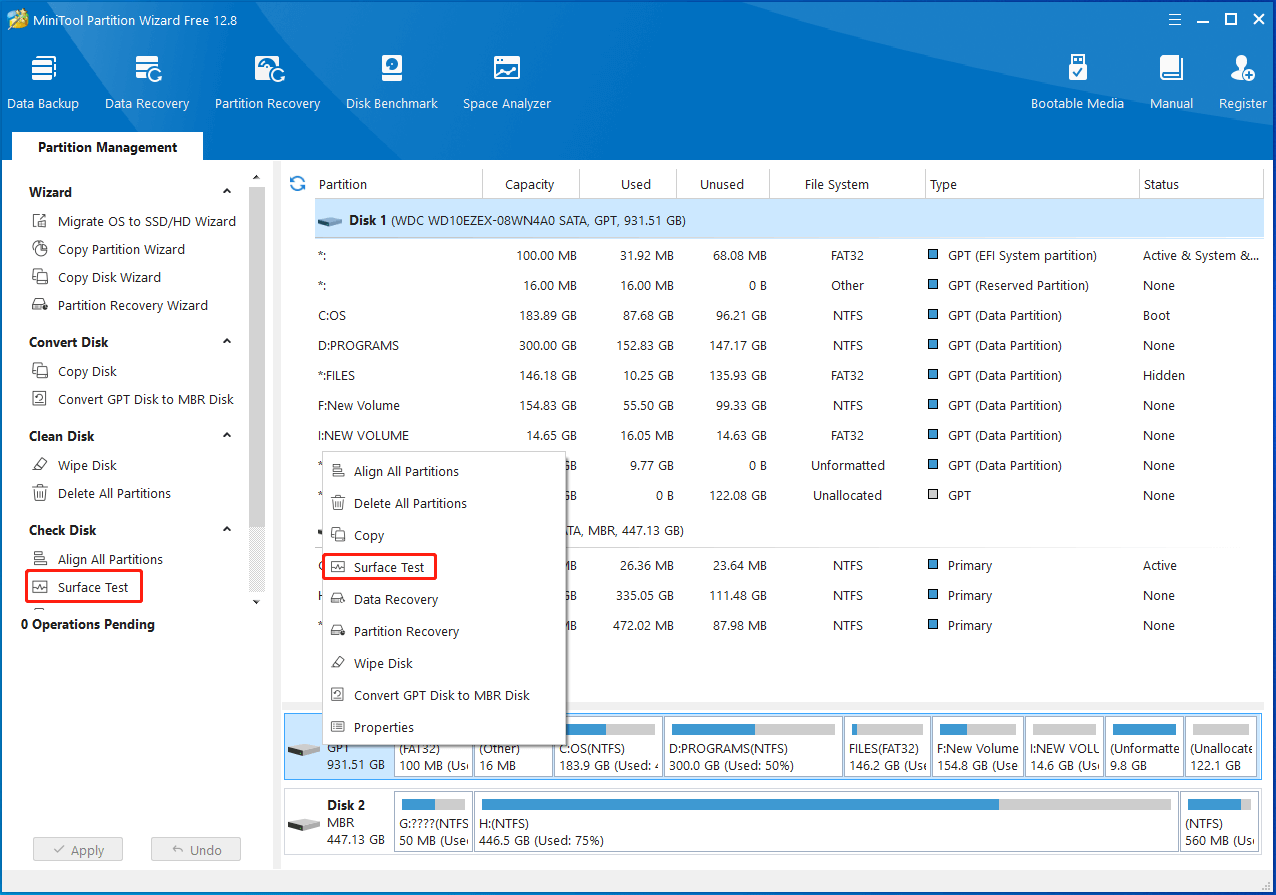
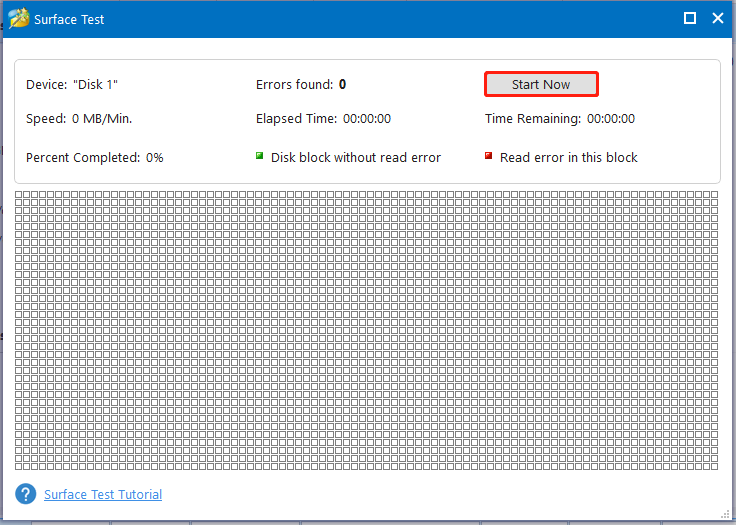
Step 2: In the Surface Test window, click the Start Now button to begin the process. Once the scan process ends, the complete scan result will be shown to you. If any blocks in the scan area are marked with red color, it means that the drive contains bad sectors. If so, transfer all the data to another storage device and then shield bad sectors or replace the disk. You can refer to this bad sector repair guide to remove them.
Bottom Line
This post introduces the basic information, importance, and selection of SSD endurance. Based on that, it tells you how to perform an SSD endurance test, how to increase SSD endurance, and how to check SSD health conditions. Simply put, this post is a comprehensive guide to SSD endurance.
If you encounter any problems while using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please directly contact us by sending an email to [email protected]. We will help you work out them as soon as possible.



User Comments :