What is the difference between MBR and GPT, and MBR VS GPT, which one is better for SSD? This post will answer those questions. For the better performance of your computer, this article will teach you how to initialize an MBR or GPT disk without losing data using a professional partition manager, MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Hard Disk Style: MBR and GPT
In general, MBR and GPT are two types of hard disks. You might have noticed that before using a new hard drive, Windows will prompt a disk initialization using their built-in Disk Management tool through the message “You must initialize a disk before Logical Disk Manager can access it“.
You should choose to initialize any data storage device you are using for the first time to either MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table).
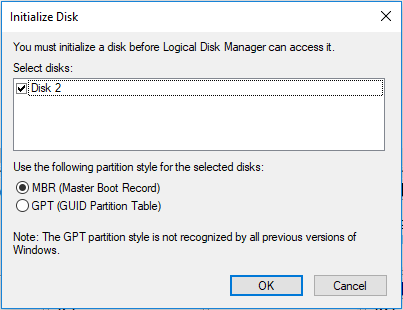
Since Windows initialize to MBR by default, it is natural for most people to directly click “OK” to perform this initialization without choosing GPT.
However, after a period of time, MBR might not be able to meet the performance needs of SSD or your storage device anymore. That is when you have to change your disk to GPT.
So, what exactly is the difference between MBR and GPT, and which one should you use for SSD? See the following part to know much information.
MBR or GPT for SSD
MBR VS GPT Layout
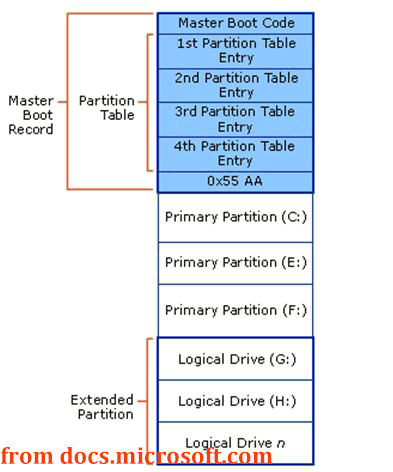
MBR, short for Master Boot Record, is an old standard to manage the partitions in a hard disk that is used extensively by many people. MBR refers to a specific boot sector at the very beginning of the hard disk and it holds some information on how the partitions are organized in a hard disk.
Generally speaking, MBR is made up of three sections:
1. Executable code called the Master Boot Code, which is used to
- Scan the partition table for active partitions
- Find the starting sector of the active partition
- Load a copy of the boot sector from the active partition into memory
- Transfer control to the executable code in the boot sector
2. Partition table for the disk
3. Disk signature
In short, MBR loads up the OS boot code or procedure from the active partition. Here is the MBR disk layout:
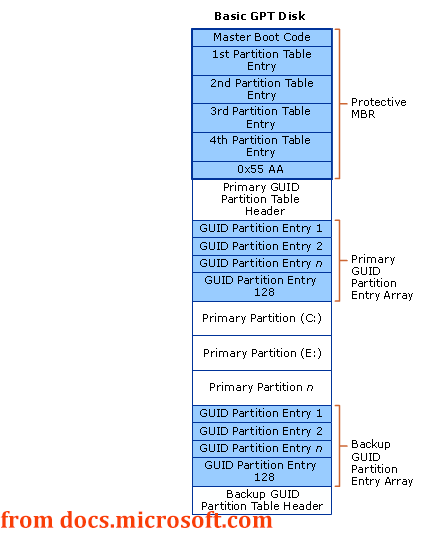
GPT, short for GUID Partition Table, is another disk type and the latest standard for the hard disk partition table layout using globally unique identifiers (GUID) to define the partition.
MBR uses 32 bits to store logical block address (LBA) and size information on a traditional 512-byte disk sector. MBR is becoming obsolete and being replaced by GUID.
GPT adopts primary and backup partition structures that are located, respectively, at the beginning and the end of the disk to provide redundancy.
Since GPT has a Protective MBR at the beginning of its partition table, it also uses logical block address (LBA) rather than relative sectors to identify partition structures.
Here is the GPT disk layout below:
Want to know more about the disk layouts of MBR and GPT? Read Basic Disks and Volumes Physical Structure now.
The Difference between MBR and GPT
After learning so much information about GPT VS MBR for SSD in layout, now let’s make a comparison for them in detail. When comparing MBR disk and GPT disk, you can clearly get four evident differences.
① MBR VS GPT Partition Number
MBR: Master Boot Record contains a 64-byte partition table made up of four partition tables entries, each using 16 bytes. Therefore, MBR can accommodate four primary partitions.
To create more partitions, the fourth partition can be changed to an extended partition to accommodate more logical drives. Microsoft supports up to 128 sub-partitions.
In summary, MBR disk supports up to four primary partitions, or three primary partitions plus an extended partition with up to 128 logical drives.
GPT: The partition table header of a GPT disk defines the usable blocks on the disk, as well as the number and sizes of the partition entries that make up the partition table.
EFI requires a minimum of 16,384 bytes reserved for partition table. That is, the partition table contains 128 partition entries of 128 bytes each, meaning that you can create up to 128 primary partitions on a GPT disk.
② MBR VS GPT Disk Size
In addition to the vast differences in the number of partitions, MBR and GPT also differ in disk sizes.
MBR limits its maximum addressable storage space to 2TB with each sector being 512 bytes. That is, even if an MBR disk has a storage space of larger than 2TB, you will find the disk space outside of 2TB to be “unallocated” in Disk Management.
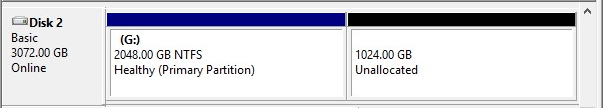
On the other hand, GIP allocates 64 bits for logical block addresses, hence allowing a maximum disk size of 264 sectors. With each sector being 512 bytes, it is equivalent to 9.44 ZB (1 ZB is 1 billion terabytes) or 8 ZiB. Summing it up, GPT disk supports up to 18EB in capacity.
③ MBR VS GPT Security
MBR and GPT also have different levels of security.
Comparing the layouts of MBR and GPT, we can see that at the beginning of the disk is a primary GUID partition table header and at the end of the disk is the backup GUID partition table header.
It is significant to note that GPT contains a CRC32 checksum for itself and for the partition table. Its firmware, bootloader and operating system can use the checksum to diagnose the partition table. Once errors are detected on the primary GPT, it is allowed to recover the whole partition table from the backup GUID partition header.
This is an outstanding advantage of GPT compared to MBR. Once the partition table is corrupted, the MBR disk is unusable. In this aspect, GPT has a higher level of security than MBR disk.
④ MBR VS GPT OS Support
The above content mentioned MBR VS GUID Partition Table in three aspects, moreover, you also need to pay attention to the supported operating system and BIOS.
Generally speaking, legacy BIOS only supports MBR and UEFI only supports GPT.
When comparing MBR and GPT in OS support, note that all operating systems can be installed on the MBR disk. However, on the contrary, not all Windows systems support GUID Partition Table.
OS Support on GPT
- Windows Vista 32-bit and XP 32-bit, and the early operating systems including Windows 2000, Windows MS-DOS/NT, Windows 95/98 can’t support reading, writing and booting from GPT disk. In Windows XP 64-bit, GPT disk can be used for data storage instead of system installation.
- All versions of Windows Vista/XP/7/8/8.1/10, Windows Server 2003/2008/2012/2016 can use GPT disk to save data to. But only 64-bit editions on UEFI-based systems can be used as system disks.
- Linux and Mac OS X10.6+ support GPT disk for data storage and OS boot requires UEFI BIOS.
MBR or GPT for SSD: Which One Is Better
MBR VS GPT, which one is better for SSD in terms of performance?
Long story short, we believe that GPT is better for the following reasons:
- It supports more than four primary partitions on SSD
- It supports storage (more than 2TB compared to MBR)
- It is more compatible with the newer UEFI-based systems
- More security
However, GPT is not always the right choice. If its hardware, firmware or software requirements can’t be met, you can only use MBR. The reasons could be that: your motherboard doesn’t support UEFI boot, or you still use an old Windows OS, or you install 32bit Windows 7 to an SSD.
In conclusion, choose one according to your actual need for better performance.
Hot article: MBR vs. GPT Guide: What’s The Difference and Which One Is Better
MBR VS GPT SSD, Make a Conversion?
For the best performance, you might one day need to convert your disk to MBR or vise. How to reinitialize a disk to MBR or GPT without losing data? Actually, it is very simple to achieve this with a professional partition manager.
Here we recommend the MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition since it provides many reliable features to manage your disk and partitions in Windows 7/8/10 including the ability to convert the disks between MBR and GPT. Try out this amazing software by downloading and installing MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition here.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Important:
If you want to alter the system disk, do the followings in advance in case of any accidents after the conversion.
To demonstrate GPT/MBR conversion, we will use Professional Edition as an example.
Convert GPT to MBR
As mentioned before, not all operating systems can be installed on a GPT disk.
Suppose you want to install a second OS in addition to an existing OS on your computer - for example, Windows 7 32-bit on a GPT disk. Windows will stop you with the “Windows cannot be installed to this disk. The selected disk is of the GPT partition style” error.
In this case, you need to convert this hard drive from GPT to MBR.
Step 1: Launch this software. Then choose the GPT disk, and then select “Convert GPT Disk to MBR Disk“.
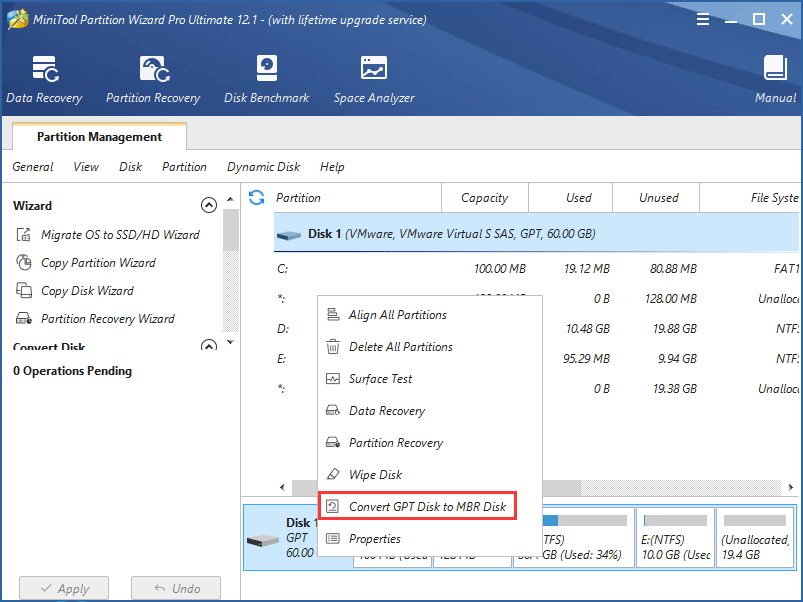
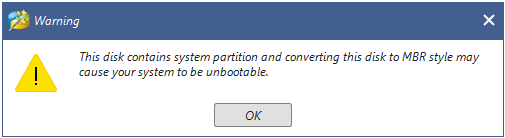
Step 2: Click “Apply” to execute this conversion. The earlier OS can now be installed on your disk.
Some of you might be reluctant to use a third-party partition manager but prefer Windows Disk Management instead. However, for a data disk, the procedure might not work with Windows Disk Management unless you intend to delete all volumes. “Convert to MBR Disk” is greyed out.
Moreover, this free tool can’t be used to convert OS disk. Therefore, in order to avoid data loss, MiniTool Partition Wizard should be a good choice.
Convert MBR to GPT
To create more partitions, make full use of your disk with more than 2TB, or solve the “Windows cannot be installed on this disk. The selected disk has an MBR partition table. On EFI systems, Windows can only be installed on GPT disks” error message, you need to convert MBR to GPT disk. MiniTool Partition Wizard also offers a feature to initialize MBR to GPT without losing data.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Click the MBR disk, and then select “Convert MBR Disk to GPT Disk” in the action pane.
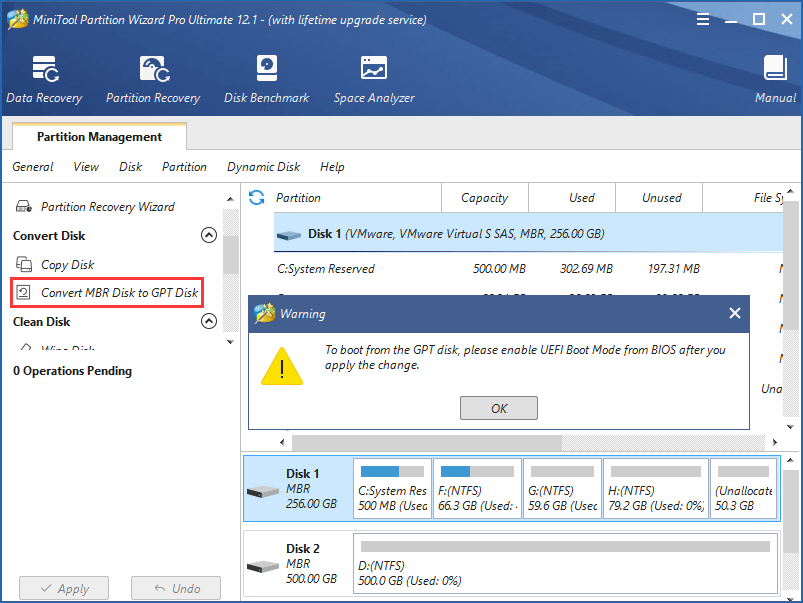
Step 2: Hit “Apply” to execute this change. After finishing this conversion, you can create up to 128 partitions on your SSD or make full use of the disk space on a 2TB+ disk.
Bottom Line
Now, all the information about MBR VS GPT is told to you. And you clearly know the difference between MBR and GPT, GPT VS MBR for SSD: which one is better and how to initialize disk MBR or GPT without losing data with MiniTool Partition Wizard.
If you have any suggestion or question, please send an email to [email protected] or leave a comment below.

User Comments :