Do you want to know about ZFS vs Ext4? If you have no idea about how to choose between the two file systems, you can read this post, in which MiniTool Partition Wizard will compare them in detail.
Introduction to ZFS and Ext4
ZFS is a high-performance file system developed by Sun Microsystems and has been ported to several platforms such as Linux and FreeBSD, providing powerful features such as snapshots, replication, and checksums for data integrity verification.
Ext4 is a journaling file system developed by a team led by Theodore Ts’o. It is a successor to the Ext3 file system. In 2008, the stable version of Ext4 was officially announced and became the official recommended default file system for Linux.
ZFS vs Ext4
Trying to choose between ZFS and Ext4 file systems? Then, we will compare ZFS and Ext4 in Performance, Reliability, and Accessibility aspects.
# 1. Performance
In terms of performance, both ZFS and Ext4 offer good levels of speed and reliability, but they also have their own unique advantages and disadvantages.
ZFS is a modern file system designed from the ground up to provide high-performance storage capabilities. It leverages advanced data integrity checksums, copy-on-write snapshots, and RAID support for optimal performance on all types of hardware. ZFS is ideal for large enterprise setups where scalability is critical. ZFS has proven to be highly reliable.
Ext4 became a widely used file system because of its ability to manage large files and being a reliable file system. While it may not have all the advanced features of ZFS, it is generally faster and lighter, making it a good choice for many common workloads.
Ext4’s journaling mechanism prevents potential data loss by recording changes made during write operations so that any failures can be quickly identified and repaired without resorting to restoring backup copies or performing time-consuming manual repairs.
In terms of performance, both ZFS and Ext4 offer high levels of speed, but in different approaches. Ultimately, which filesystem to choose is a matter of personal preference. In terms of overall performance, there’s no clear winner between the two.
# 2. Reliability
ZFS uses copy-on-write technology to guarantee that data is written atomically. If an interruption occurs during a write, the write will succeed or be aborted entirely. This makes it very reliable and no damage can occur. It also has built-in redundancy features such as RAIDZ, which allow you to store data on multiple disks, each with its own set of parity information for recovery if one of the disks fails.
Ext4 lacks redundancy features like ZFS. Therefore, Ext4 is more susceptible to data corruption if an interruption or power failure occurs during a write operation. On the other hand, however, it supports larger file sizes (up to 16TB) than earlier versions such as ext3 or FAT32, giving users greater flexibility in storage capacity.
Overall, both solutions offer good reliability. If you need guarantees against corruption, use ZFS, otherwise, if speed is a concern, you should use Ext4.
# 3. Accessibility
ZFS provides users with great flexibility in managing data. It supports multiple filesystems in the same pool, allowing users to organize their data into separate directories and apply unique settings to each directory. This makes it easy to quickly find a specific file without searching through tons of irrelevant information.
Ext4 provides a simpler solution for filesystem configuration, requiring no additional setup. Ext4 does not require any special configuration from the user and provides a simple experience for those unfamiliar with more advanced file system configuration requirements.
In terms of accessibility, both ZFS and Ext4 offer users great options.
Bonus: How to Format Your Drive to Ext4 on Windows
In some cases, you may need to format your drive to Ext4 on Windows. You can’t use Windows built-in tools to format a drive to Ext4. Therefore, to format a drive to Ext4 on Windows smoothly, it’s highly recommended you use MiniTool Partition Wizard. The steps are as follows:
Step 1: Download and install MiniTool Partition Wizard on your PC. Then launch it to get its main interface. If you want to format an external drive, please connect it to your Windows beforehand.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
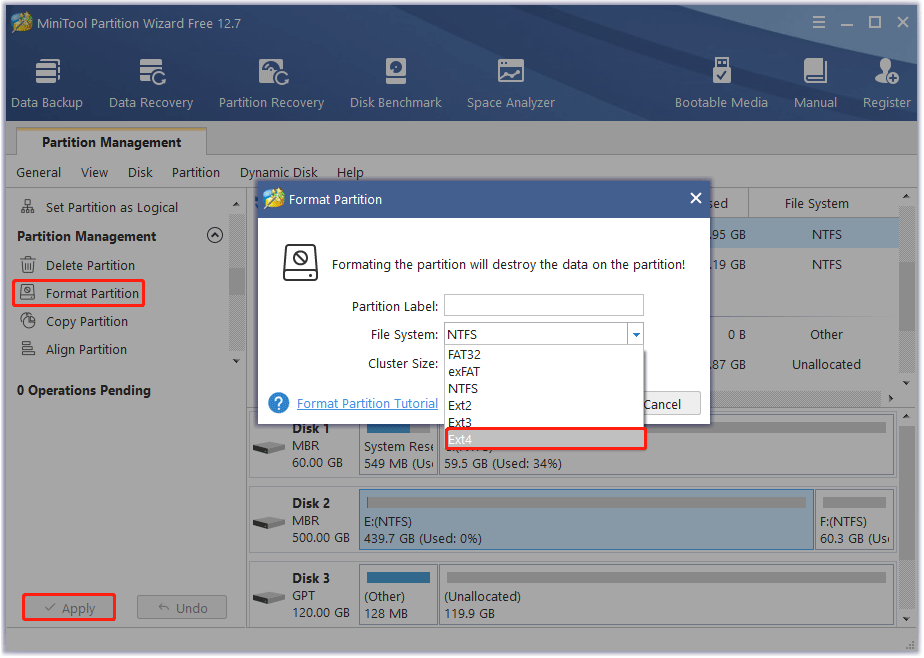
Step 2: In the main interface, click the drive that you want to format and click on Format Partition from the left pane.
Step 3: In the pop-up window, select the Ext4 file system type from the drop-down menu and click on OK to save changes. Also, you can set Partition Label and Cluster Size based on your needs.
Step 4: Click on the Apply button to execute this formatting.

![Introduction to Linux File System [Structure and Types]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2020/08/linux-file-system-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :