Today, businesses are increasingly faced with the decision of choosing between virtual server vs physical server to meet their computing needs. This post from Partition Magic explores the key differences between them, their respective benefits and drawbacks, and the scenarios in which each is most suitable.
What Is a Physical Server?
A physical server, also known as a dedicated server, is a single machine that provides computing resources exclusively to a single client or organization. These servers are composed of hardware components such as CPUs, RAM, storage drives, and network interfaces, all housed within a single physical chassis.
Physical servers are standalone hardware units dedicated to providing computing resources for various applications and services. Here are the key features of physical servers.
#1. Independence
A physical server is an independent hardware device with its own processor, memory, hard disk and other resources, and can run operating systems and applications independently.
#2. Customization and Control
Physical servers provide complete control over hardware components and configurations, allowing for customized settings, as well as the flexibility to install and configure any operating system, software, or application without restrictions to meet specific requirements.
#3. High Performance and Reliability
Physical servers are known for their stability and reliability, with fewer points of failure than in a shared environment. Their dedicated resources ensure that applications run at optimal speed without interference.
#4. Security
The physical server is used exclusively by a single organization, ensuring that the data is not shared or accessed by other parties.
Drawbacks of Physical Servers
Physical servers provide a robust and reliable computing environment, but it has some drawbacks:
- Physical servers typically require a large investment due to the initial investment in hardware and ongoing maintenance and operational costs.
- Scaling physical servers is challenging and time-consuming. Adding resources requires the purchase and installation of new hardware, which can lead to downtime and increased costs.
- Physical servers can suffer from underutilization of resources. Since servers are dedicated to a single organization, there may be underutilization of server capacity.
What Is a Virtual Server?
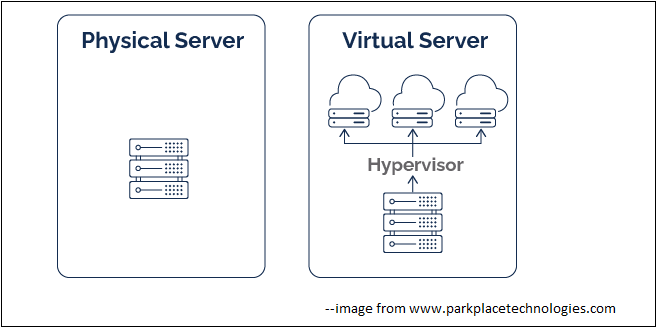
Virtual servers are software-based versions of physical servers. They utilize virtualization technology to create multiple isolated environments on a single physical server.
VMware is a typical virtualization software that uses virtualization technology to run multiple operating systems and applications on a single physical server.
Here are the key features of virtual servers:
#1. Resource Sharing
Virtual servers are divided on physical servers through virtualization technology, so resources are shared. However, each virtual server has resources allocated to it (such as processor, memory, disk space, etc.), which can be used and managed without affecting other virtual servers.
#2. Independence and Isolation
Virtual servers run on physical servers, and each virtual server has an independent operating system, file system, and resources, just like an independent server. This allows each virtual server to run and be managed independently without being affected by other virtual servers.
#3. Flexibility and Portability
Virtual machines support a variety of operating systems and applications, providing flexible deployment methods. They can also be easily moved or copied between different physical hosts to achieve migration and disaster recovery.
#4. Scalability
Virtual servers can be expanded or shrunk as needed. Users can flexibly adjust the configuration of virtual servers according to their business needs.
#5. Security
Virtualization technology can isolate different virtual servers, ensuring that the data and applications of each virtual server are isolated from each other, improving security.
Virtual servers are an affordable and flexible solution that can provide users with an independent and customizable server environment. But managing a virtualized environment can be complex, especially in large-scale deployments. It requires expertise and tools to ensure optimal performance, security, and resource allocation.
Choosing Between Virtual Server vs Physical Server
In the realm of information technology, the choice between virtual server vs physical server is pivotal. Next are some scenarios in which each option might be more suitable.
When to Choose Physical Servers
- Applications that require high performance, such as database servers, high-frequency trading platforms, and large-scale scientific simulations, may benefit from the dedicated resources of physical servers.
- Organizations with stringent security and compliance requirements, such as those in the financial and healthcare sectors, may prefer physical servers to ensure data isolation and regulatory compliance.
- Some legacy applications are not compatible with virtualization technology and must run on physical servers. In such cases, physical servers are the only viable option.
When to Choose Virtual Servers
- Organizations looking to reduce IT costs through hardware consolidation and improved resource utilization will benefit from virtual servers. Virtualization allows for more efficient use of existing resources and can reduce the need for additional hardware.
- Businesses with fluctuating workloads or rapidly changing requirements will find virtual servers advantageous. The ability to quickly scale resources up or down and to deploy new VMs as needed provides significant operational flexibility.
- Virtual servers are ideal for implementing robust disaster recovery solutions. The ease of backing up and restoring VMs ensures minimal downtime and data loss in the event of a failure.
Bottom Line
Both virtual and physical servers have their own advantages and disadvantages. Ultimately, the choice between virtual server vs physical server should be based on a thorough evaluation of an organization’s specific needs and long-term goals. By carefully considering these factors mentioned in this post, hopefully it will help you make an informed decision.


User Comments :