SSDs have become the go-to storage solution for many users due to their superior speed, reliability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional HDDs. One of the key metrics to understand when evaluating the longevity and durability of an SSD is the Terabytes Written (TBW). This post from Partition Magic will cover everything you should know about SSD TBW.
What Is SSD TBW
TBW stands for Terabytes Written and it represents the total amount of data that can be written to an SSD before it is expected to fail. It is an endurance rating provided by the manufacturer that indicates the lifespan of the SSD based on the amount of data written to it over time.
The importance of TBW lies in its ability to predict the longevity and reliability of an SSD. Unlike HDDs, which rely on mechanical parts that can wear out over time, SSDs use NAND flash memory, which degrades with each write cycle. Therefore, knowing the TBW of an SSD can help users estimate how long the drive will last under their specific usage conditions.
For example, an SSD with a TBW rating of 150 TB means that you can write a total of 150 terabytes of data to the drive before the likelihood of failure increases. So, if a user writes around 10 GB of data per day to an SSD with a TBW of 150 TB, the drive is expected to last for approximately 15,000 days, or over 41 years.
Factors Influencing TBW
However, real-life usage can vary significantly. There are several factors that can influence the TBW of an SSD:
#1. NAND Flash Type
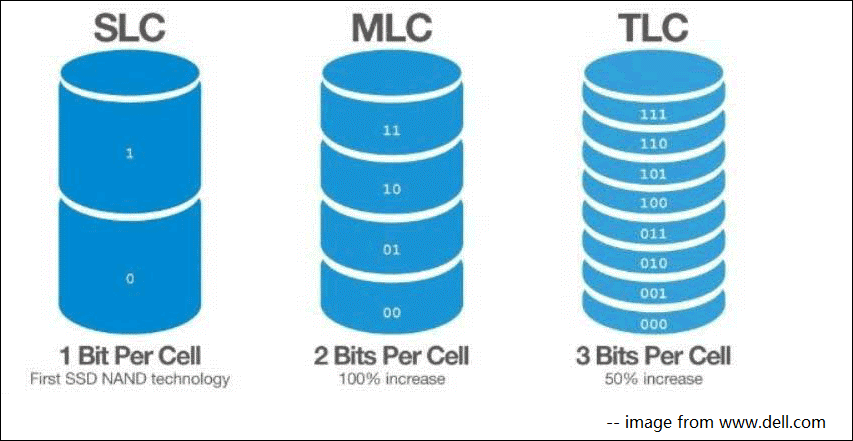
The type of NAND flash memory used in the SSD plays a crucial role in determining its TBW. Single-Level Cell (SLC) NAND can handle more write cycles compared to Multi-Level Cell (MLC) and Triple-Level Cell (TLC) NAND. As a result, SSDs with SLC NAND typically have a higher TBW rating compared to those with MLC or TLC NAND.
#2. Wear Leveling
Wear leveling is a process used by SSDs to distribute write and erase cycles evenly across all NAND cells. Effective wear leveling can significantly extend the lifespan of an SSD by ensuring that no single cell wears out prematurely.
#3. Write Amplification
Write amplification refers to the phenomenon where the actual amount of physical data written to the NAND cells is greater than the amount of logical data intended to be written. Lower write amplification leads to a longer lifespan for the SSD, as it reduces the number of write cycles.
#4. Workload and Usage Patterns
The type of workload and how the SSD is used also impact its TBW. For example, an SSD used in a read-intensive application will generally last longer than one used in a write-intensive environment.
How to Check TBW on SSD
Checking the TBW on an SSD is important to monitor its health and ensure it is within the manufacturer’s specified endurance limits. Here are 2 methods you can use to check the TBW on an SSD:
1. Use Manufacturer’s SSD Management Software
Many SSD manufacturers provide proprietary software that allows you to monitor the health and performance of your SSD. Such software often includes information on TBW. For example:
- Samsung Magician: For Samsung SSDs
- Crucial Storage Executive: For Crucial SSDs
- WD SSD Dashboard: For Western Digital SSDs
- Kingston SSD Manager: For Kingston SSDs
You can visit the manufacturer’s website and download the appropriate SSD management software. Then, open the software and navigate to the drive health or status section, and look for a metric labeled as Total Bytes Written, Lifetime Writes, or something similar to get the TBW information.
2. Use CrystalDiskInfo
CrystalDiskInfo is a user-friendly tool that provides detailed information about your SSD, including TBW. Follow the steps below to check the SSD TBW:
Step 1: Visit the CrystalDiskInfo download page and download the latest version. Install the software by following the on-screen instructions.
Step 2: Open CrystalDiskInfo. It will automatically detect all connected drives and display their health status.
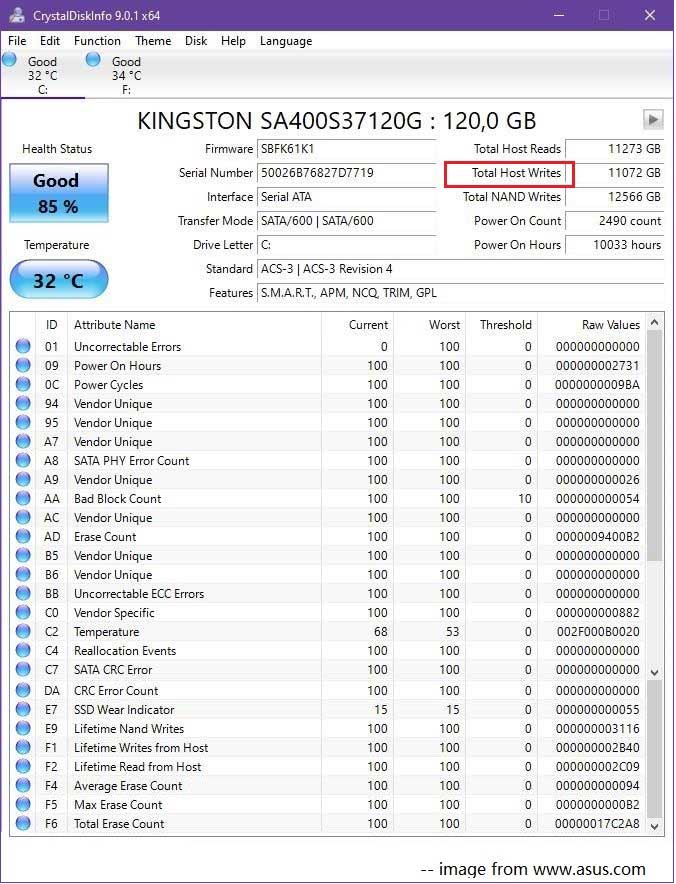
Step 3: Select your SSD from the list of drives. Look for attributes named Total Host Writes or Total NAND Writes. These values represent the TBW of your SSD.
In addition to CrystalDiskInfo, MiniTool Partition Wizard is a good choice if you want to know more about your SSD’s performance, such as checking the health of SSD. Its Disk Benchmark feature can help you test disk performance. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and click Disk Benchmark on the tool bar.
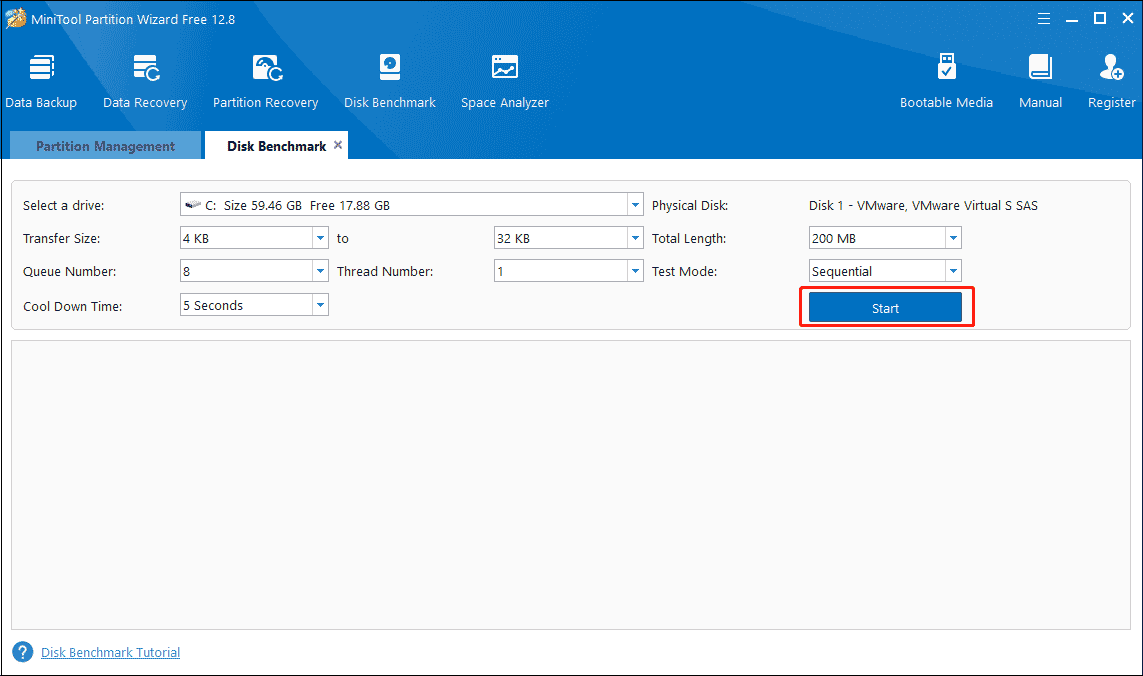
Step 2: Select a partition you want to check, set parameters, and then click Start to test the disk performance.
The parameters are as follows:
- Select a drive: All the drives in this PC are listed here, and users can drop down the list to select a disk or volume to test its performance.
- Transfer Size: The size of the data transferred at one time, ranging from 1KB to 2048KB.
- Total Length: The total amount of data to transfer, ranging from 100MB to 4096MB.
- Queue Number: It ranges from 1 to 512.
- Thread Number: Select how many threads are used to test the speed of the drive. It ranges from 1 to 64.
- Test Mode: There are three modes for users to choose: Sequential, Random, and Sequential & Random.
- Cool Down Time: It is used to reduce the hard drive temperature.
Bottom Line
Understanding TBW is essential for selecting the right SSD and ensuring its longevity and reliability. This post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of SSD TBW, covering its definition, importance, influencing factors. Hopefully, this post can help you to choose the best SSD for your specific requirements.


![How to Measure Disk Performance Easily [Step-By-Step Guide]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2019/06/disk-performance-test-thumbnail.jpg)
User Comments :