Software encryption and hardware encryption are effective ways to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Each method has distinct advantages and disadvantages. This post from Partition Magic explores software vs hardware encryption, their benefits, drawbacks, and their applications in securing data.
Understanding Software Encryption
Software encryption involves the use of software programs to encrypt and decrypt data. This method relies on the computing resources of the host system, utilizing its CPU to perform encryption tasks. Popular examples of software encryption tools include BitLocker, VeraCrypt, and FileVault.
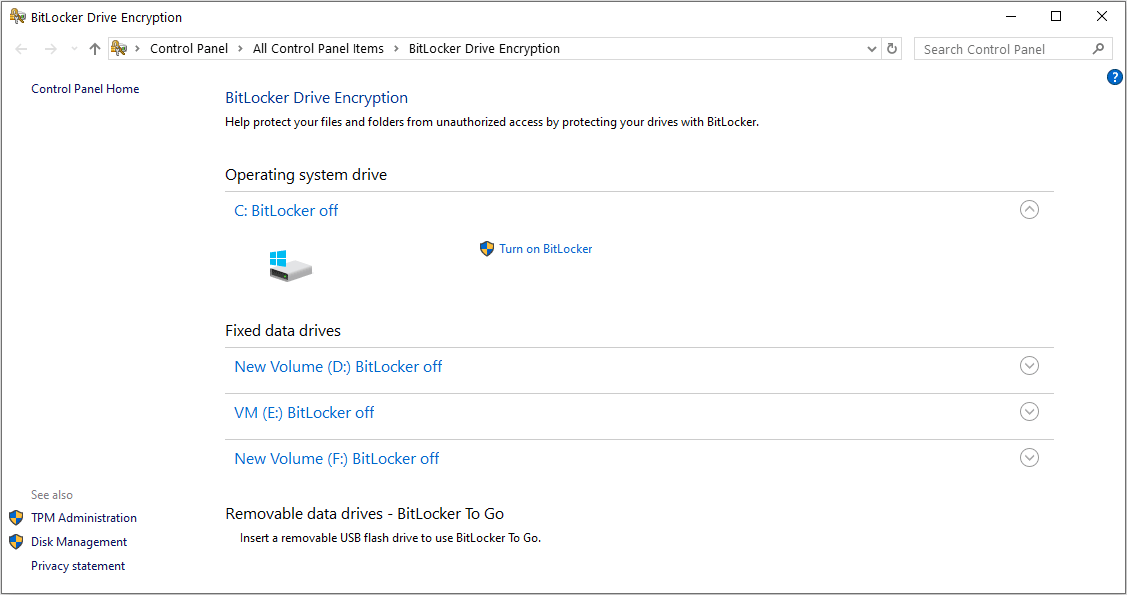
Read the following parts to know the advantages of software encryption.
- Flexibility: Software encryption is highly adaptable, allowing users to apply encryption to various types of data and storage devices. It can be used on different operating systems and integrated with other software applications.
- Cost-Effective: Software encryption is more affordable because it does not require specialized hardware. Users can use their current computing resources without spending additional investment on encryption hardware.
- Ease of Deployment: Deploying software encryption is straightforward, often requiring just the installation of an encryption program and configuration of encryption policies. This simplicity makes it accessible for individual users and small organizations.
- Regular Updates: Software encryption tools can be regularly updated to address vulnerabilities and enhance security features. This ongoing development ensures that encryption methods remain robust against emerging threats.
Like other encryption methods, software encryption has some drawbacks.
- Performance Impact: Since software encryption relies on the CPU, it can impact system performance, especially on resource-constrained devices. Encryption and decryption processes may slow down operations, affecting productivity.
- Vulnerability to Malware: Software encryption is susceptible to malware and other cyber threats that can compromise the host system. If the system is infected, encryption keys and encrypted data can be at risk.
- Complexity in Management: Managing encryption keys and policies can be complex, particularly in large organizations with extensive data and multiple devices. Improper key management can lead to data loss or breaches.
Understanding Hardware Encryption
Hardware encryption involves dedicated hardware components to perform encryption tasks. These components can be integrated into storage devices, such as self-encrypting drives (SEDs), or embedded in specialized security modules, like Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs).
If you have it, you’ll see a Security processor section on the screen.
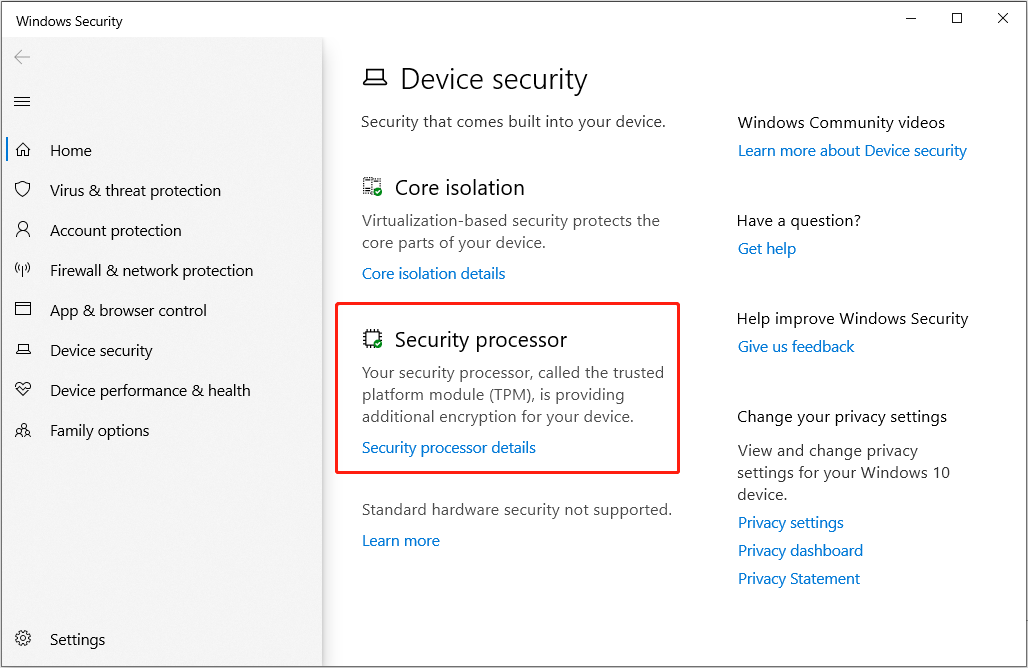
For detailed information, you can refer to following contents to learn the pros and cons of Hardware encryption:
Pros:
- Enhanced Security: Hardware encryption provides better security by isolating encryption keys and processes from the host system. This isolation reduces the risk of keys being compromised by malware or unauthorized access.
- Performance Efficiency: Since encryption tasks are offloaded to dedicated hardware, the performance impact on the host system is minimal.
- Tamper Resistance: Many hardware encryption devices are designed to be tamper-resistant. They can detect and respond to physical tampering attempts, adding additional protection for encrypted data.
- Simplified Key Management: Hardware encryption often includes built-in key management features, simplifying the process of generating, storing, and managing encryption keys. This ease of management reduces the risk of human error.
Cons:
- Cost: The primary drawback of hardware encryption is the cost. Specialized hardware components can be expensive, making this solution less accessible for individuals and small organizations with limited budgets.
- Potential for Obsolescence: As hardware encryption technology evolves, older hardware may become obsolete.
- Limited Flexibility: Hardware encryption is typically tied to specific hardware devices and may not be easily transferable or applicable to other storage media.
Software vs Hardware Encryption
Here, the software vs hardware encryption is explained from different perspectives.
Performance
Software encryption can be applied to any data type and storage device, offering versatility. but Software encryption relies on the host system’s CPU and memory, which can significantly impact performance, especially during intensive encryption or decryption tasks.
Hardware encryption can process encryption and decryption much faster than software solutions, especially for large data sets.
Security
Software can be patched regularly to address vulnerabilities and improve security features. But software encryption is vulnerable to malware attacks, such as keyloggers and ransomware, which can capture encryption keys or corrupt encrypted data.
Hardware encryption devices are designed to be tamper-resistant, providing a higher level of physical security. Encryption processes are isolated from the main system, reducing the risk of exposure to malware or OS vulnerabilities. However, if there is a vulnerability in the hardware firmware, fixing it can be difficult.
Cost
Typically, software encryption solutions are less expensive to implement because they do not require specialized hardware. However, over time, potential performance impacts can lead to higher operating costs.
The upfront cost of hardware encryption solutions can be high. But once the hardware is purchased, the cost is fixed and there is no need to pay extra for performance-related upgrades.
Use Cases
For personal data protection, such as encrypting files and folders on a personal computer, software encryption is often sufficient. Small businesses with limited budgets can benefit from software encryption solutions to secure sensitive information, such as customer data and financial records.
Large organizations with extensive data and high-security requirements often opt for hardware encryption. In data center environments, hardware encryption is essential to safeguard massive amounts of data stored on servers and storage devices.
Government agencies and military organizations require the highest levels of data security. Hardware encryption provides the robust protection needed to secure classified and sensitive information against sophisticated threats.
As with anything in life, there are pros and cons to each encryption method, and deciding which method to use ultimately depends on your specific needs and priorities.
Bottom Line
Both software and hardware encryption have unique advantages for different application scenarios. This post compares the two encryption methods. Ultimately, the choice between software and hardware encryption depends on the specific needs, budget, and security requirements of the user or organization. Hopefully, users can get effective information from this post.

![How to Choose the Best Encrypted Flash Drive [Top 10 Choices]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2021/08/encrypted-flash-drive-thumbnail.png)

User Comments :