When setting up a new operating system, one of the critical decisions involves determining the appropriate size for the boot partition. The boot partition is a vital component of your system, housing the files necessary for the initial stages of the operating system boot process. This post from Partition Magic will delve into the recommended size for boot partition.
What Is Boot Partition?
A boot partition (also called a boot volume or a boot drive) is a portion of a storage device (such as an HDD or an SSD) that holds boot loader and other important files for starting your computer.
#1. Windows
On Windows, the partition that holds the boot loader is often referred to as the System Reserved or EFI system partition. This partition also contains the Boot Manager code, Boot Configuration Database, and other startup files.
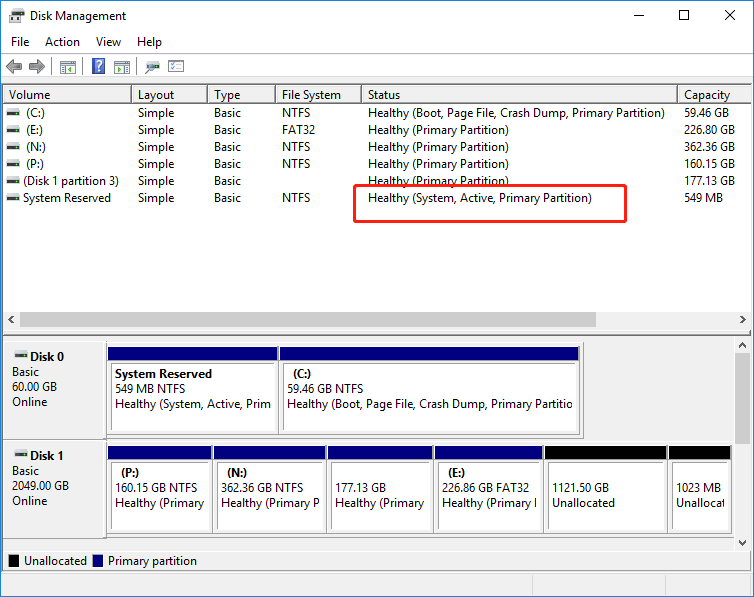
#2. Linux
Linux distributions typically require a separate `/boot` partition. This partition contains EFI, GRUB, the Linux kernel, and other fundamentals required to boot the operating system. When your computer boots up, it will look in the boot partition for the files needed to load the operating system.
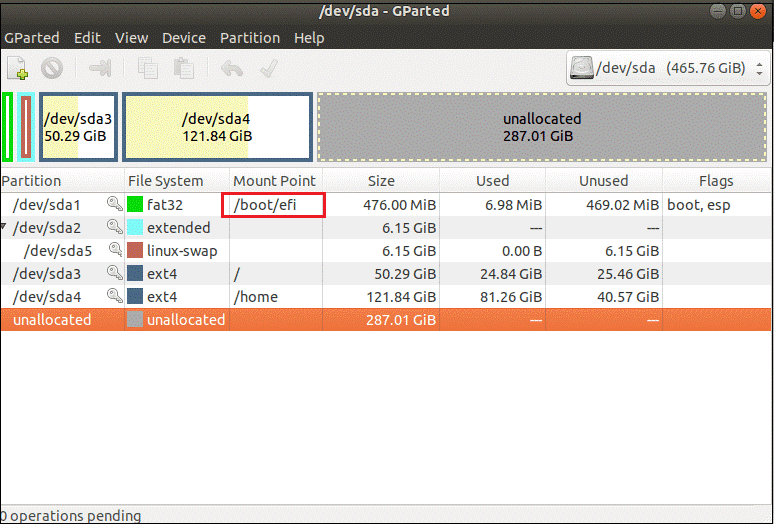
Recommended Sizes for Different Operating Systems
What’s the recommended size for boot partition? In general, it is affected by the following factors.
- Dual-Boot Systems: For computers that have two or more operating systems, the boot partition size should accommodate the needs of each OS. For instance, if dual-booting Windows and Linux, ensure that the combined boot partition sizes meet the requirements of both systems.
- File System Types: The file system type, such as FAT32, NTFS, and Ext4, affects the boot partition size. Each file system has different overheads like metadata, journaling, and system reserved space.
- System Architecture: The boot partition size may also be influenced by the system architecture like 32-bit and 64-bit, and the boot mode like BIOS and UEFI. UEFI systems typically require a larger boot partition than BIOS systems and 64-bit systems benefit from larger boot partition than 32-bit systems.
- File Size: The size of bootloader and kernel files also affects the boot partition size.
Based on the factors explained earlier, the recommended size for boot partitions for different scenarios can be summarized as follows:
For Windows, Microsoft recommends a System Reserved partition size of at least 500 MB. However, during a typical installation, Windows might create a boot partition of around 100-550 MB by default. To ensure smooth updates and avoid future complications, many experts’ recommended size for boot partition is at least 1 GB.
For most modern Linux distributions, a `/boot` partition of 512 MB to 1 GB is sufficient. Some distributions, like Ubuntu, might need only 200-500 MB, while others with more extensive kernel and initramfs files might require more space. Allocating around 1 GB ensures there is ample room for multiple kernel versions and future updates.
If you want to increase your boot partition size, you can use the professional partition management tool – MiniTool Partition Wizard, with its Extend Partition feature, you can easily extend the size of the boot partition. Here is the detailed guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
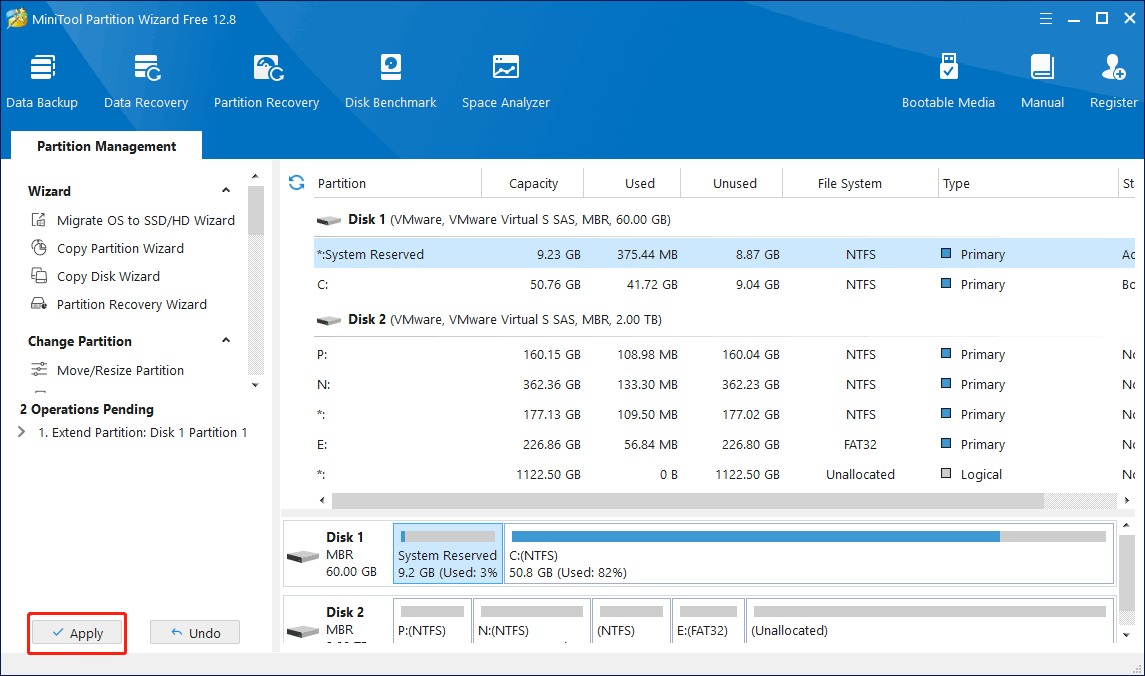
Step 1: Install and launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to get the general disk partition map. Select the boot partition and choose Extend Partition from the left operation panel.
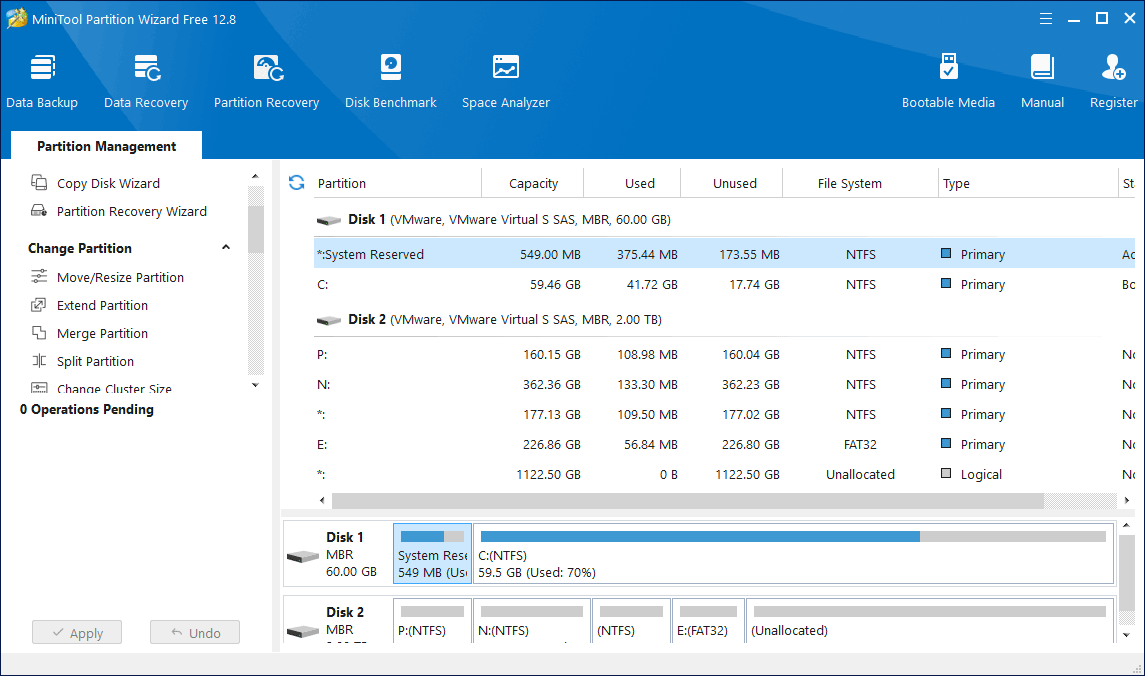
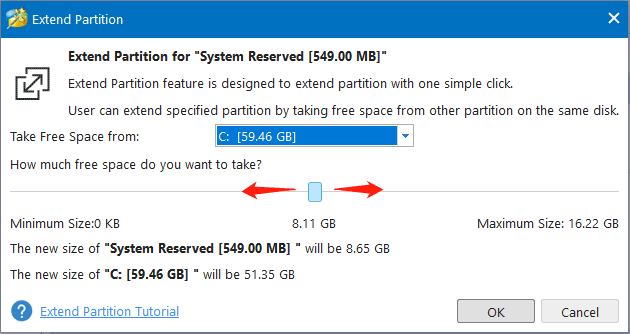
Step 2: Increase the size of the boot partition in two steps:
- Select a partition or unallocated space from the drop-down Take Free Space from list to extend the boot partition. Any partition or unallocated space on the same disk can be used.
- Drag the sliding handle left or right to decide how much space to take. After that, click OK to continue
Step 3: In the main interface, you can preview the changes in the disk map. You can check whether the result is successful by seeing if the boot partition has become larger. Then, click Apply to save all changes.
Bottom Line
In this post, we discussed boot partition along with its various components and the recommended size for boot partitions in case of different operating systems. No matter what operating system you are using, you can learn about the best partition size for your PC in this post!


User Comments :