You may receive the memory error code 2000-0122, 2000-0123, or 2000-0251 while using computers. What causes the issue and how to solve it? Well, you can find the answers in this post of MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Due to various reasons, you can receive memory error 2000-0122, 2000-0251, or 2000-0123. Some common reasons are summarized as follows. Once you get the error code, find the root cause by referring to them.
- RAM fails to perform any test.
- RAM is bad or faulty.
- There is no physical memory in your system.
- You boot your device excessively.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
You may also like: Learn Common Gigabyte Beep Codes and Fix Them Effectively
Way 1: Check and Remove the RAM Module
The RAM may fail and stop working because of some technical faults. Besides, the faulty RAM could trigger some other errors on your Windows 10/11 computer. After you receive memory error code 2000-0122, 2000-0123, or 2000-0251, you should check the RAM module and remove it if necessary. Here are the detailed steps.
Step 1: Open the Settings app by holding the Windows and I keys.
Step 2: In the main interface of Settings, click System.
Step 3: Scroll down the left panel until you find About. Then move to the right side of the window to check your PC’s RAM usage under Device specifications for Installed RAM.
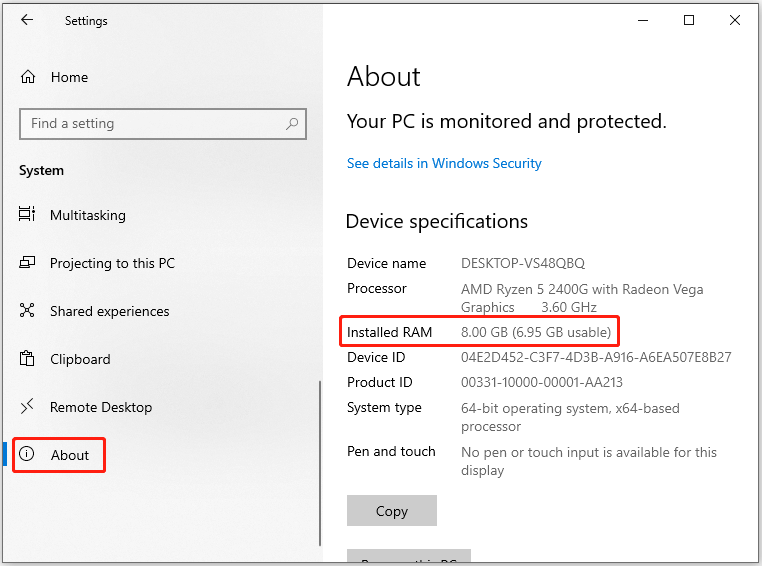
Step 4: If the RAM usage is displayed accurately, confirm if the error still persists. On the contrary, restart your computer and check the RAM usage. If it’s still inaccurate, proceed with the instructions below.
- Open the laptop or desktop PC case.
- Locate the RAM modules and make sure it’s properly seated or connected to the slot.
- Remove the RAM modules one by one. For instance, if you have 2 sticks of RAM installed, put one in and leave the second out. If it fails, try it again.
Way 2: Perform a Memory Test
The memory error code 2000-0122, 2000-0123, or 2000-0251 may indicate something wrong with the RAM. So, it is necessary to perform a memory test once you receive one of these memory error codes. To do that, simply follow the steps below.
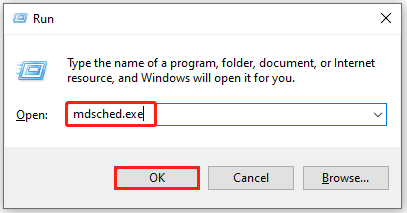
Step 1: Press the Windows and R keys simultaneously to call out the Run window.
Step 2: Type mdsched.exe in the Run window and click OK to open Windows Memory Diagnostic.
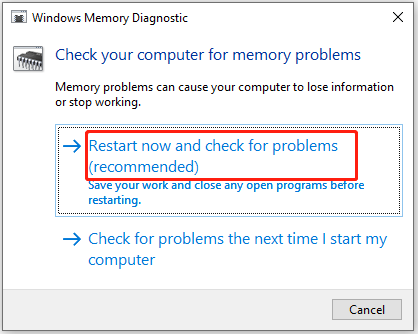
Step 3: In the pop-up window, click on the Restart now and check for problems (recommended) option. Then your computer will restart automatically.
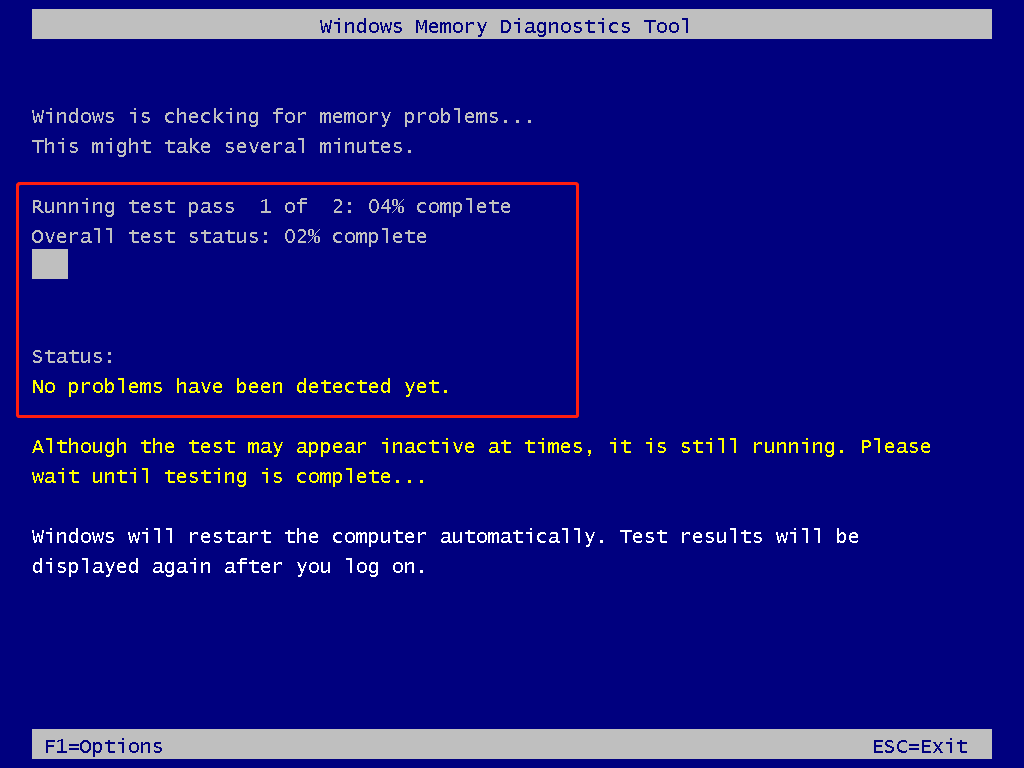
Step 4: After your PC restarts, the Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool will start to test the RAM. You can see the progress and RAM status on the prompted screen.
Step 5: Once the test process ends, your computer will load up automatically. Press the Windows and X keys to open the Start menu and then click Event Viewer. Then you can view the details of the test result. Once you find issues with your RAM, upgrade or replace RAM immediately.
Way 3: Run Hardware Diagnostics on the Computer
If you can access the Dell splash screen, run a built-in or offline diagnostic test at Dell.com with the Dell Support Assist. To run a hardware test with the embedded utility, start your computer and keep pressing the F12 key to access the one-time boot menu. Then choose Diagnostic on the menu to run the hardware scan.
Alternatively, run the diagnostic by pressing and holding the Fn key and turning on the system at the same time. Once the diagnostic scan starts, release the Fn key. According to the diagnostic result, take corresponding actions to fix memory error 2000-0122.
Way 4: Update BIOS
If memory error code 2000-0122, 2000-0123, or 2000-0251 still persists, update your BIOS manually. You need to reset the BIOS to the default settings first if you have made changes to the BIOS settings. The ways to update BIOS vary depending on the PC brands. Here are the BIOS update tutorials of some popular PC brands.
- HP BIOS update
- ASUS BIOS update
- American Megatrends BIOS update
- Flashing Gigabyte motherboard BIOS with Ubuntu
How to get rid of memory error code 2000-0251, 2000-0122, or 2000-0123? Well, this post offers you 4 ways. Pick one method from them to troubleshoot the issue.

![Keyboard or Mouse Works in BIOS but Not in Windows [5+ Fixes]](https://images.minitool.com/partitionwizard.com/images/uploads/2023/09/keyboard-or-mouse-works-in-bios-but-not-in-windows-thumbnail.jpg)

User Comments :