Hyper-V is the most preferred choice for enterprise-grade virtualization users and was created by Microsoft. As a result, it becomes easy for businesses to run their IT workloads and existing hardware resources on cloud technology with amazing flexibility and scalability. This post from Partition Magic will take a closer look at Hyper-V P2V.
What Is Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform developed by Microsoft, enabling the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server. It is a hypervisor-based technology, which allows multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a host computer, providing a way to consolidate workloads and optimize resource utilization.
Hyper-V is a key component of Microsoft’s virtualization and cloud strategy, integrated into Windows Server and available as a standalone product known as Hyper-V Server.

After a brief definition, let’s move to the key functions of Hyper-V:
- It allows a high-performing virtualization layer to overcome all guest activities and can be tuned to nullify its impact on virtualized operating systems.
- It dynamically allocates balanced resources to virtual machines, and it can support up to 1,024 virtual machines on a single host.
- It can move different virtual machines between different Hyper-V hosts.
- It offers high-performing drivers for Linux and Windows guest operating systems.
- It allows live backup of virtual machines and their near real-time replication to remote hosts.
- It supports non-uniform memory architecture (NUMA) at the guest and virtual machine levels.
- It allows off-loaded data transfer (ODX) for file conversions on associated storage systems.
What Is Physical-to-Virtual (P2V) Conversion?
Hyper-V Physical-to-Virtual (P2V) conversion is the process of transforming physical machines (servers, desktops, or workstations) into virtual machines running on Microsoft’s Hyper-V platform, and this migration enables organizations to take advantage of the benefits of P2V virtualization. Some of the benefits of P2V are described below.
Cost Savings
By converting physical machines into virtual ones, organizations can reduce their reliance on physical hardware, leading to significant cost savings. Virtual machines (VMs) require less physical space, power, and cooling compared to their physical counterparts. This reduction in infrastructure costs can be substantial, especially for large data centers.
Improved Resource Utilization
Virtualization allows for better utilization of computing resources. Physical servers often run below their capacity, leading to wasted resources. By consolidating multiple physical servers into virtual machines on a single physical server, organizations can maximize their hardware utilization, reduce idle time, and improve overall efficiency.
Simplified Management and Maintenance
Managing virtual machines is typically easier than managing physical machines. Hyper-V provides a centralized management console, enabling administrators to manage, monitor, and maintain VMs from a single interface. Tasks such as backups, updates, and patches can be performed more efficiently in a virtualized environment.
Enhanced Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Virtual machines can be easily backed up, replicated, and restored, enhancing an organization’s disaster recovery capabilities. Hyper-V includes features like live migration and replica, which allow for seamless movement and replication of VMs between hosts, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss in case of hardware failure or other disasters.
How to Realize Hyper-V P2V Conversion?
With a detailed understanding of P2V and Hyper-V, it is time to implement Hyper-V P2V conversion. Before you start the conversion, perform a full backup of the physical machines to prevent data loss during the conversion process. And now, you can follow the steps below to use Disk2vhd to perform the conversion.
Disk2vhd is an efficient utility that can create VHD versions for Microsoft Hyper-V virtual machines or Microsoft Virtual PC. The quick steps for Hyper-V P2V conversion using Disk2vhd are:
Step 1: Start by downloading Disk2vhd on a physical server. Right-click on the version and select Run as Administrator.
Step 2: After running Disk2vhd, you will be prompted with a window. You can convert a physical disk to a virtual disk in this window. Choose the right flags and volumes to include. After that, click Create to execute the operation.
- Prepare for use in Virtual PC: If you intend to make the disk compatible with the deprecated Microsoft virtual PC, you should check this option.
- Use Vhdx: If you want the final virtual disk to be in the vhdx format, check this option.
- Use Volume Shadow Copy: If you are working on a running system and do not want to interfere with the state of the system, choose this option. Besides, this option aims to enable you to have a smoother conversion process. You don’t have to worry about file-in-use popups or inconsistencies in the system state with this option checked.
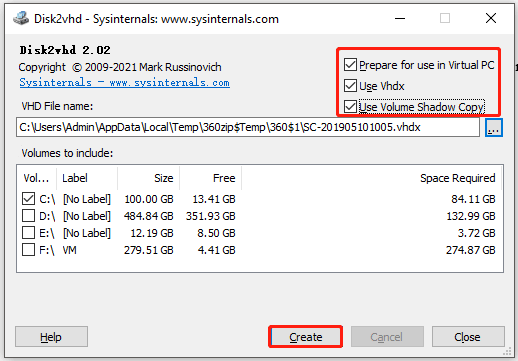
Step 3. Select the destination for the VHDX file created by pressing Use Vhdx and wait for the disk conversion to VHDX format. Then, press Close to finish the disk to VHD export successfully, and this file is easily used to create virtual machines.
Bottom Line
Hyper-V P2V conversion is a powerful process that enables organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure by migrating physical machines to virtual environments. By understanding the fundamentals of Hyper-V and the P2V conversion process, organizations can effectively implement this strategy to achieve a more agile and resilient IT framework.


User Comments :