VFAT and FAT32 are the two old file systems developed by Microsoft. Although they are very similar, since FAT32 is the successor of VFAT, they have some differences. This post from Partition Magic will explore the features and limitations of the two file systems for users who are interested in FAT32 vs VFAT.
FAT In General
The first version of FAT file system was developed in 1977. It was intended to be used by MS-DOS and early versions of Windows OS. FAT and its successors had received major adoption in the OS world at that time. Four versions of FAT were developed: FAT12, FAT16, FAT32, and exFAT (sometimes called FAT64).
Each version was intended to fix problems in the last version. Most notably, each version of FAT significantly increased the size of the cluster, which means that each FAT version increased the theoretical threshold of the file system size.
You may have heard of VFAT, which usually appears in Linux systems. Some people may want to know about FAT32 vs VFAT and this post talks about this topic.
What Is FAT32?
FAT32, or File Allocation Table 32, is a file system designed to organize and manage files on storage devices such as hard drives, USB flash drives, and SD cards. It is a variant of the FAT (File Allocation Table) file system, which has evolved over time from FAT12 and FAT16 to accommodate increasing storage capacities and file sizes.
FAT32 file system was introduced by Microsoft in 1996 with the release of Windows 95 OSR2 and has since become one of the most widely used file systems due to its broad compatibility and simplicity. Key features of FAT32 include:
- FAT32 supports disk partitions up to 2 terabytes (TB) in size.
- FAT32 uses smaller clusters compared to FAT16, which reduces wasted space on the storage medium. This is because smaller clusters mean less unused space at the end of each file.
- FAT32 is compatible with almost all operating systems, including various versions of Windows, macOS, Linux, and many embedded systems.
FAT32 has been a pivotal file system in the evolution of data storage, offering a balance of simplicity, compatibility, and efficiency for a wide range of applications. However, it still has some limitations.
- FAT32 is prone to fragmentation, where files are broken into pieces and scattered across the storage medium. This can slow down file access time and overall system performance over time.
- It has a maximum file size limit of 4 gigabytes (GB). This means any individual file cannot exceed this size, which can be restrictive for large files such as high-definition videos or large software applications.
- FAT32 does not support features found in more modern file systems like NTFS, such as file compression, encryption, and detailed access permissions.
Sometimes, you may want to convert FAT32 to NTFS to get better storage capacity and security, it is recommended to use MiniTool Partition Wizard. This powerful software not only can help you convert FAT32 to NTFS, but also has comprehensive disk partition management functions, such as Copy Partition, Merge Partition, Create Partition, Resize Partition, and so on.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Run MiniTool Partition Wizard to get its main interface. Then, select the FAT32 partition and choose Convert FAT to NTFS feature from the left action panel.
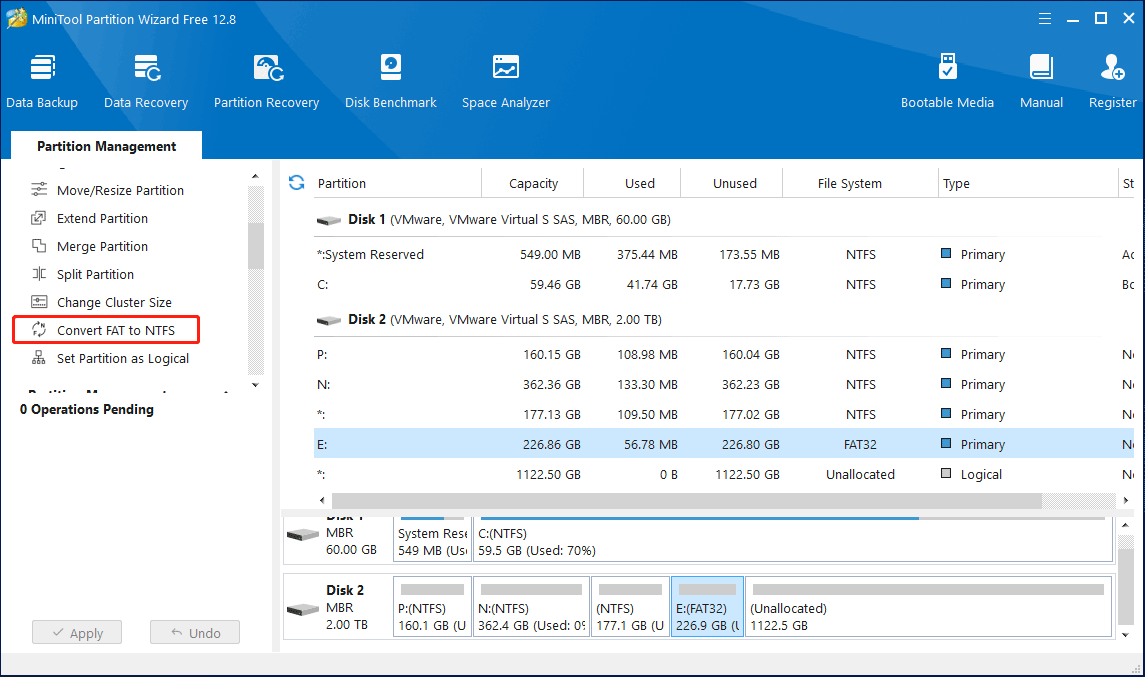
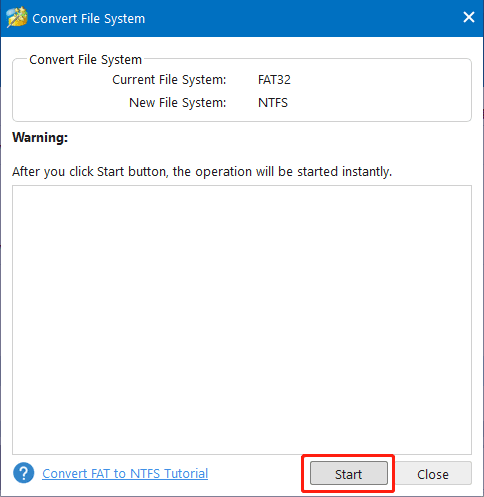
Step 2: In the pop-up window, you can view the current file system and the target file system. Then click Start button to begin the operation.
What Is VFAT?
VFAT, or Virtual File Allocation Table, is an extension of the traditional FAT (File Allocation Table) file system, introduced by Microsoft in Windows 95. The primary purpose of VFAT is to support long file names, which was a significant improvement over the 8.3 filename format used in the earlier FAT12 and FAT16 file systems. Key features of VFAT include:
- VFAT allows for file names up to 255 characters, overcoming the restrictive 8.3 filename format of FAT12 and FAT16.
- VFAT achieves long file name support by using a technique called LFN (Long filename). This is a special directory entry that stores the additional characters of long file names while keeping the traditional 8.3 format entry for compatibility.
- VFAT maintains backward compatibility with older FAT systems. This means that it retains the basic structure of FAT16 but adds the capability to store long file names in a way that older systems can still recognize and access the files, albeit under their short names.
VFAT file system was an essential development in the evolution of file systems, However, it has some drawbacks:
- Since VFAT is not a standalone file system but rather an extension of FAT, it inherits many of FAT’s limitations, such as the maximum volume size and the inefficiencies associated with cluster sizes.
- With the advent of more advanced file systems, VFAT has largely been superseded. Modern file systems like NTFS, exFAT, and those used in Unix-like systems (e.g., EXT4, Btrfs) offer better performance, security, and features.
FAT32 VS VFAT
Now we have a primer on the two FAT file systems. However, some users have responded that on Ubuntu the EFI partition type shown is VFAT, but return to Windows and see that the EFI partition type is FAT32. So why is it showing different file types in different desktop environments? It actually has to do with their compatibility.
Both FAT32 and VFAT have broad compatibility across a wide range of operating systems and devices. VFAT is compatible with any FAT pointer size, so you can use VFAT-12, VFAT-16, or VFAT-32. However, FAT32 has wider compatibility with newer devices and systems, making it a more versatile choice for modern storage needs.
So, in this case, VFAT is FAT32. there is nothing wrong with it showing up as VFAT in Ubuntu (or other Linux systems).
In addition to compatibility, FAT32 VS VFAT comparison has a lot of factors to look up:
- File Name Support: The primary difference between FAT32 and VFAT lies in file name support. While FAT32 retains the 8.3 filename format, VFAT extends the FAT system to support long file names up to 255 characters. This makes VFAT more user-friendly in terms of naming files.
- Volume and File Size: FAT32 supports much larger volumes (up to 2 TB) compared to the FAT16 system that VFAT extends, which is limited to 2 GB volumes. However, both FAT32 and VFAT share the same maximum file size limit of 4 GB, which can be a drawback for modern applications needing to store large files.
- Use Cases: FAT32 is commonly used for removable storage devices like USB flash drives and SD cards, as well as in multi-OS environments where cross-platform compatibility is essential. VFAT, while still relevant, is primarily used in legacy systems where long file name support is needed without moving to a more modern file system.
Bottom Line
FAT32 and VFAT have both played crucial roles in the evolution of FAT file systems, each addressing specific limitations of their predecessors. In this post, we discussed FAT32 vs VFAT. I hope you can get effective information from this post.


User Comments :