Ext4 (Extended Filesystem 4) is a popular file system used in Linux environments due to its robustness and performance. However, Windows does not natively support Ext4, necessitating third-party tools for the creation process. This post from Partition Magic outlines the steps to create Ext4 partition on a Windows operating system.
What Is the Ext4 File System?
EXT4 (Fourth Extended File System) is a file system used in Linux that is the successor to Ext3. However, due to stability concerns, some Linux kernel developers did not accept the EXT3 extension. They suggested forking the EXT3 source code and renaming it EXT4.
Subsequently, the EXT3 filesystem maintainers announced new plans for EXT4 in 2006. EXT4 is a major improvement over EXT3. Many of the improvements to the Ext4 file system were originally developed by the Cluster filesystem from 2003 to 2006 to expand storage limits and improve performance. Here are some main features of EXT4:
- Larger file system/file size: EXT3 supports a maximum file system size of 16TB and a maximum file size of 2TB, while EXT4 supports a maximum of 1EB (1EB = 1024PB = 1024 * 1024TB = 1024 * 1024 GB) file system size and maximum file size of 16TB, because EXT4 adds 48 bits block addressing.
- More sub-directories: EXT3 currently supports only 32,000 sub-directories, while EXT4 removes this limitation and theoretically supports an unlimited number of sub-directories.
- Log verification function: EXT4 adds a verification function to the log data. With this function, you can quickly check whether the log data is corrupted or not, to avoid recovering data from corrupted logs causing greater data corruption. Moreover, EXT4 combines the two-phase logging mechanism of EXT3 into one phase, which improves security and performance at the same time.
Why Cannot Windows Built-In Tools Create EXT4 Partitions?
Windows operating systems, developed by Microsoft, are designed primarily to support the file systems most commonly used within the Windows ecosystem, such as NTFS (New Technology File System) and exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table).
EXT4 is tailored to the needs and architecture of Linux operating systems and is not compatible with Windows. So, Windows 11/10 cannot recognize the EXT4 partition. Next, I will show the scenarios where Disk Management and CMD commands are unable to create Ext4 partitions.
In Disk Management, you do not have the option to format the partition as EXT4 because of file system incompatibility. There are only two default disk partitions here – FAT32 and NTFS.
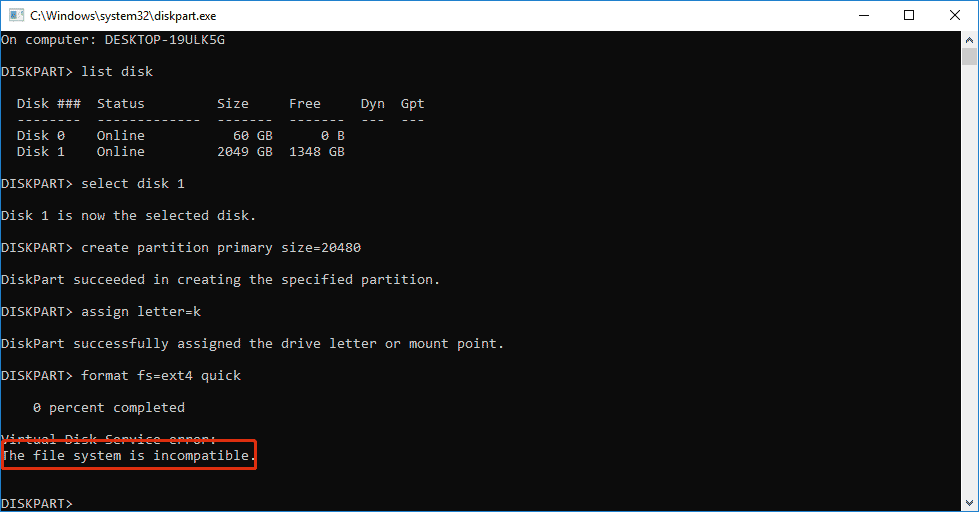
In DiskPart CMD, you cannot create EXT4 volume, too. After you enter the commands, the system displays the error message: The file system is incompatible.
Therefore, you cannot create an EXT4 partition under Windows unless you are running a dual-boot system or third-party software. Here, I recommend you to use the professional partition manager – MiniTool Partition Wizard to create an EXT4 partition on Windows easily.
Now, you can follow the steps below to let Windows 11/10 create Ext4 partition:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Launch the MiniTool Partition Wizard to enter its main interface. On the main window, right-click on the unallocated space on your hard drive and select Create Partition.
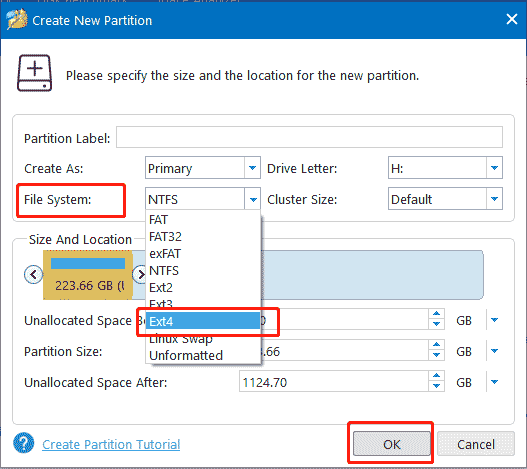
Step 2: Drag the arrows to determine how much space the partition will occupy, or enter the size of the partition to be created in Partition Size. Then, drop down File System, select Ext4, and click OK.
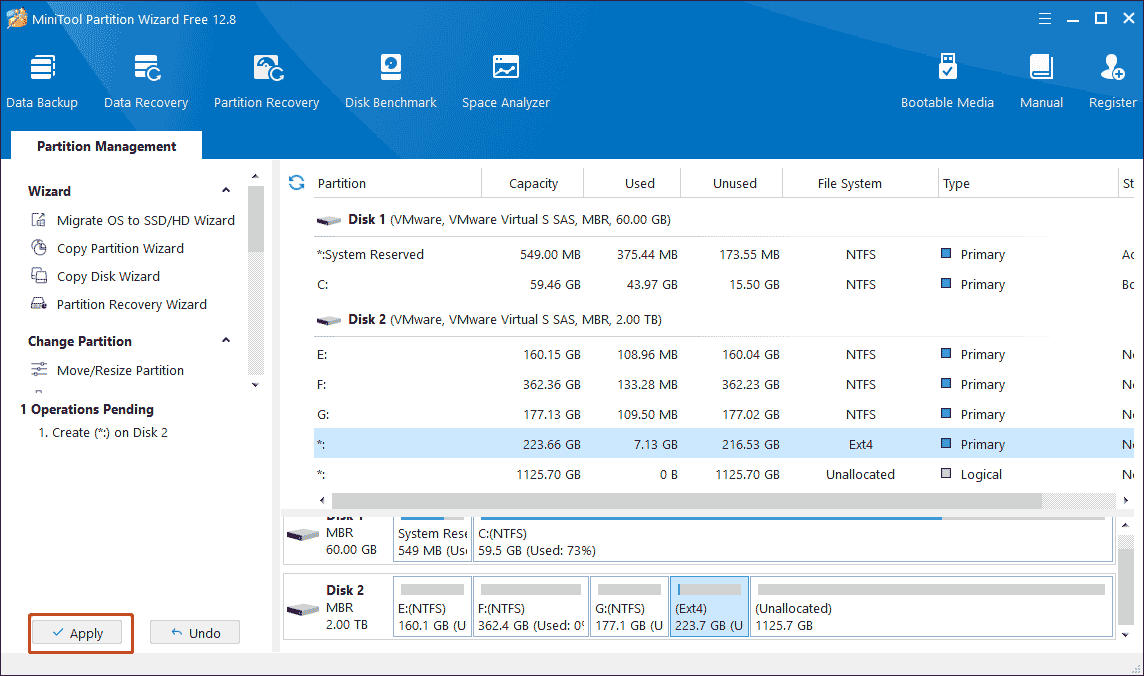
Step 3: Click Apply to execute the changes.
You can refer to the following posts to understand the differences between different file systems:
- NTFS vs. FAT32 vs. exFAT – Differences and How to Format
- Ext4 vs NTFS vs HFS+: Differences and Which One Should You Use
- ReFS vs NTFS: What’s the Difference Between Them?
Bottom Line
Creating an Ext4 partition on a Windows operating system can seem daunting, but with the right tools and guidance, it becomes a straightforward task. In addition, if you have any problems when using MiniTool Partition Wizard, you can always contact us via the email [email protected]. Thanks in advance.


User Comments :