APFS and NTFS are designed to meet the specific needs of their respective operating systems. Users are quite interested in APFS vs NTFS. In this post from Partition Magic, I will help you recognize their definitions and highlight the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of both.
What Is APFS?
In the realm of modern computing, file systems play a crucial role in managing how data is stored and retrieved on disk drives. Two prominent file systems are APFS (Apple File System) and NTFS (New Technology File System), each tailored for different operating systems and environments.
APFS file system, introduced by Apple in 2017 with macOS High Sierra, is designed to replace the older HFS+ file system. APFS is optimized for modern storage technologies, particularly flash and SSD drives, which are prevalent in Apple’s product lineup. Key features of APFS include:
- Space Sharing: APFS allows multiple file systems to share the same storage space dynamically, allocating storage as needed. This is especially beneficial for SSDs, where efficient space management is critical.
- Cloning: APFS supports instant cloning of files and directories, creating copies without duplicating the physical data, thus saving storage space and time.
- Snapshots: APFS can create snapshots of the file system at any given point, allowing users to revert to a previous state quickly and easily. This is particularly useful for backups and system recovery.
- Encryption: APFS provides robust encryption options, including support for both full-disk and per-file encryption, with multiple keys used to enhance security.
- Optimized for SSDs: APFS is designed to take full advantage of the speed and efficiency of flash storage, providing faster read and write operations compared to older file systems.
Like any other file system, APFS has some drawbacks. It lacks a variety of features that other file systems have. These include: Checksums of user data, Byte-addressable, non-volatile random-access memory, Data compression, Data deduplication.

What Is NTFS?
NTFS is created by Microsoft and introduced in 1993 with Windows NT 3.1. Windows NT and Windows 2000 are the primary operating systems using the NTFS file system. Nowadays, NTFS is the most widely used file system in Windows, especially for its system drive and most internal hard drives.
As a modern and advanced file system, NTFS has many features. For detailed information, you can refer to following contents to learn its pros and cons:
Pros:
- File Compression: NTFS supports file compression, which helps save disk space by reducing the size of files stored on the disk.
- Encryption: The Encrypting File System (EFS) allows users to encrypt individual files and directories, adding a layer of security to sensitive data.
- Support Large Files: NTFS supports very large files and it nearly has no realistic partition size limit by changing cluster size.
- Disk Quotas: Administrators can set limits on the amount of disk space that users can consume, helping to manage storage resources efficiently.
- Data Recovery: NTFS includes a journaling feature that keeps track of changes to the file system, which helps in recovering data in case of a system crash or power failure.
- File Permissions and ACLs: NTFS uses Access Control Lists (ACLs) to specify detailed permissions for files and directories, enhancing security by controlling access at a granular level.
Cons:
- Compatibility: The smartphone operating system Android does not support NTFS, which is the biggest drawback. In addition, NTFS-formatted drives won’t work on Mac computers, and you’ll need third-party software to handle them.
- Performance and Bandwidth: With NTFS, both of these elements of the file system fluctuate wildly. Users will notice unpredictable changes in speed and bandwidth.
NTFS’s robustness and feature set make it a preferred choice for environments that require secure and reliable data storage, such as enterprise servers and personal computers running Windows.
If you need to do some actions to your hard disks like formatting a partition to FAT32/NTFS/exFAT, you can use the professional partition manager-MiniTool Partition Wizard.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
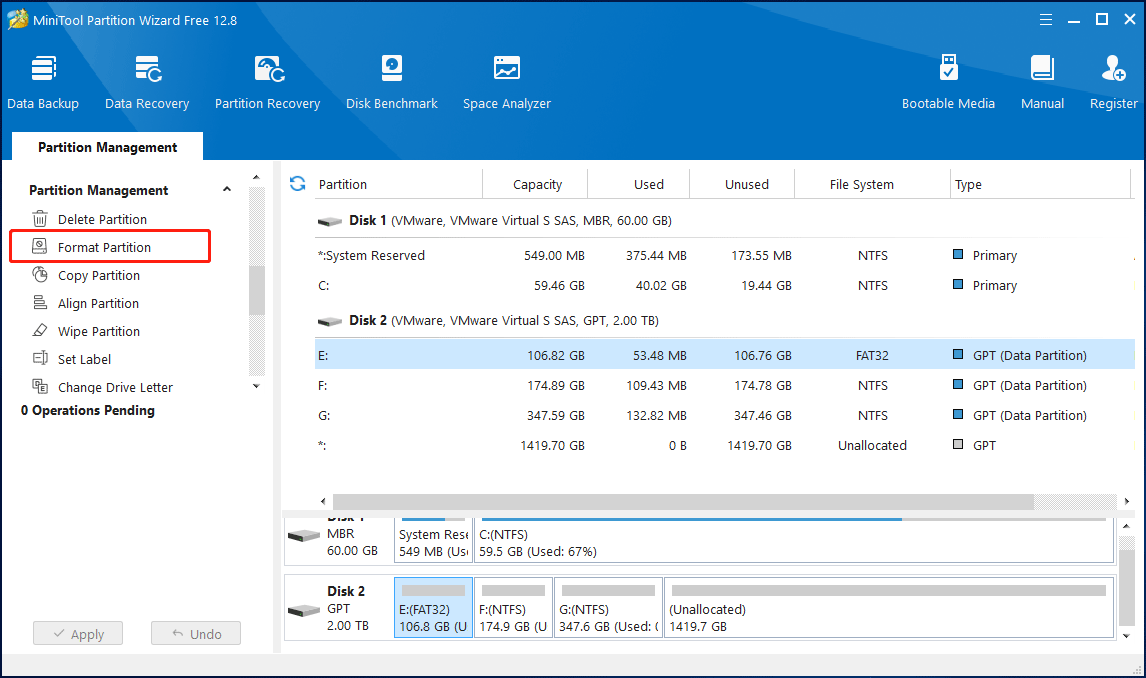
Step 1: Download MiniTool Partition Wizard and launch it to get its main interface.
Step 2: Right-click the partition you want to format and select Format Partition from the left panel.
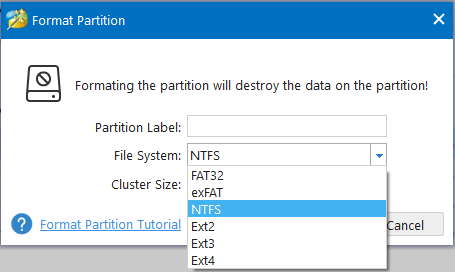
Step 3: At this window, you can format the drive’s file system to FAT32, NTFS, exFAT, Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, satisfying all your needs. After resetting these parameters, you can click OK.
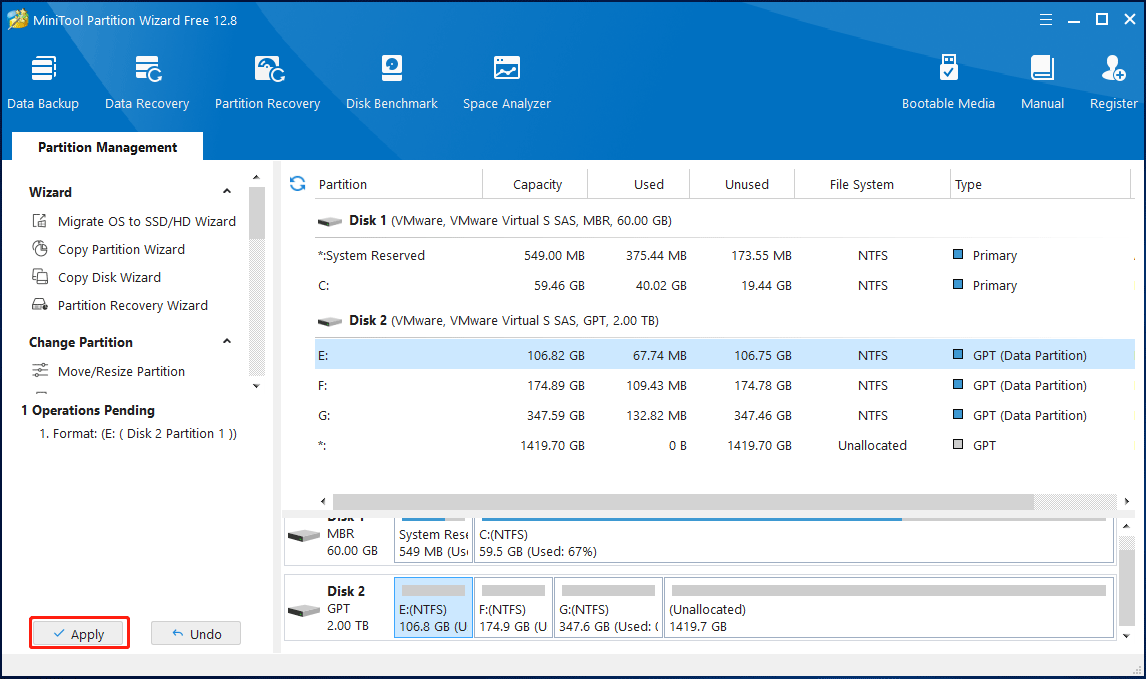
Step 4: Click Apply to allow the pending operation.
If you want to know the differences between NTFS and other file systems, you can refer to these posts:
- NTFS vs. FAT32 vs. exFAT – Differences and How to Format
- Ext4 vs NTFS vs HFS+: Differences and Which One Should You Use
APFS VS NTFS
APFS VS NTFS comparison has a lot of factors to look up:
- Performance: NTFS is highly efficient when dealing with both traditional spinning hard disk drives and SSDs. However, APFS is specifically designed to take advantage of the speed and performance characteristics of flash memory. The latter performs better in environments where SSDs and flash memory are used.
- Security: Both file systems provide strong security features, but APFS includes advanced multi-key encryption.
- Data Recovery: NTFS uses journaling for data integrity, whereas APFS uses snapshots for efficient system recovery.
- Compatibility: NTFS is widely supported across Windows systems, whereas APFS is exclusive to Apple’s ecosystem.
Bottom Line
NTFS and APFS are designed to meet the specific needs of their respective operating systems. NTFS provides reliability and extensive features for Windows environments, while APFS offers modern, efficient storage solutions for Apple devices. Understanding these differences helps users and organizations choose the right file system for their storage requirements.

User Comments :