What is data sanitization? What are data sanitization methods? This article will give you answers. This article will also give you explanations to DoD 5220.22-M method, ATA security erasure, crypto erase, and tell you the differences between wipe, erase, format, and delete.
What Is Data Sanitization
Data sanitization is defined as a process of deliberately, permanently, and irreversibly removing or destroying the data stored on a memory device (including HHD, SSD, CD/DVD, USB, mobile devices, etc.), which is used to make data unrecoverable to avoid privacy leak.
If information disclosure would have no impact on organizational mission, or would not result in damage to organizational assets, or financial loss or harm to any individuals, data disposal without sanitization could be considered. Otherwise, data sanitization should be taken to protect data privacy.
Data sanitization is achieved through three major methods: physical destruction, degaussing, and data erasure.
Physical Destruction
Physical destruction is adopted on the condition that the information has high security categorization. It will completely destroy the media and make the data stored on the media unrecoverable even in a laboratory environment.
The physical destruction methods include disintegration, pulverization, melting, incineration, and shredding. Besides, when the media is disintegrated or shredded, the residues must be reduced to edge dimensions of 5 mm and surface area of 25 mm2.
Because physical destruction will destroy media, it is not recommended except that the media is not needed anymore. Besides, if a complete destruction is not accomplished, there is still possibility of recovering data in laboratory environment.
Degaussing
Degaussing is a process of exposing the magnetic media to a strong magnetic field of a degausser to disrupt the recorded magnetic domain. This method is relatively efficient in purging diskettes, damaged or inoperative media, and media with large storage capacity. And it also makes data unrecoverable even in laboratory environment.

However, degaussing work of modern high-density disk is more difficult than that of older disks like magnetic tape and floppy disk. Modern high-density disk degaussing requires higher magnetic field, in other words, more bulk and expensive degauss equipment, which also means higher cost.
In addition, although degaussing will not cause damage to media, it will also make the media lose economic value and unusable.
Data Erasure
Data erasure (sometime referred to as data clearing or data wiping) will sanitize media by using software or hardware products to overwrite storage space on the media with non-sensitive data. The non-sensitive data will cover not only the logical storage location of a file, but also all addressable locations.
This method is mainly applied on writable media to protect the confidentiality of information against data, disk, or file recovery utilities. In other words, the data stored on the media won’t be recovered by any software, but there is still possibility of recovering data in laboratory environment.
Delete
When users delete a file on computer, maybe they just put the file into Recycle Bin. They can restore the file from recycle bin easily. But if users have emptied the Recycle Bin or deleted the file permanently, recovering the deleted files would take some efforts.
When files are deleted, they are just marked as such. The file index to file location on hard drive is removed so that the computer can’t find the file. And the space where the file is stored is marked to allow new data to be input.
But actually, the original files still exist on the hard drive before they are overwritten by other data, which means that they can be easily recovered by software. Users can recover deleted files, and at the same time, they can also retrieve deleted partitions.
How to delete partition?
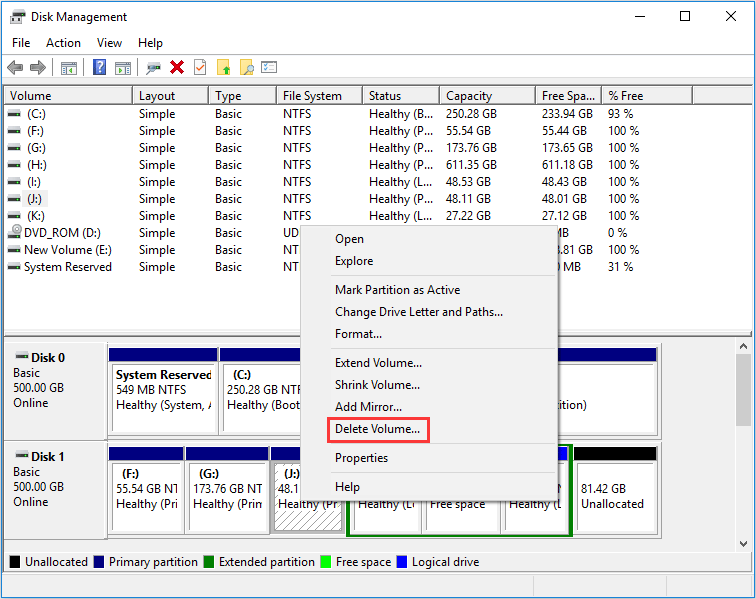
As we all know, users can right click on a file and select Delete to remove a file. However, deleting a partition is more complicated. Users should press “Windows + R” keys and type “diskmagmt.msc” in Run window to open Disk Management. Then, right click a partition and select Delete Volume to delete it.
How to retrieve data or partitions?
Data recovery and partition recovery often need the help of third-party software. MiniTool Partition Wizard is recommended because it’s versed in this problem.
Here is a tutorial on data recovery with MiniTool Partition Wizard.
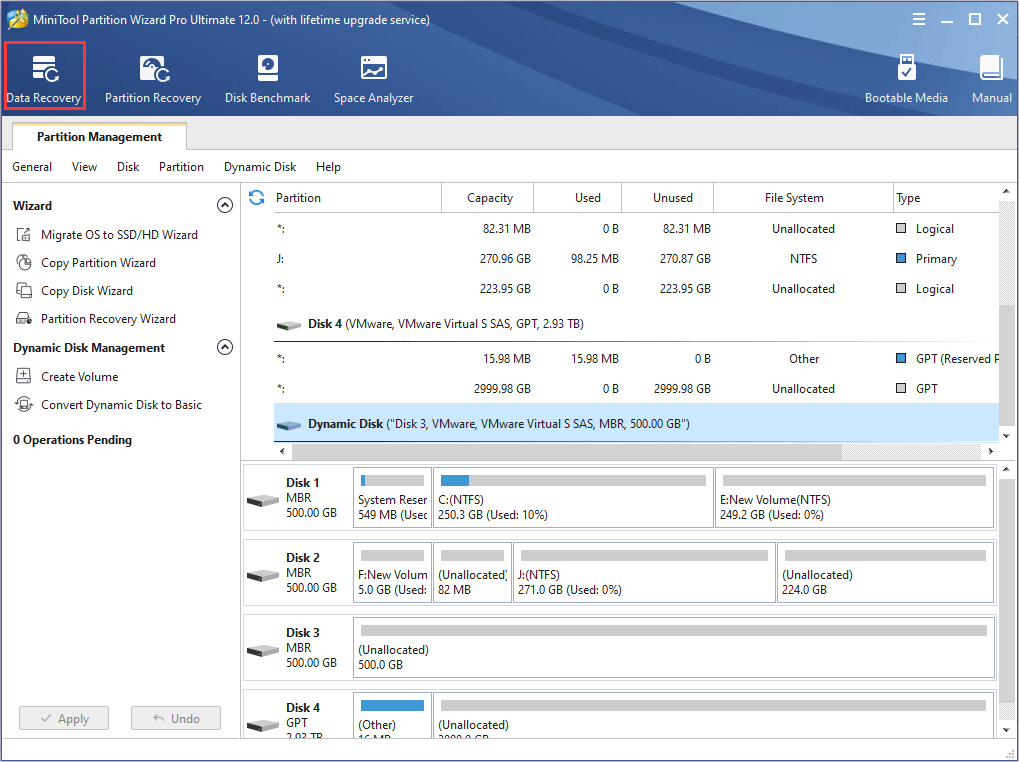
Step 1: Buy MiniTool Partition Wizard and launch it to get its main interface. Click Data Recovery.
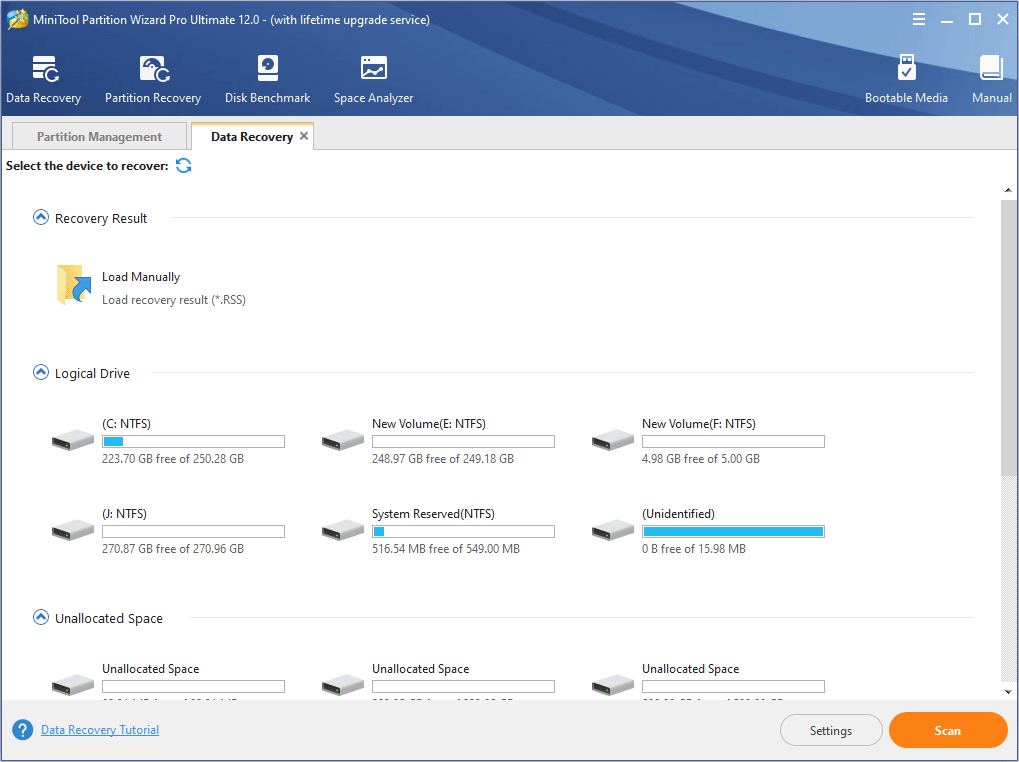
Step 2: Choose a partition, unallocated space, or hard disk where the file is deleted. And then click Scan.
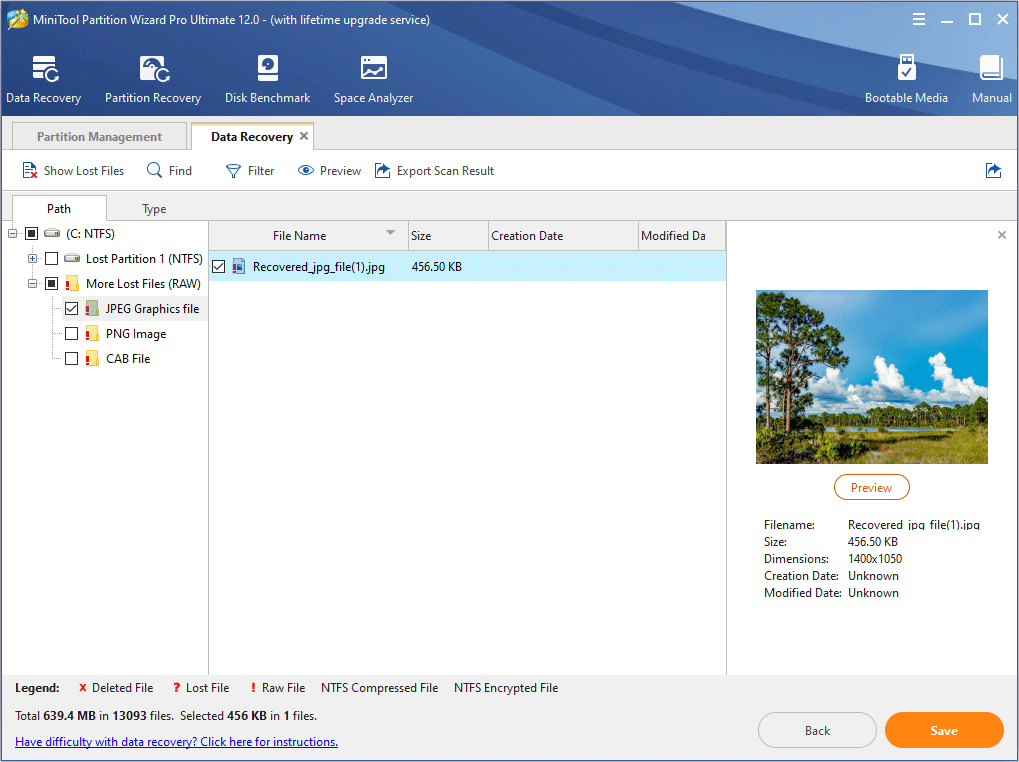
Step 3: Find the deleted files and then click Save.
Here is a tutorial to partition recovery with MiniTool Partition Wizard.
Step 1: Buy MiniTool Partition Wizard and launch it to get its main interface. Click Partition Recovery.
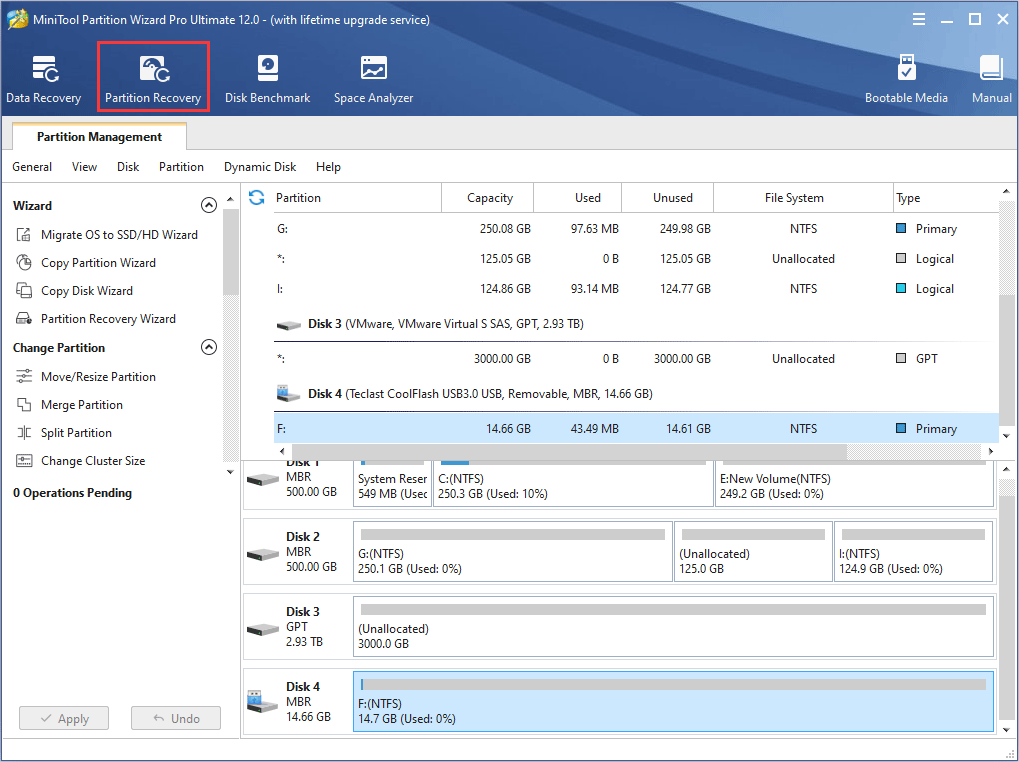
Step 2: Follow partition recovery wizard to retrieve partition.
Attention:
- If the partition was just deleted, users can choose quick scanning mode. Otherwise, users should choose full scanning mode.
- Both existing partitions and lost partitions that need to be recovered should be checked. Otherwise, some partitions may be lost after the recovery.
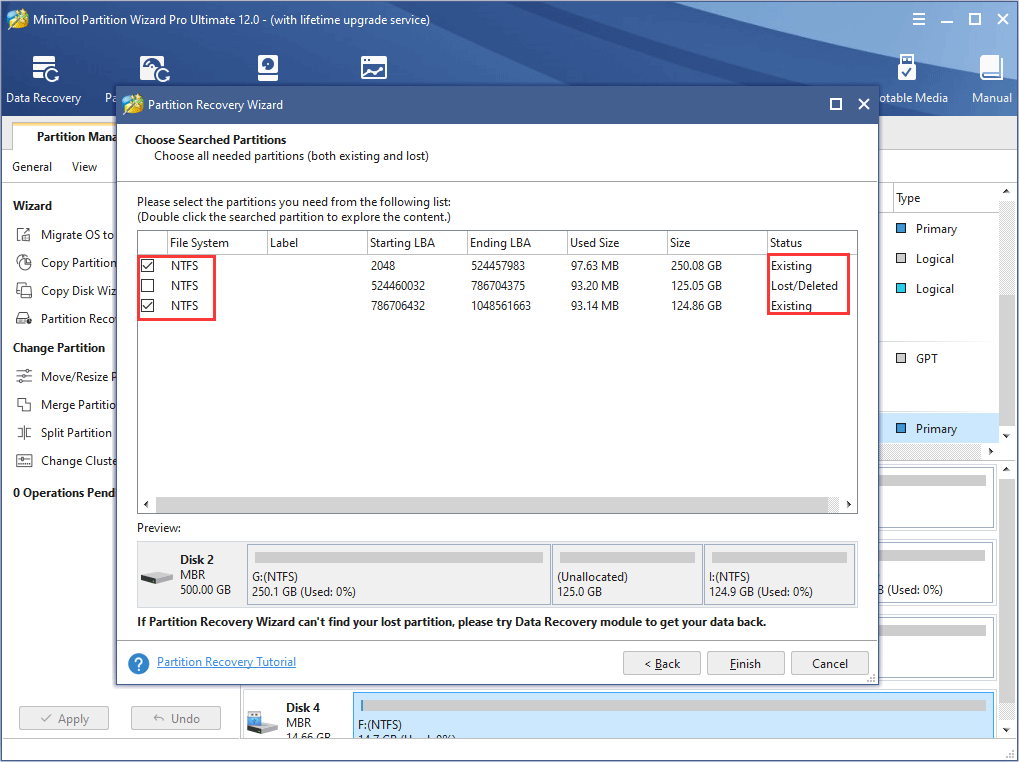
Step 3: Click Apply button on the toolbar to carry out the operations.
Format
Formatting includes low-level formatting (it is physical formatting and usually operated by manufacturer) and high-level formatting (you may want to know What Is Disk Formatting). Only high-level formatting can be carried out on computer by users.
How to format a partition?
Users can format a partition through opening File Explorer and right-clicking a partition and then selecting Format. They can also do so in Disk Management to format a partition. However, the two ways are all quick format. To carry out full format, users should uncheck “Perform a quick format”.
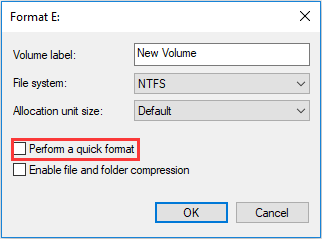
As mentioned above, high-level formatting includes quick formatting and full formatting (click Quick Format vs Full Format to know more).
Quick format is similar to delete to some extent. Quick format also just marks the partition as “formatted” and destroy the indexes to the file locations. But the data is still on the hard drive and can be recovered before it is overwritten.
Click How Do I Unformat Hard Drive to get the data retrieve steps.
As for the full format, it is a little different from quick format. And whether the data can be recovered depends mostly on operating system version. In Windows XP and earlier versions of Windows, full format is similar to quick format to some extent, so the data can be recovered by software.
However, in Windows Vista and later Windows versions, full format will add overwriting step. It will not only “delete” files and scan for bad sectors, but also overwrite the original data with zeroes, which will make data recovery difficult for software.
Erase
When users erase a file, it means that the file is removed completely and can’t be recovered by software. The data erase ways include wiping, shredding, and so on. Besides, the erasure process often contains overwriting step.
Wipe
Wiping is one of erasure methods. It is often used to erase data on a large scale (for example, partitions, and entire hard drives). Wiping will overwrite data on the entire partition and erase everything on it, including the previous deleted data. As for shredding, it aims to erase a piece of data such as one or more files and folders.
Delete vs Format vs Erase vs Wipe
Many users are always confused about delete, format, erase, and wipe. They use these words interchangeably. However, they are different to some extent. But actually, erase and wipe are so similar that most people refer to data erase as data wiping.
Data Wiping Method
Generally speaking, if data is erased, it is hardly recovered by software. However, there is still possibility of retrieving data through more advanced technology. So, in order to avoid information leak, data erasure standards come out.
DoD 5220.22-M
In various data erasure standards, DoD 5220.22-M, published by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) in the National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual (NISPOM), is still applied widest, although it has been replaced by NIST standards and guidelines.
DoD 5220.22-M (3 passes) method is implemented in the following way.
- Pass 1: overwrite data with zeros and followed by verification.
- Pass 2: overwrite data with ones and followed by verification.
- Pass 3: overwrites data with random characters and followed by verification.
The verification will ensure that the content was actually overwritten in the right way.
Generally speaking, advanced data erase needs the help of third-party software. And software designed for data erasure should allow users to select a specific standard according to unique needs.
Free Data Wiping Software
MiniTool Partition Wizard can wipe partition for free. Besides, it also provides several wiping methods for users to choose.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here is a tutorial.
Step 1: Download MiniTool Partition Wizard and launch it. Right click a partition and select Wipe Partition.
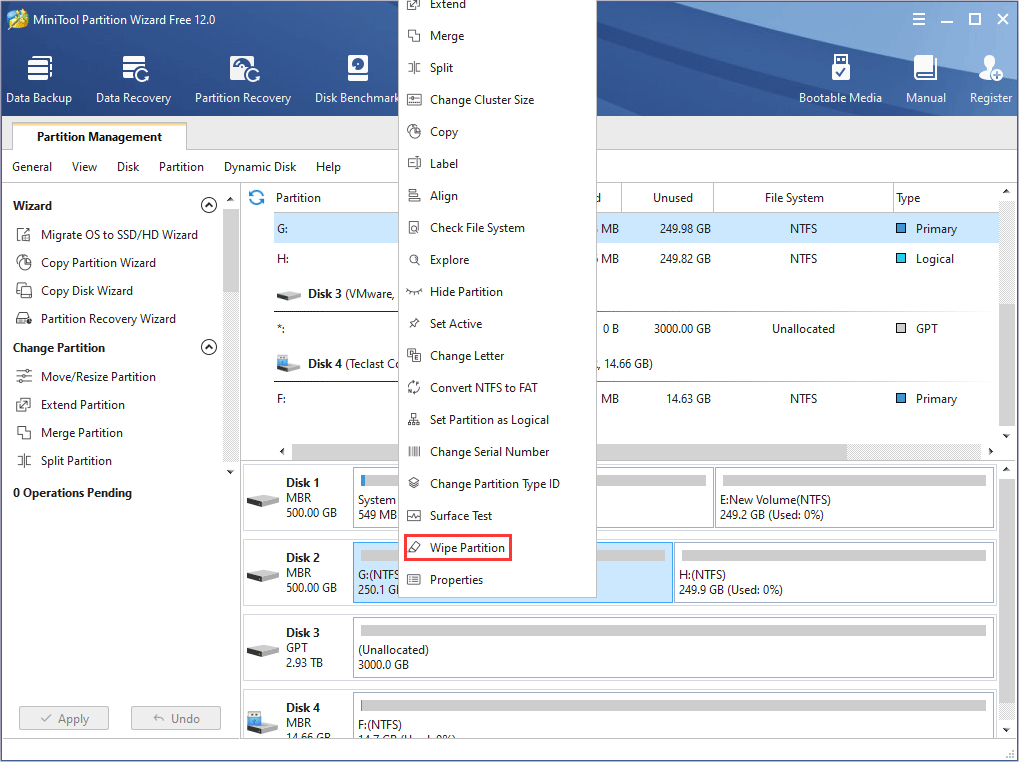
Step 2: Select wiping method.
Attention:
- Fill sectors with Zero and Fill sectors with One: They just write the same code to the partition, which is similar to full format in Windows.
- Fill sectors with Zero &One: It will randomly write zeros and ones to partition, which makes data more unrecoverable.
- DoD 5220.22-M (3 passes): It is recommended if users want to get rid of the data permanently.
- DoD 5220.28-STD (7 passess): It provides higher security level for data because it has more passes than DoD 5220.22-M (3 passes).
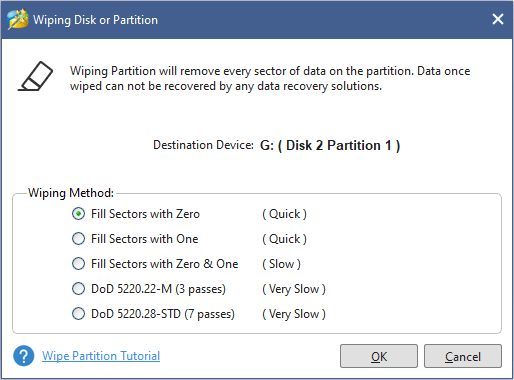
Step 3: Click Apply button to execute the wiping operation.
ATA Security Erasure and Cryptographic Erasure
As technology develops, ATA security erasure (secure erase) and cryptographic erasure (crypto erase) are put forward to sanitize data.
ATA secure erase is only applied on disk with ATA interface. On many laptops, ATA security is integrated into the BIOS. ATA security erasure is firmware secure erase command that will wipe the entire contents of a drive at hardware level.
ATA secure erase commands will release stored electrons to reset all storage cells as empty. It will restore disk to factory default and recover disk performance fully. This process will cover all regions, including protected storage service regions such as system area data, metadata, HPA, and DCO.
Crypto erase achieves data sanitization through erasing the encryption key of a storage device to make data on it unreadable. The encryption algorithm must be at a minimum of 128 bits so that the encrypted data can’t be decrypted.
When crypto erase is mentioned, self-encrypting drives must be touched upon. SEDs feature always-on encryption which reduces the possibility that unencrypted data is inadvertently retained on the device.
Besides, the encryption on the storage device can provide access to the API call to storage device to remove the encryption key. Then a new key will replace the old key so that the old key and the encrypted data can be unrecoverable.
Surely, it is suggested that overwriting process or secure erase is operated after crypto erase to make sure more advanced data privacy.
Here are explanations to data sanitization and data sanitization methods. Click to Tweet
Bottom line
If you are still confused about data sanitization and data sanitization methods, please leave a comment below. Or, if you have another explanation for them, please leave a comment. Surely, if you have problem in data sanitization, or in recovering data or partition, please email to [email protected] for help.

User Comments :