Windows 10 Storage Spaces vs. RAID, what is the difference? How do I choose from them? This article will give you answers! Besides, it will also give you a guide to data protection.
About RAID
RAID (Redundant Arrays of Independent Drives) technology combines multiple drives into a drive array with huge capacity. It will also utilize the multiple drives to improve the performance of the drive array, including MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure) and fault-tolerance.
RAID Types
RAID has three types: external disk array cabinet (so called hardware RAID), internal disk array card (so called hardware-assisted RAID), and software simulation (so called software RAID).
Hardware RAID uses a RAID card to connect drives with computer. The RAID controller on the card combines drives into a virtual volume. Besides, hardware RAID also includes special I/O processing chip and array buffer. These devices make hardware RAID have best performance. But generally speaking, hardware RAID is expensive and is usually applied in servers.

Hardware assisted RAID needs a RAID card and drivers provided by manufacturers. However, Hardware assisted RAID lacks special I/O processing chip, so it will occupy the resources of CPU. This RAID will also provide fault-tolerance and improve performance. Besides, this RAID is only suitable for RAID 0 and RAID 1.
Software RAID combines multiple drives into a logical volume through Disk Management feature provided by operating system. Software RAID can also provide data redundancy. However, it will reduce the performance of disk subsystem by 30%.
How to create software RAID on Windows 10? Here is a tutorial.
Step 1: Press “Windows + R” keys and type “diskmgmt.msc” in run box to open Disk Management.
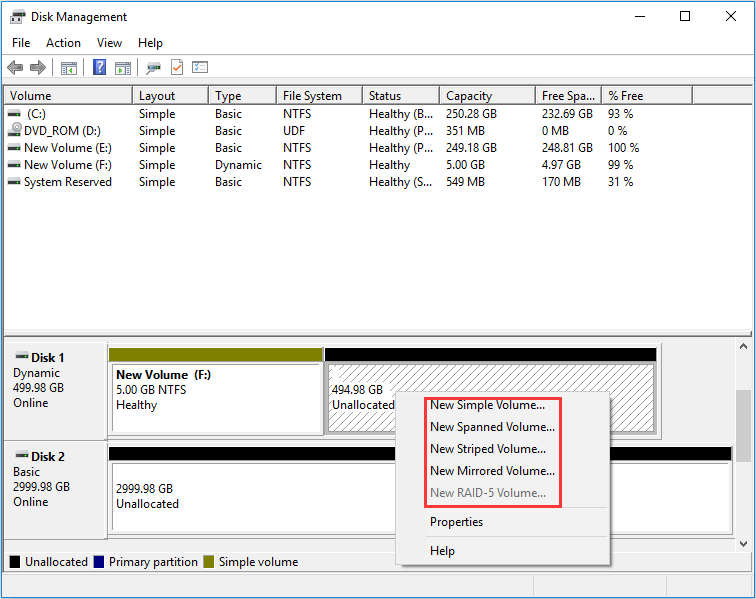
Step 2: Create a RAID.
- Right click the whole disk to convert it from basic disk to dynamic disk.
- Right click unallocated space and choose “New x Volume”(“X” can be “Striped”, “Mirrored”, or “RAID-5”).
- Follow the wizard to select disks, and set volume size, drive letter, file system, and cluster size.
If users want to convert dynamic disk to basic disk, please click here to get a tutorial.
Common RAID Levels
The common RAID levels include the following: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10/01.
RAID 0 is also called striped volume. It combines at least two drives into a big volume. It not only increases the capacity of disk, but also improves its performance by dispersing continuous data into multiple drives for access.
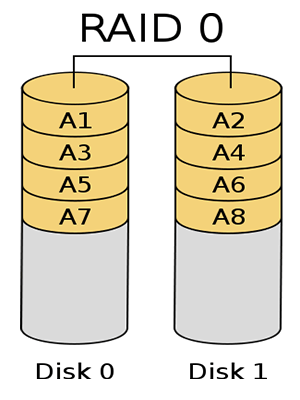
The dispersal of continuous data I/O requests improves the performance by making every disk deal with the part of data requests allocated to it in parallel so as to fully utilize the Throughput of Bus. However, it can’t provide data redundancy. Hence, its data reliability is the lowest one.
RAID 1 is also called mirrored volume. It also needs at least two drives (usually an even number). It realizes data redundancy through making a disk back up the data on another disk, which sequentially causes situation that the usable space is only a half of the disk array.
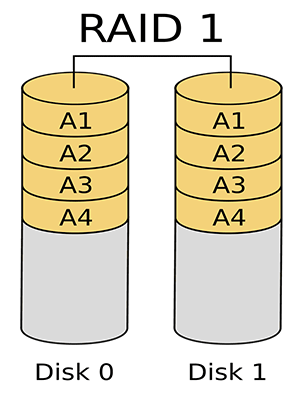
Besides, it can also improve the reading performance because it can read data from the backup drive when the original drive is busy. However, the writing speed is slowed down because the backup and error verification.
RAID 10/01 is also called RAID 1+0 or RAID 0+1. It is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1 and needs at least four drives. It can not only read/write data on multiple drives in parallel to improve access speed, but also provide data redundancy by making backup of each original drive.
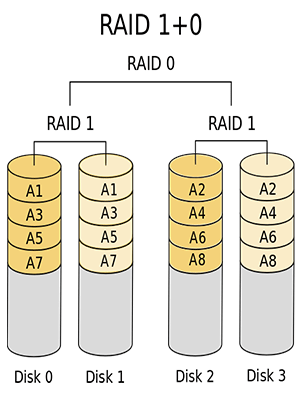
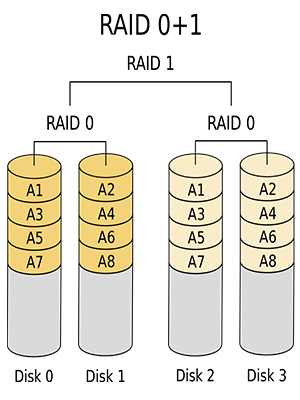
However, it also only uses a half space of disk array. Besides, it will also cause higher CPU usage.
RAID 5 needs at least three drives. It will access data and parity check information crosswise on all drives. The reading speed of RAID 5 approaches that of RAID 0 because the I/O requests can also be simultaneously responded by all drives except that RAID 5 has extra parity check information that occupy a disk.
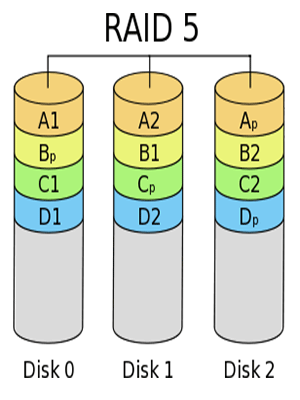
However, the writing speed of RAID 5 is slower than that of a single disk because RAID 5 will read old data and write extra parity check information when writing data (so called write performance impairments).
About Windows 10 Storage Spaces
Storage Spaces is a Windows built-in technology. Users can utilize this technology to group multiple drives together into a storage pool and then use the capacity of the pool to create virtual drives named storage spaces. This technology can help users to protect their data from drive failure through mirroring data and extend storage space through adding drivers to PC.
How to use Windows 10 storage spaces? Here is a tutorial.
Step 1: Create a storage pool.
- Type “manage storage spaces” in Windows search box.
- Click Manage Storage Spaces button to open it.
- Click “Create a new pool and storage space”.
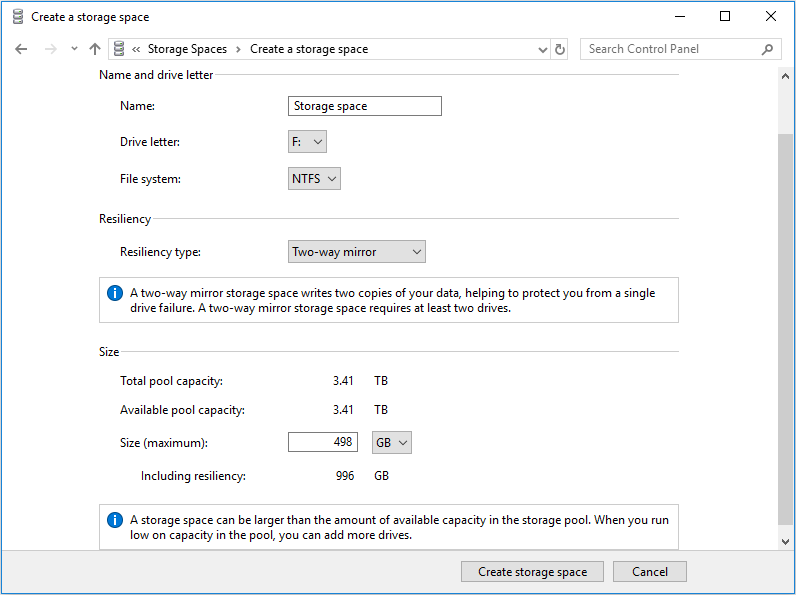
Step 2: Create storage space.
- Choose file system: NTFS or ReFS.
- Choose resiliency type: Simple (no resiliency), Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror, or Parity.
Attention:
ReFS (Resilient File System): It is compatible with most of NTFS. It can verify data corruption automatically and try to recover it. Besides, the combination of ReFS and Windows 10 Storage Spaces can provide better data protection. At the same time, there are performance improvements in dealing with hundreds of millions of files.
Simple (no resiliency): This type needs at least one drive and will write one copy of data. So, it won’t protect data from drive failure (click to know how to recover data from a failed hard drive). However, similar to RAID 0, it can improve read/write performance through adding drives.
Two-way mirror: It needs at least two drives and will write two copies of data and it will protect data from a single drive failure. It is similar to RAID 1.
Three-way mirror: It needs at least five drives and will write three copies of data. The usable space is a third of the total capacity. But it will protect data from two simultaneous drive failures.
Parity: It needs at least three drives and writes data with parity information. It will protect data from a single drive failure. It is similar to RAID 5.
Windows 10 Storage Spaces vs. RAID
Actually, Windows 10 storage spaces feature can also realize software RAID to some extent. However, the Windows Storage Spaces has some difference from RAID and we can’t say that it is inferior to RAID. Let’s see the difference of Windows 10 Storage Spaces vs. RAID.
Sockets
Generally speaking, RAID has socket limitation except for software RAID. The number of sockets is determined by physical RAID controller. However, Windows 10 Storage Spaces and software RAID don’t have this limitation.
Management
Generally speaking, operating system treats RAID as one disk. So, if the disks in hardware RAID have different capacities, space wasting will occur. However, Windows 10 Storage Spaces will not cause this waste because operating system can still operate single drive.
Besides, Windows 10 Storage Spaces has ReFS, which can make users free from trouble of data verification.
Performance
As for read write speed performance, many people have tested. They find that the sequential reading/writing speed of RAID 0 is approximately twice that of Storage Spaces simple mode. However, their 4K reading/writing speeds are almost the same.
Besides, the sequential reading speed of RAID 1 is slightly faster than that of Storage Spaces two-way mirror mode. But the sequential writing speed of RAID 1 is approximately half that of Storage Spaces two-way mirror mode. Their 4K reading/writing speeds are almost the same.
However, reading/writing speed in the Storage Spaces parity mode will be much slower than that in hardware RAID 5.
But Windows Storage Spaces still have its advantages like no fee and data protection. Users can try it. And if users are using SSD, Storage Spaces are recommended.
If you are interested in testing their performance by yourself, click disk performance test to know how to test them.
How to Back up Data and Manage Partition with MiniTool Partition Wizard
When users want to create Storage Spaces with formatted drives, please back up data in advance. If there is a lot of data on the drive, MiniTool Partition Wizard can help to back up easily. Besides, this method can also avoid data loss.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here is the tutorial.
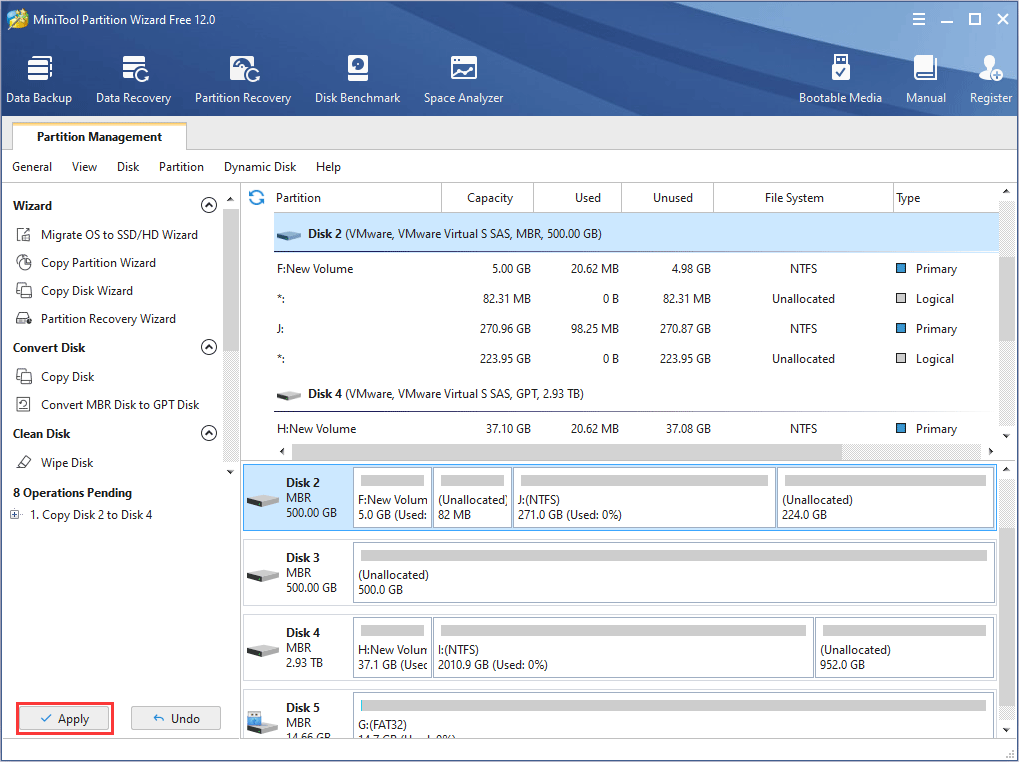
Step 1: Download MiniTool Partition Wizard and launch it to get its main interface.
Step 2: Right click a disk and choose Copy (This feature is not free when the disk is a system disk).
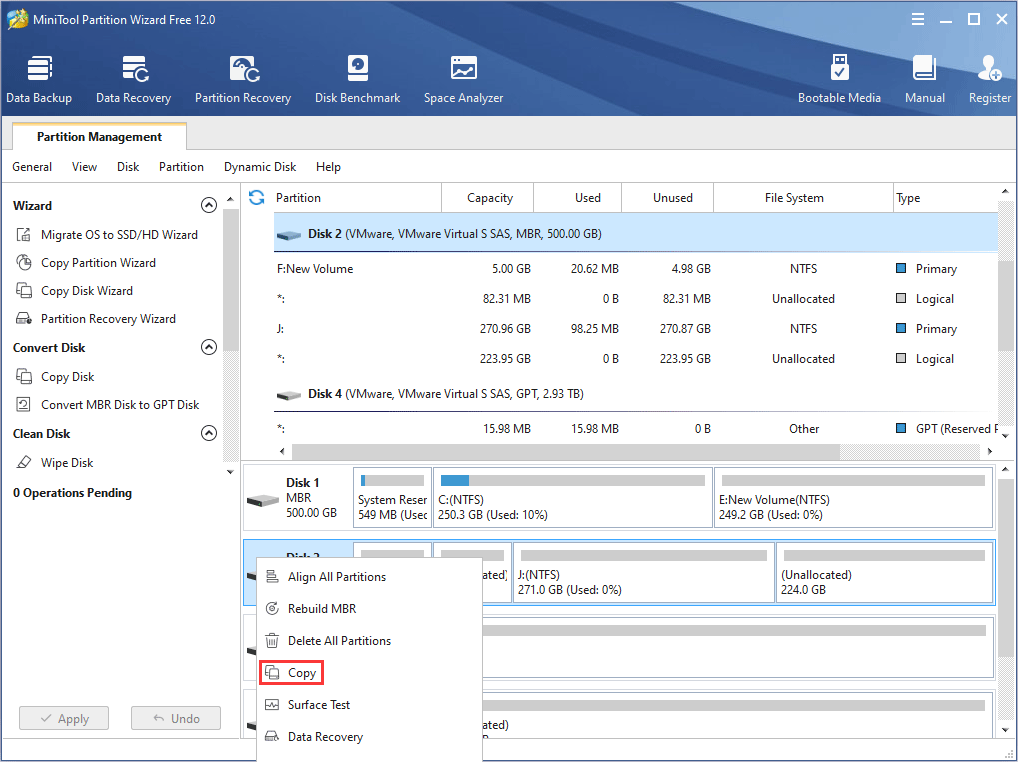
Step 3: Select a target disk where the data will be copied to, and click Next.
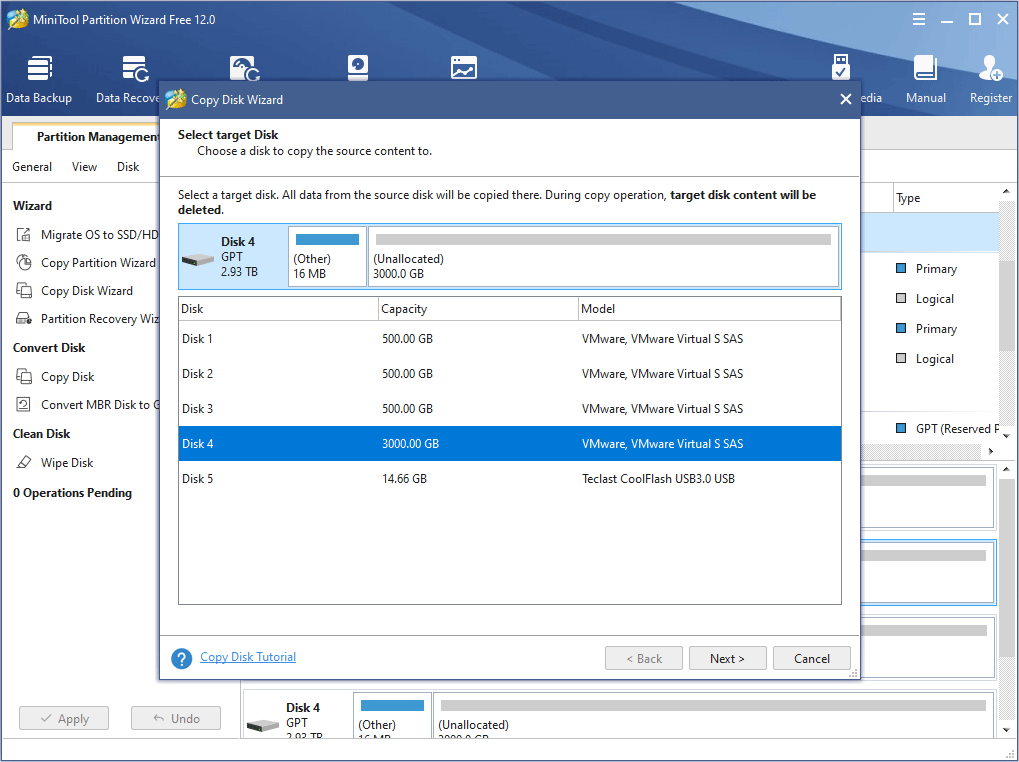
Step 4: Choose copy options and adjust disk layout. And then click Next.
- Fit partitions to entire disk: All the partitions on the original disk are shrunk or extended by an equal proportion to fill the entire target disk.
- Copy partitions without resizing: All the partitions on the original disk are copied into the target disk without changes in size or location.
- Align partitions to 1 MB: It is 4K alignment, which is recommended for improving computer performance.
- Use GUID partition table for the target disk: MBR can only recognize and use 2TB disk space at most. This option can convert MBR to GPT, thus users can use the disk space beyond 2 TB. This feature is not free.
- Disk Layout and Change Selected Partition: These two boxes are used together. Users click a partition in the Layout box, and then they can resize this partition in the Change Selected Partition box by dragging arrows or typing partition size value.
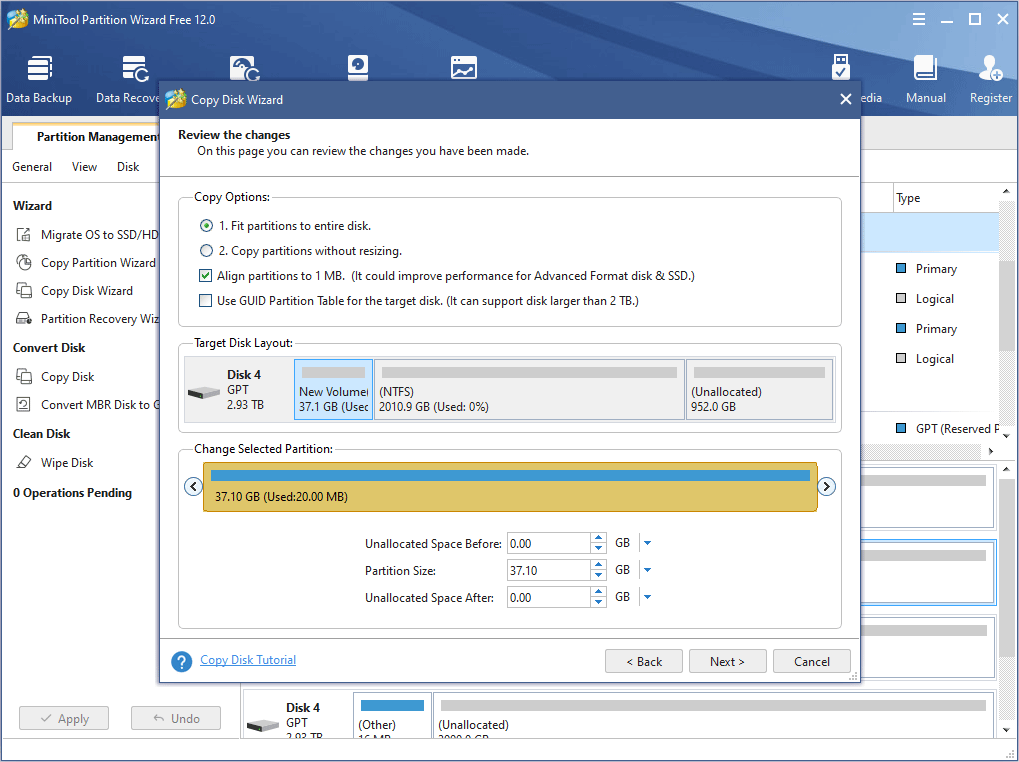
Step 5: A note window pops up. Read it and click Finish.
If the copied disk is a system disk, users can set firmware to boot from the target disk. If the copied disk is just a data disk, users can ignore this note and click Finish.
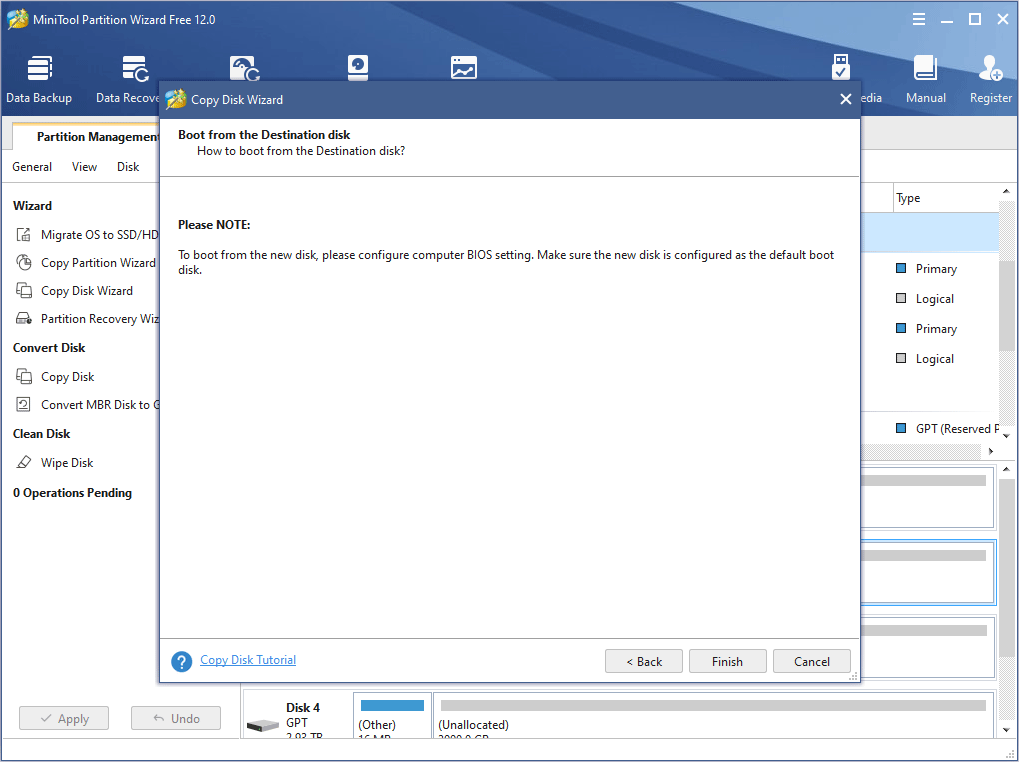
Step 6: Click Apply button to execute the pending operations.
If users format a drive with important files on it mistakenly when creating storage pool, or if other Storage Spaces data loss situations occur, users can also recover data with MiniTool Partition Wizard. Please click here to know how to recover data from failed Storage Spaces.
Surely, please read how to recover data from hardware RAID if users are facing RAID data loss.
In addition to data backup and data recovery, MiniTool Partition Wizard can also help users manage storage space and RAID partitions. For example, splitting, merging, and so on. It is always versed in disk management.
Bottom Line
If you still have confusion with Windows Storage Spaces vs. RAID or anyone of them, please leave a comment below for discussion. Or if you have any suggestions, please also leave a comment. We may adopt them in next update.
If you are facing data loss in Storage Spaces or RAID and you don’t know what to do, please email to [email protected] for advice.
Windows 10 Storage Spaces vs RAID FAQ
- Connect the storage drives to your Windows 10 PC.
- Type “manage storage spaces” in Windows search box.
- Click Manage Storage Spaces button to open it.
- Click “Create a new pool and storage space“.
- Choose file system: NTFS or ReFS.
- Choose resiliency type: Simple (no resiliency), Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror, or Parity.
Windows 10 supports RAID. This OS is compatible with hardware RAID and can also create software RAID. To create a software RAID, you just need to:
- Press “Windows + R” keys and type “diskmgmt.msc” in run box to open Disk Management.
- Right click the whole disk to convert it from basic disk to dynamic disk.
- Right click unallocated space and choose “New x Volume“(“X” can be “Striped”, “Mirrored”, or “RAID-5”).
- Follow the wizard to select disks, and set volume size, drive letter, file system, and cluster size.

User Comments :