Nowadays, SSDs are gradually popularized. Some users may wonder whether RAID is still useful today. In this post, MiniTool explains SSD vs RAID. You can get a conclusion after reading it.
In the past the idea was to reduce Pr processing bottle necks by using 3+ HDDs in a RAID configuration. With SSDs can we now skip the RAID controllers and put all our raw video and output video files on 1 SSD? Or maybe have a smaller SSD for Windows 10 and CC apps and a larger SSD for project and video files? — community.adobe.com
In the past, people boosted PC performance by using HDDs to compose RAID 0. However, when SSDs are gradually popularized, they are considering whether it is time to replace RAID with SSD. This post elaborates on SSD vs RAID. You can make a decision after reading it.
SSD vs RAID 0 Performance
As we all know, there are several common RAID forms including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 5, etc. Among these RAID forms, RAID 0 is the best way that can improve performance. When using mechanical hard drives in RAID 0, the performance can be improved greatly—it can reach read and write speeds almost comparable to SSDs.
Theoretically, the more disks added to RAID 0, the better the performance of RAO 0. However, the RAID 0 performance is limited by a number of factors, including RAID controller throughput and processor speed. So, when the number of disks reaches a critical point, the performance is the best. If the number is lower or higher, the performance will fall off.
According to benchmarks conducted by Tom’s Hardware to measure the performance scaling of a RAID 0 system, the sweet spot for RAID 0 performance rests at six drives, although this may vary based on the controller or specifications of the PC.
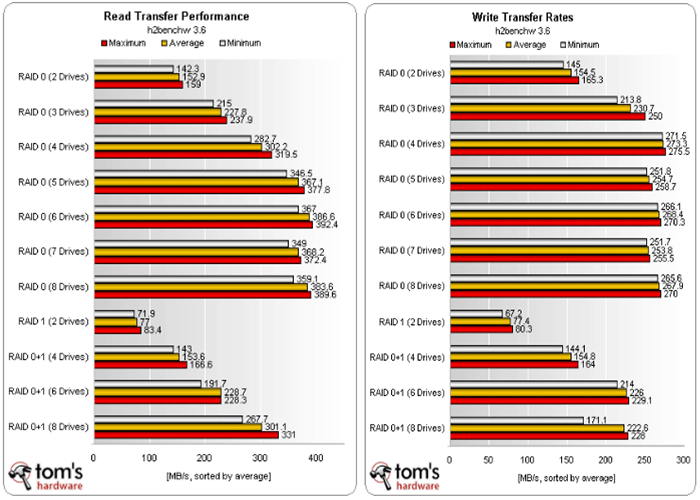
When RAID 0 is composed of 6 drives, it provides read and write speeds of 386.6MB/s and 268.4MB/s respectively, which are very close to those of an SSD. But SSDs will almost always offer better performance. Thanks to NAND flash memory, most SSDs can offer read and write speeds at around 500MB/s.
So, we can make a conclusion that SSD performs better than RAID 0. Apart from this, compared with SSDs, RAID 0 has other disadvantages:
- The more disks added into RAID 0, the more failure points RAID 0 has. This means that RAID 0 faces higher risk of failure.
- If one drive fails, the entire array is lost.
RAID’s Future
If you just pursue performance, you can replace your HDD RAID 0 storage with an SSD. But, if you are using other RAID forms and pursuing data redundancy and uptime protection, RAID is irreplaceable, especially for data center, cloud storage, or other enterprises.
In addition, you can replace HDDs in RAID with SSDs, but you can’t replace RAID with an SSD. RAID is still an effective method to improve storage performance, add capacity, and protect the integrity of data across multiple volumes.
Actually, nowadays, some people may consider using SSDs to compose RAID. There is no doubt that SSD RAID 0 can perform better than a single SSD. Another reason why people consider using SSD in RAID is that SSD has no move parts, which means more durable and longer lifespan. Although SSDs are leading the way, RAID is also not outdated.




User Comments :