Introduction to Overall Hard Drive System
In forums, some people ask questions like SATA vs SSD, NVMe vs SSD, SATA vs NVMe, etc. To some extent, this indicates that they are confused about hard drive system, because SATA and SSD are not in the same category. In this part, I will introduce the whole hard drive system to you.
1. What is a hard drive?
The hard drive we often say refers to the device that stores all the data of your computer, from the operating system files that govern your PC, the important work document that you absolutely can’t lose, to the game also important to you.
2. How are hard drives classified?
According to different standards, hard drives can be divided into different types. For example:
- According to storage medium, hard drives can be divided into HDD (using magnetic track to store data), SSD (using flash memory to store data), and SSHD (SSD + HDD).
- According to connector, hard drives can be divided into IDE hard drive, SATA hard drive, SCSI hard drive, SAS hard drive, M.2 drive, U.2 drive, etc.
- According to size, hard drives can be divided into 2.5-inch hard drive, 3.5-inch hard drive, etc. 3.5-inch hard drives are used in desktop, and 2.5-inch hard drives can be used in both laptop and desktop.
- According usage, hard drives can be divided into internal/external hard drive (the drive is installed inside the PC or not), PC/PS4/Xbox one hard drive (actually, there is not much difference), desktop/enterprise hard drive (different target customer group), NAS hard drive, surveillance hard drive, etc.
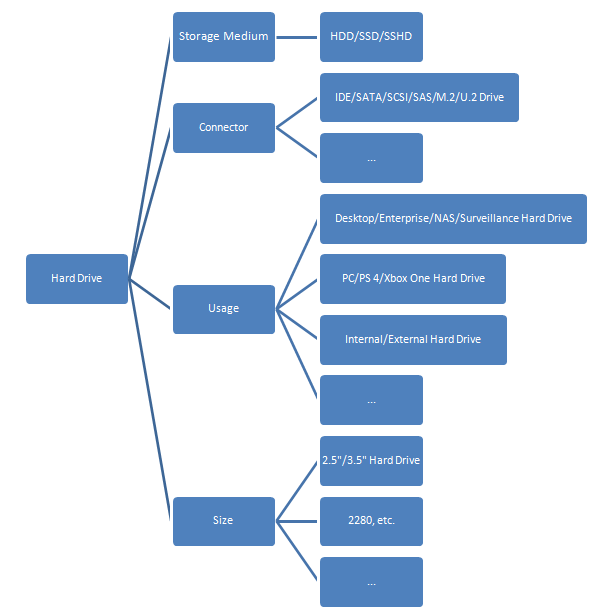
After reading the above contents, you can know that SATA refers the connector of the hard drive, while SSD lays emphasis on the storage media of the hard drive.
Different Types of Hard Drives: Which One Should You Choose
SATA vs SSD
In this part, I will answer the following questions: What is SATA hard drive? What is SSD? In addition, when it comes to SSD vs SATA, what’s the difference between them? And, what’s the relationship between them?
What Is SATA Hard Drive?
Apparently, SATA hard drive refers to hard drive equipped with SATA connector (bus). Then, what is SATA? Or, what does SATA mean? Usually, when a hard drive uses SATA connector, it means that this hard drive is using SATA bus. Then, what is bus? What does bus do? You may have new questions. To solve these problems, I will introduce how a hard drive works with the computer.
When a hard drive is produced, people should consider how to connect it to the computer and how to transfer data between the hard drive and the computer. To solve those problems, people make bus standards. SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) bus is one of such standards.
A bus usually defines the following items:
- Physical characteristic: It’s related to the plug and socket of the wires. It usually defines the plug and socket’s geometric size, shape, pin number, and pin arrangement order, etc.
- Functional characteristic: It refers to the function of each signal line (wire), such as the address bus used to represent the address code; the data bus used to represent the transmitted data, and the control bus used to represent the commands and status of operations on the bus.
- Electrical characteristic: It refers to the signal direction on each signal line and the effective level range of the signal.
- Time characteristic: It’s also called logic characteristic and usually defines when the signals on each signal line are valid during the bus operation. The effective timing relationship agreement of this signal ensures the correct operation of the bus.
In general, when you get the bus of a hard drive, you can get the speed range easily. Then, please keep reading to get to know SATA speed.
Since the first SATA bus release, many advanced SATA bus versions has been released so far. Its main releases are displayed in the following list:
- SATA 1.0: released in 2003; 1.5 Gbit/s (150 MB/s).
- SATA 2.0: released in 2004; 3 Gbit/s (300 MB/s).
- SATA 3.0: released in 2009; 6 Gbit/s (600 MB/s).
- SATA 3.2 (SATA Express): released in 2013; 16 Gbit/s (1.97 GB/s).
Apparently, SATA 1.0 and SATA 2.0 have been obsolete, but SATA 2.0 socket may still exist in some old devices. At present, SATA 3.0 is the main stream of hard drive interface (because higher speed hard drive is very expensive still). As for SATA Express, its popularization process can be said to be quite a failure.
As a result, the SATA Express protocol was replaced by the NVMe protocol, and the SATA Express physical port was also replaced by the follow-up M.2 and U.2. The motherboard and hard drive carrying the SATA Express interface is also quite few.
What Is SSD?
According to Wikipedia, a solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. Put it simply, an SSD is a hard drive using flash memory.
Unlike SATA that is related to hard drive external structure (the connector), SSD is related hard drive internal structure. When we talk about SSD, we usually compare it with HDD. The two types of hard drives have different internal structure and therefore have many different characteristics. Click SSD vs HDD to know more.
In general, a typical SSD is composed of the following parts: a connector/bus, an SSD controller, several flash memory chips, and an optional DRAM (serving as cache). The following picture shows a SATA SSD’s structure and an M.2 SSD’s structure.
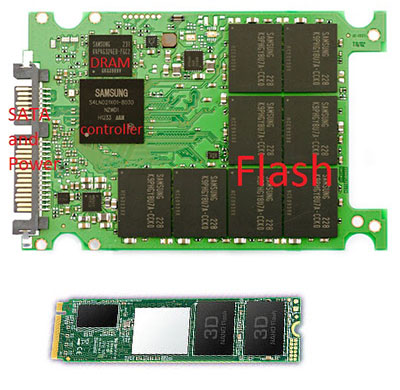
The SSD controller is responsible for connecting the storage unit (flash memory) to the interface, so that the data can be transmitted to the computer; and responsible for the completion of various instructions within the SSD, such as data reading and writing, wear leveling (WL), bad block management, error checking and correcting (ECC), garbage collection (GC), etc.
The DRAM is a chip standing next to the controller chip. It serves a buffer between the SSD controller and the NAND flash memory, making the SSD process data faster.
SSD flash memory chips usually are NAND flash memory chips. NAND flash is a non-volatile storage technology, that is, data can still be saved after power failure. It has many advantages like low power consumption, low price, and good performance.
To expand SSD capacity and lower the cost, manufacturers have made many efforts, for example, from plane NAND to 3D NAND, from SLC (single-level cell) to MLC (multi-level cell), TLC (triple-level cell), or even QLC (quad-level cell) NAND.
As for the SSD connector, it could be SATA, M.2, U.2, SAS or other shapes, depending what bus it supports.
Everything You Need to Know About Solid-state drive (SSD)
SATA vs SSD: Summary
SATA and SSD are not conflicted with each other. They can be in the same item: SATA SSD.
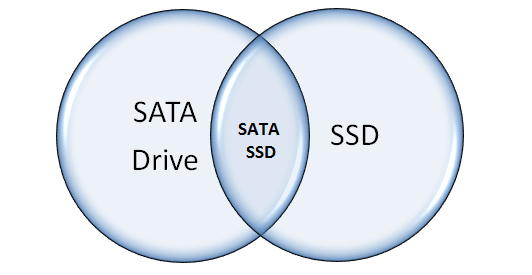
Nowadays, many people like to use SSDs. Among these SSDs, SATA SSDs are very popular. Here are some reasons:
- SATA SSDs have some variants like mSATA drive and M.2 SATA drive (M.2 SATA drive uses SATA bus and M.2 port). Therefore, it can fit various computer drive bays.
- A SATA SSD’s speed is not very slow and its price is affordable.
But SATA SSDs also have disadvantages. The biggest one is that SATA SSDs’ speed limit is 6 Gbit/s. Comparing to other SSDs like M.2 PCIe 3.0 x 4 SSD(32 Gbit/s), it’s slower. If PCIe SSDs or other higher-speed SSDs get popularized, SATA SSDs will be eliminated with no doubt.
Upgrade Hard Drive
If you want to upgrade your hard drive from HDD to SSD or from an SSD to a faster SSD, you may need the guide on how to upgrade the hard drive. The direct way to upgrade a hard drive is to back up all important data to an external hard drive, disassemble the PC to replace the hard drive, and then install OS on the new hard drive.
If you like this method, please refer to this post: How to Install Windows 10 on a New Hard Drive (with Pictures).
But if your computer is dual-booted, or you just want to migrate the OS, or in other special situations, in a word, you don’t want to use the above method, you can use the following method:
Step 1: Connect the new hard drive to the computer USB port via a connector adapter.
Step 2: Find a disk clone or OS migration program, for example, MiniTool Partition Wizard. MiniTool Partition Wizard is a powerful program. You can use it to manage your disk, migrate OS, clone disk, recover data, etc.
Step 3: Install this software on your computer (you can click the following button to download MiniTool Partition Wizard Trial Edition).
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 4: Go to the main interface of the software. Then, click on Migrate OS to SSD/HDD in the action panel.
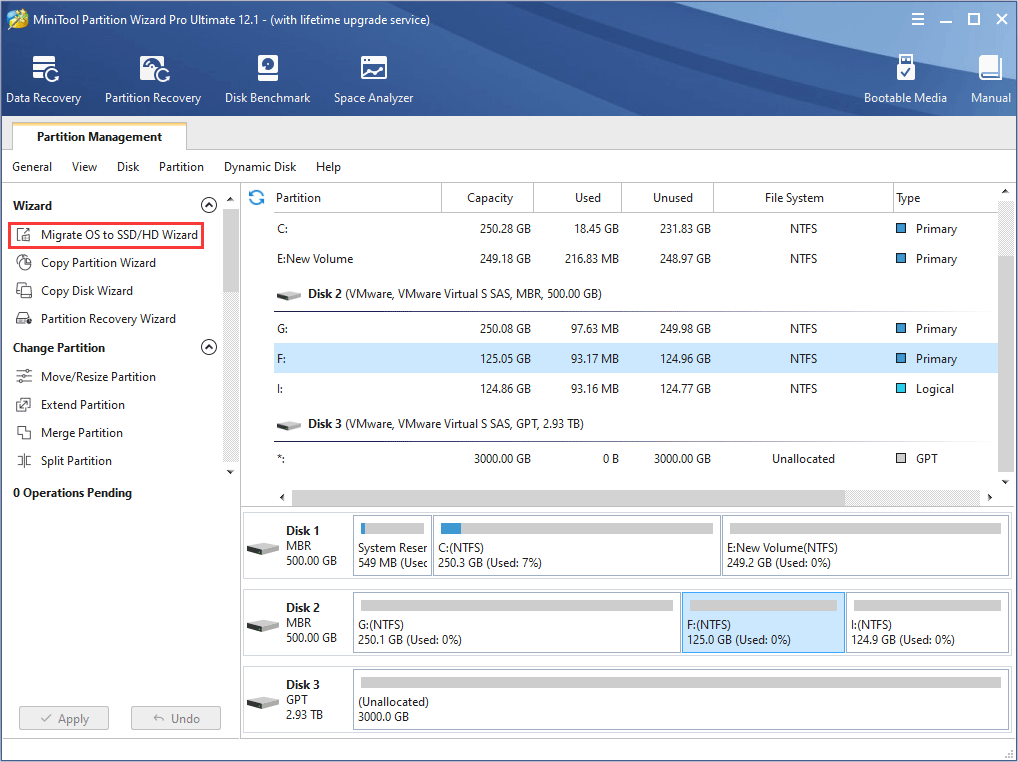
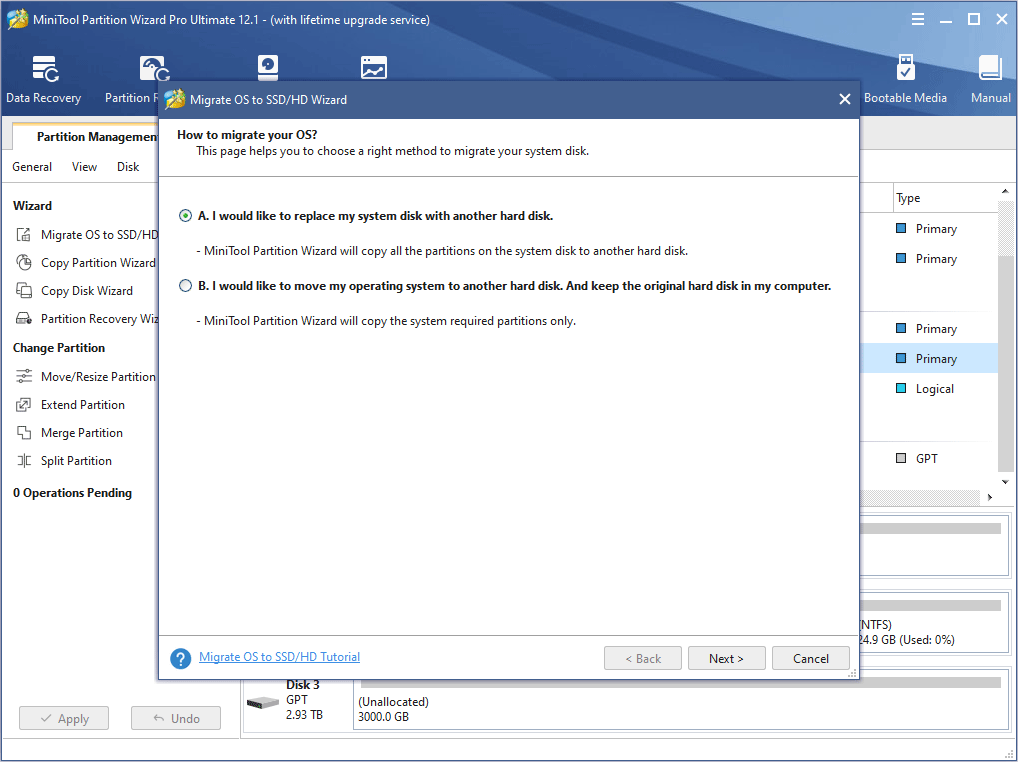
Step 5: Choose the right method to migrate the system disk and click Next. Option A allows you to clone the whole system disk, while option B only allows you to migrate the OS.
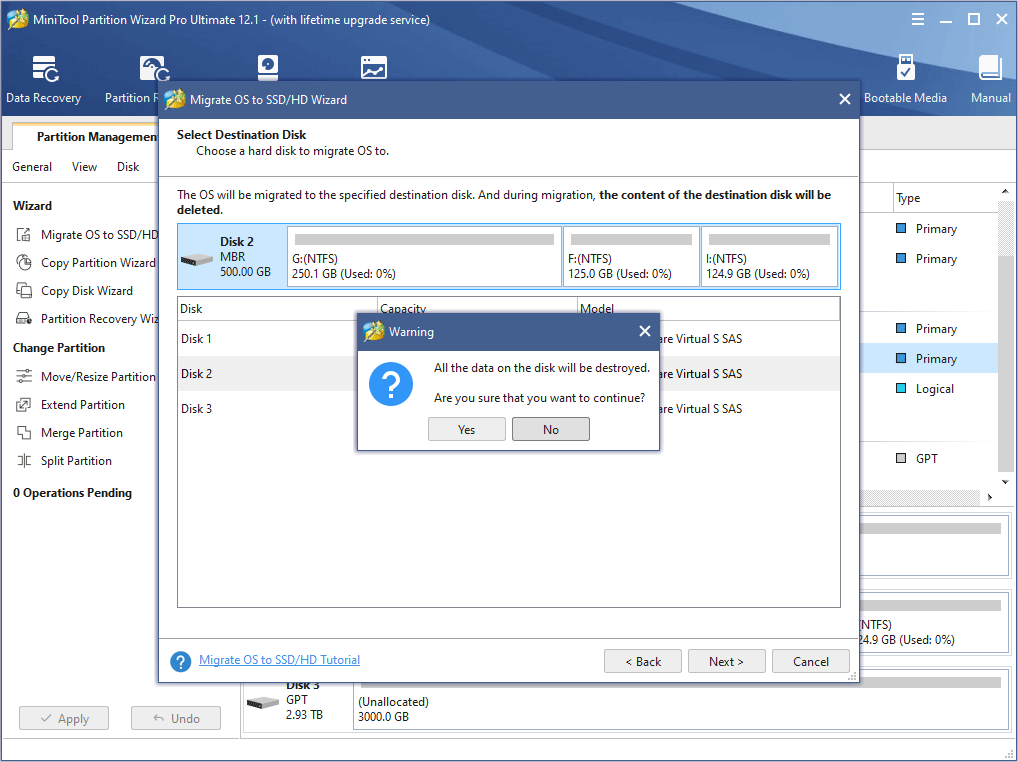
Step 6: Choose the new drive as the destination disk and then click Next.
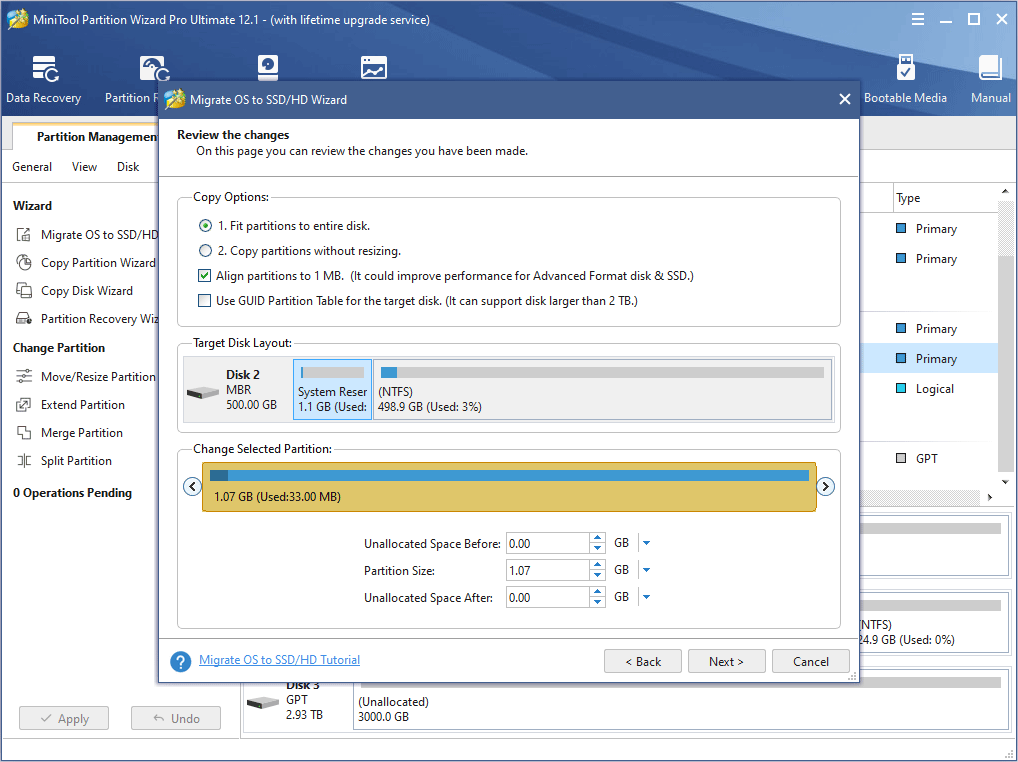
Step 7: Review changes and click Next button. In this step, you can keep default settings. But if the old disk is a MBR disk and you want to use GPT style in the new disk, you can check the box before Use GUID partition table for the target disk.
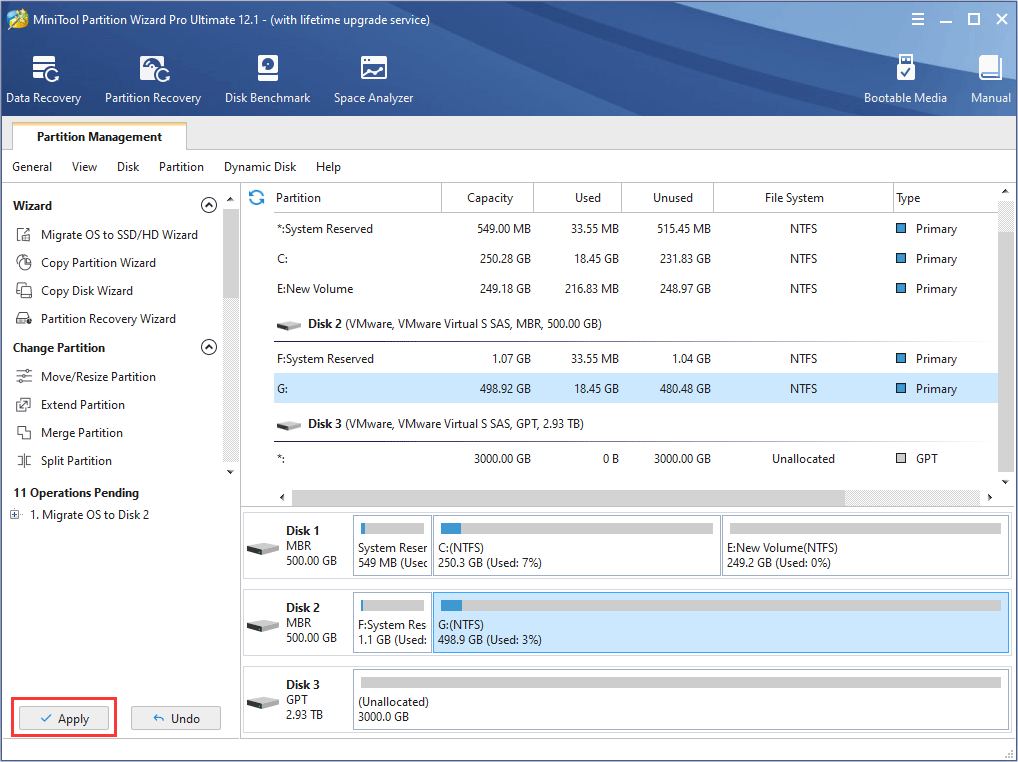
Step 8: Read a note on how to boot from the destination disk and the click Finish button. Then, click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
Step 9: Disconnect the new drive from the USB port and then disassemble the computer to install the new hard drive. As for the hard drive installation guide, you can refer to this post: How to Install a Second Hard Drive in Your Laptop and Desktop PC.
Step 10: If necessary, you should change boot order in BIOS. Then, you can boot the computer from the new drive.
Bottom Line
Is this post helpful to you? If you still have some problems with SATA vs SSD, please leave a comment below. If you have difficulty in managing disk, cloning disk, etc., please leave a comment below or email your problem at [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.

User Comments :