Hey Guys! Any thoughts on this? I am building a new Intel 8th Gen system. The NVME is so freaking amazing but is it overkill for gaming, VR, MS Office productivity? The price difference is just huge…I don’t know whether to get the M.2 1TB NVME ($449) or just a M.2 1TB SATA ($280ish) and just put the extra $170 into other areas… — hardforum.com
Everyone knows that SSDs are faster than HDDs. To boost your PC’s performance, you may decide to upgrade from HDD to SSD. But do you know that not all SSDs are made equal? I have already discussed M.2 SSD vs. SATA SSD before. In this post, I want to go a bit deeper and talk about M.2 NVMe vs M.2 SATA vs PCIe SSD.
M.2 NVMe vs M.2 SATA vs PCIe SSD
Form
At present, people are pursuing lighter and thinner laptops. To cater for this mass-market, more and more computers are designed to use lighter and thinner hard drive like M.2 NVMe SSD, M.2 SATA SSD, and PCIe SSD. Unlike 2.5-inch SATA SSDs that are 7mm thick, these SSDs are only around 3mm thick.

The above picture shows an M.2 SSD. If you plan to buy such an SSD, you just need to pay attention to 2 factors: length and width. In general, M.2 SSD has the following 3 common forms: 2242, 2260, and 2280. An M.2 SSD in form of 2280 means that it is 22mm wide and 80mm long.
M.2 2260 and M.2 2280 SSDs are usually used in desktops, while M.2 2242 SSDs are usually used in laptops. If the size is wrong, the SSD cannot be inserted into your PC.
How to Distinguish Them: 3 Factors
The reason why many people cannot distinguish among M.2 NVMe SSD, NVMe SSD, and M.2 PCIe NVMe SSD is that they can’t figure out 3 factors: bus, interface, and data transfer protocol. In this part, I will explain them to you in detail.
1. Bus
Bus is an internal structure, a common channel for CPU, memory, input, and output devices to transmit information. Bus is a transmission harness consisting of wires. It fundamentally determines the transmission speed between the SSD and the computer.
Among M.2, NVMe, SATA, and PCIe, terminologies classified as bus are SATA and PCIe.
SATA bus standard is an external bus standard for hard disk, which adopts serial connection mode. In SATA bus standard, data will be first read from the hard disk to memory, and then extracted to CPU for calculation, and then written to memory after calculation, and finally stored to hard disk.
PCIe bus standard is an internal local bus standard, which is also a high-speed serial point-to-point dual-channel high-bandwidth transmission. In PCIe bus standard, the connected devices are allocated exclusive channel bandwidth and do not share resources with other devices.
In this way, the data can be directly read to the CPU through the bus (the step of going through memory is eliminated), so that the PCI-E transfer speed is close to the maximum transmission speed. No doubt, PCIe bus standard is prior to SATA bus standard in read-write speed.
2. Interface
Interface is a standard that stipulates the physical shapes of hard drive sockets on the computer and the ports on SSDs. In the interface standard, the crucial point is the pin location. According to the pin location, you can easily identify the interface type.
Among the mentioned four terminologies, M.2, PCIe, and SATA all belong to interface (shape). But when we talk about M.2 SATA SSD or M.2 PCIe NVMe SSD, in the two phrases, SATA and PCIe usually refer to buses. As for PCIe SSD, it is usually regarded as M.2 PCIe SSD, because there is few real PCIe SSDs on the market.
M.2 interface can be divided into two types: B-key and M-key. The differences between B-key and M-key are shown as the following picture:
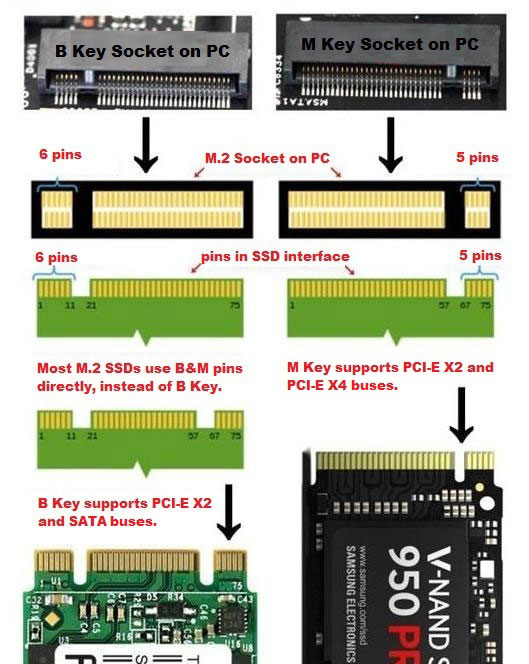
The B-Key is gradually replaced by B+M key. The B+M key SSD can be inserted into both B-Key and M-key sockets, while an M-Key SSD can only be inserted into an M-Key socket. If you want to make your computer communicate with your M.2 SSD via PCIe lanes, you should make sure the M.2 socket on your PC also supports PCIe bus.
Disk Interface – a Connection between Hard Disk and Host System
3. Protocol
Data transfer protocols work above buses and determines data transfer method. When data arrives at the SSD controller, the transmission protocol specifies how the data will be transmitted to the hard disk, such as how much data is carried in a transmission queue at one time, the size of the data transmitted at a time, and so on.
Just like traffic rules, transmission protocols regulate data transmission rules. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory express) is such a protocol and it works on PCIe bus. As for SATA bus, the data transfer protocol that works on it is AHCI.
NVMe can support 64 queues and each queue can carry 64000 instructions, so that the IOPS ability is improved greatly. By utilizing NVMe, the actual speed of PCIe SSD can be closer to its theoretical speed.
SATA vs. NVMe. Which One Is Your Best Choice?
Performance and Cost
The performance of SSD is related to buses and protocols. The performance of M.2 SSD is shown like the following 2 pictures. The two pictures will explain NVMe vs M.2 speed clearly.
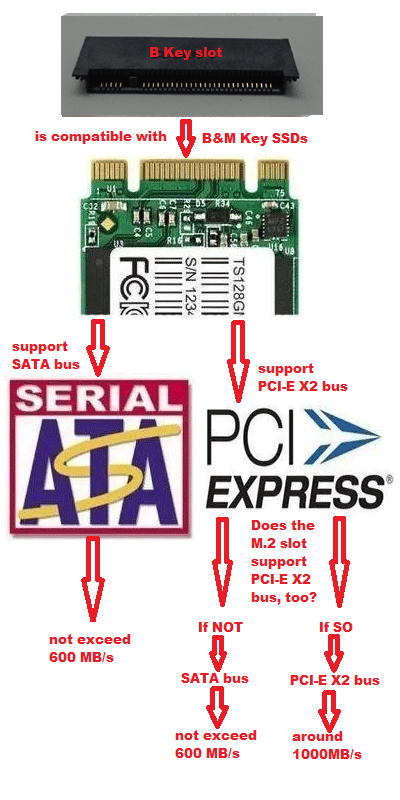
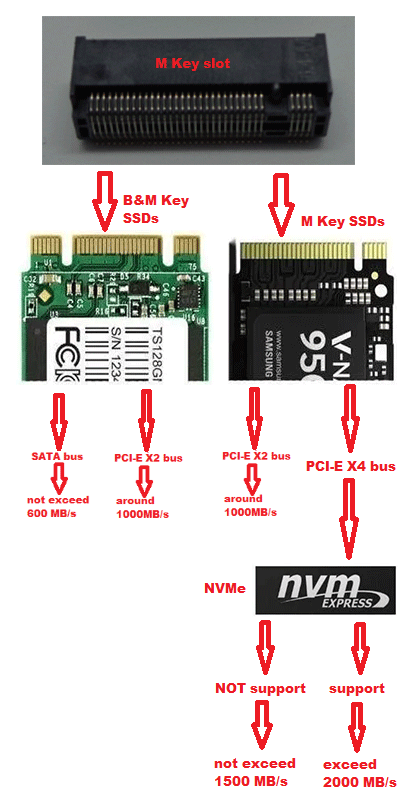
According to the above two pictures, we can make conclusion about M.2 SATA vs NVMe vs PCIe SSD: M.2 SATA SSD’s performance will not exceed 600 MB/s; PCIe SSD’s performance will not exceed 1500 MB/s; NVMe SSD’s performance can exceed 2000 MB/s.
As for the cost, there is no doubt that the better the performance, the more expensive it is. The problem is that whether you should pay extra money to get a better SSD? If you are a gamer or you often use your computer to edit video or something like that, I recommend you to buy an enough good SSD. Otherwise, ordinary SSDs can also meet the needs.
Migrate to NVMe SSD and Enable NVMe Mode
After learning about M.2 vs NVMe vs PCIe SSD, you may want to replace your old M.2 SATA SSD with a better PCIe SSD or NVMe SSD. If so, you can use software like MiniTool Partition Wizard to migrate your computer to the new SSD without data loss or reinstalling Windows. Please refer to the following steps:
Step 1: Buy an M.2 NVMe SSD and an M.2 to USB adapter. Through the adapter, you can connect your new SSD to your computer via USB interface.
Step 2: Click the above button to buy MiniTool Partition Wizard. Install it and then open it to get its main interface. Click on Migrate OS to SSD/HDD in the toolbar.
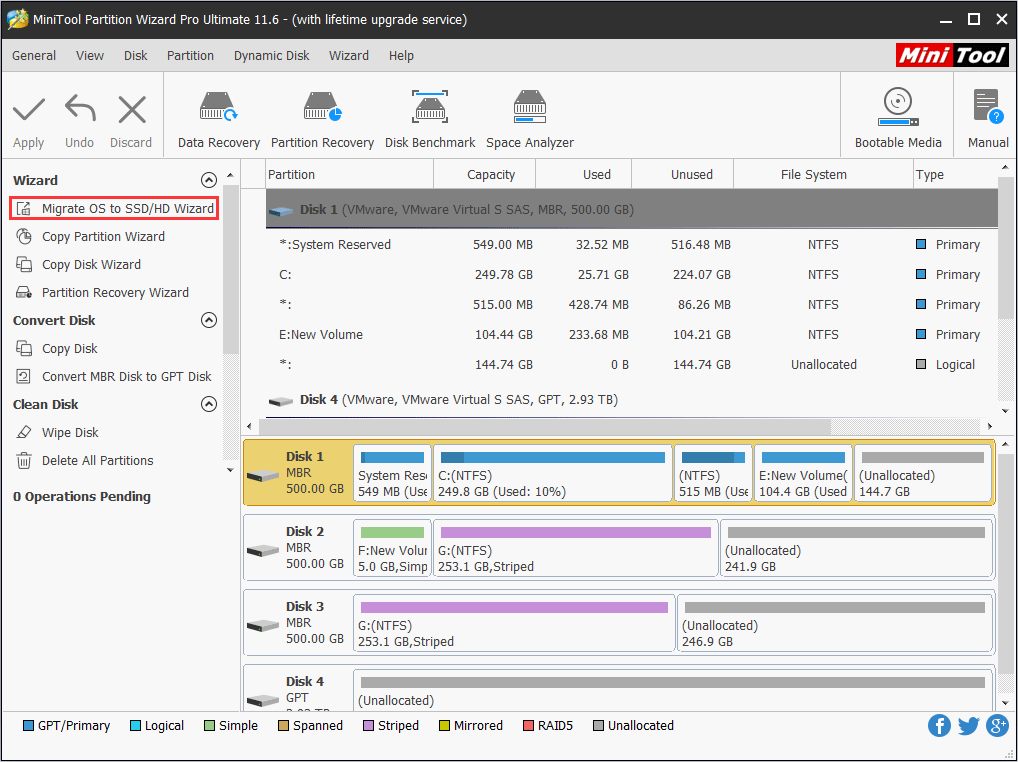
Step 3: Choose the right method to migrate the system disk and click Next.
Option A: to replace the system disk with another hard disk: The entire system disk will be copied to the new SSD. You can then boot from the new SSD and access all data from the new SSD. The old SSD can be thrown away.
Option B: to move operating system to another hard disk: Only the system and boot partitions required for OS are copied to the new SSD. You can boot from the new SSD, but the old SSD should not be thrown away because your personal files are stored in it.
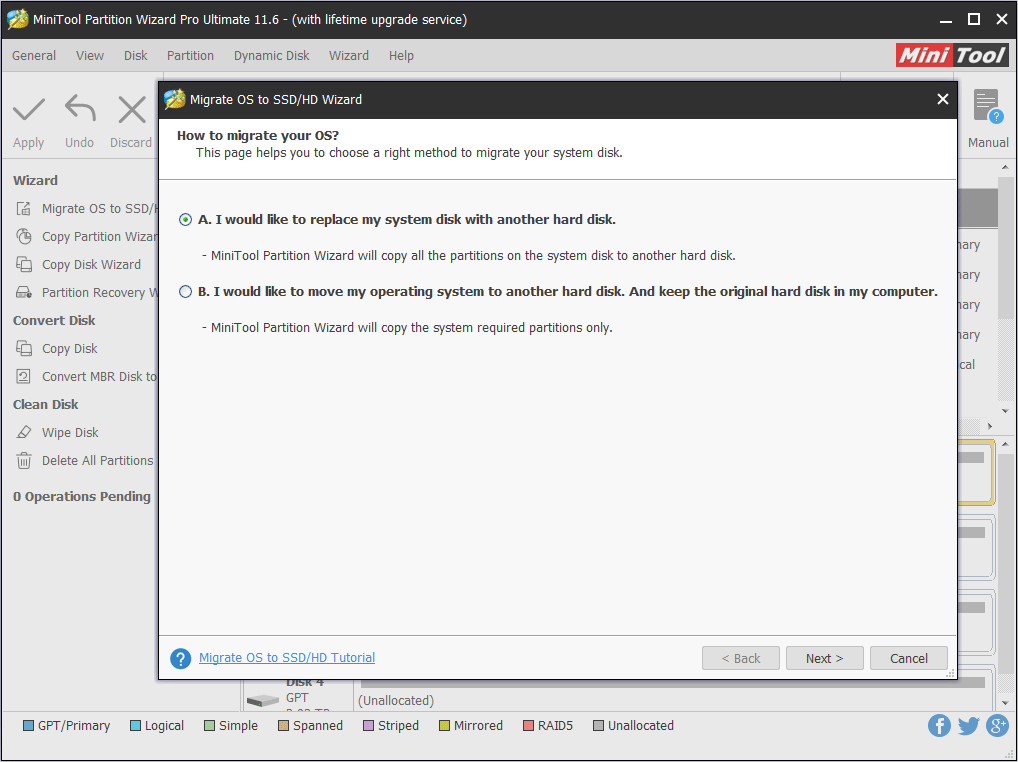
Step 4: Choose the new SSD to migrate Windows to and click Next. A warning window will pop up. Read it and click Yes.
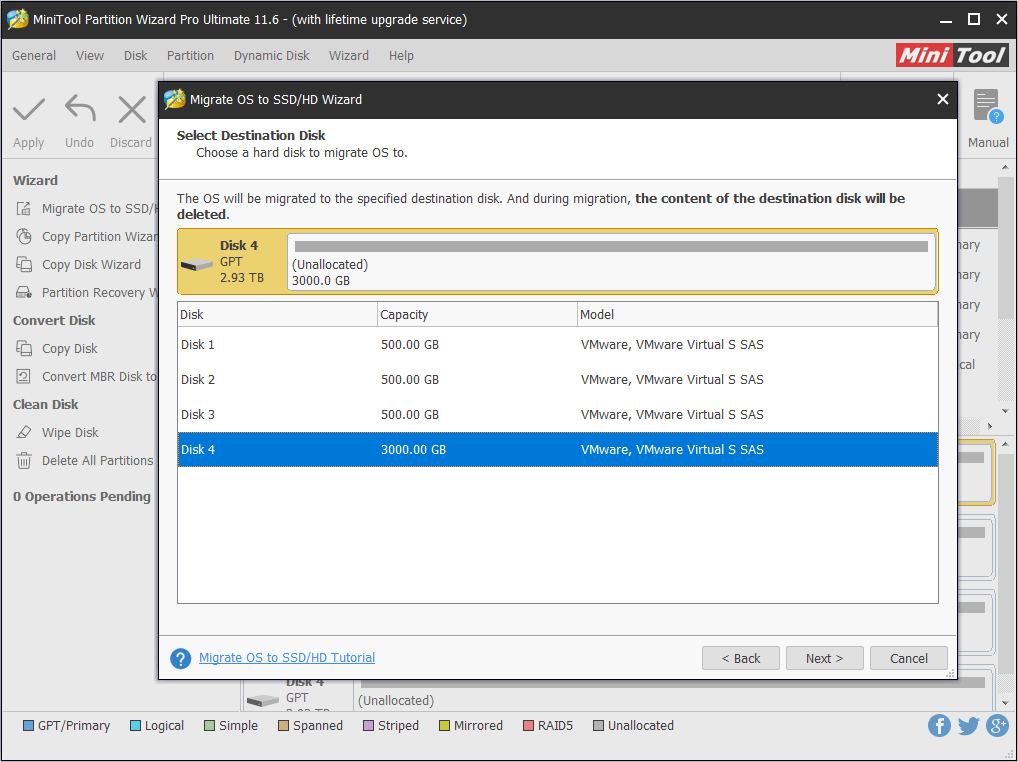
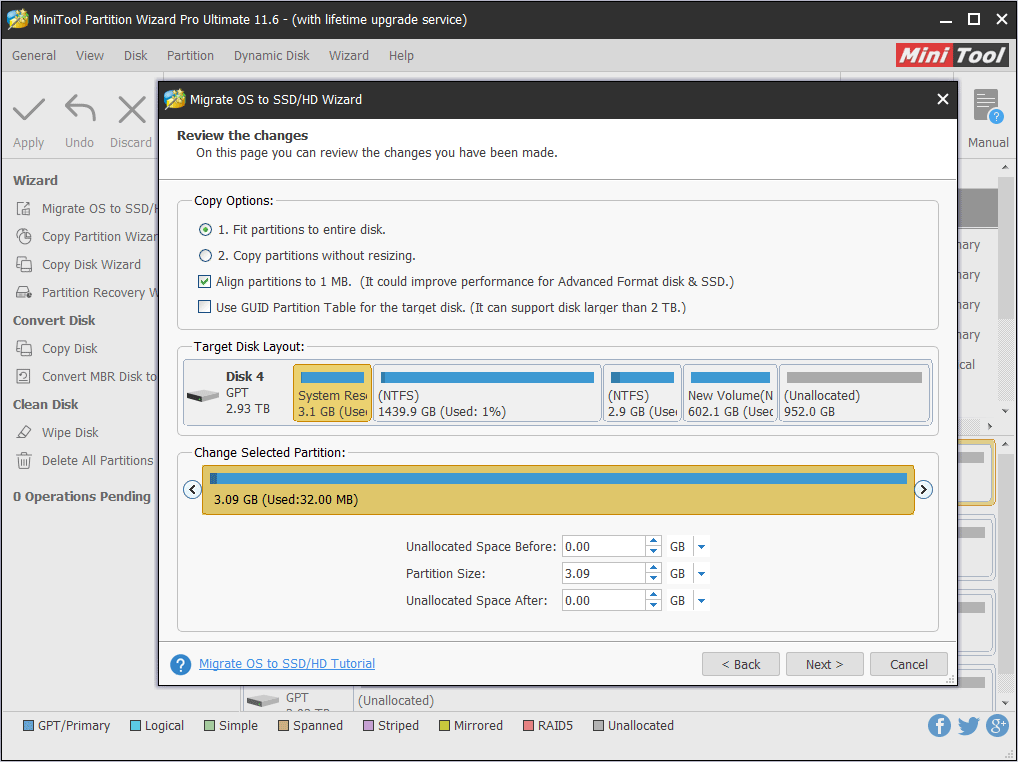
Step 5: Choose right copy options and adjust the target disk layout, and then click Next.
(1). Fit partitions to entire disk: All the partitions on the original disk are shrunk or extended by an equal proportion to fill the entire target disk.
(2). Copy partitions with resizing: All the partitions on the original disk are copied into the target disk without changes in size or location.
(3). Align partitions to 1 MB: It is recommended for improving computer performance.
(4). Use GUID partition table for the target disk: MBR can only recognize and use 2TB disk space at most. This option can convert MBR to GPT, thus users can use the disk space beyond 2 TB.
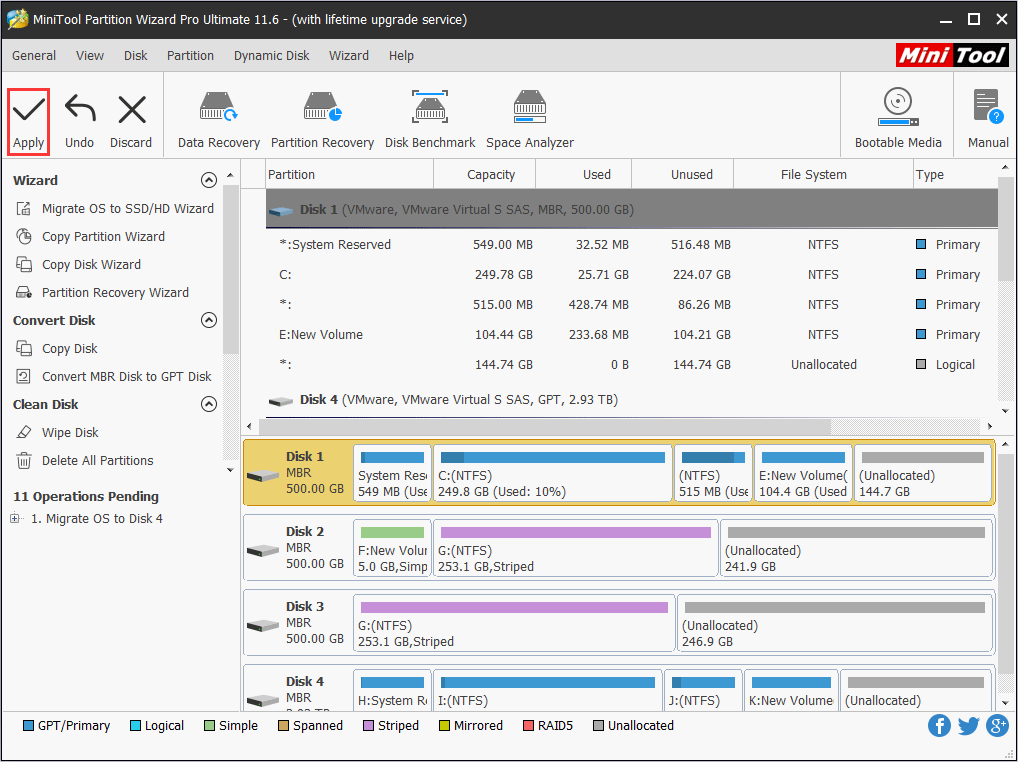
Step 6: Read the note and click Finish, then click Apply on the toolbar to execute the pending operations.
Step 7: MiniTool Partition Wizard will ask for a reboot. Click Restart Now.
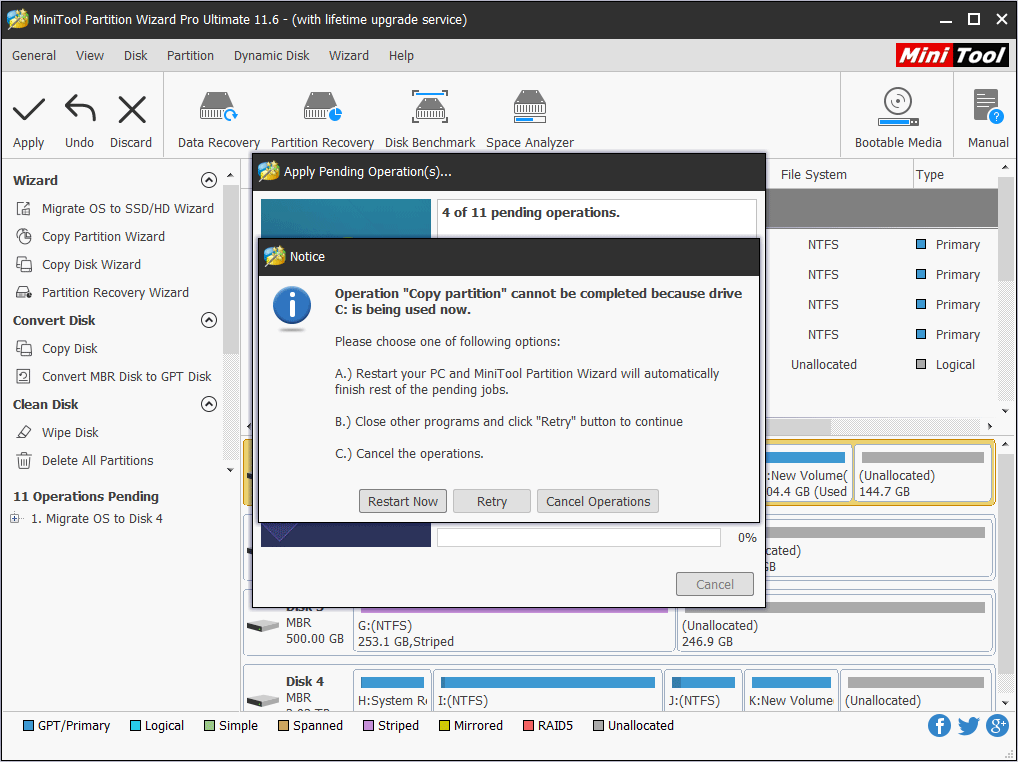
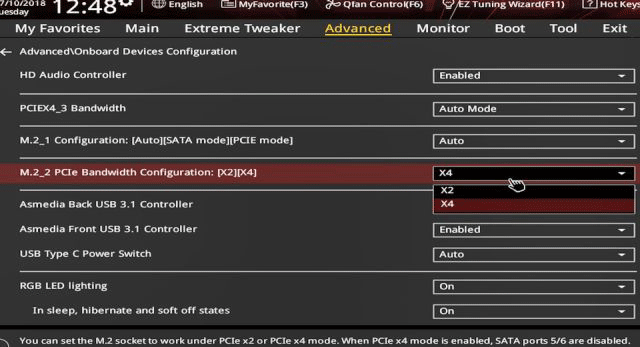
Step 8: Remove the old SSD from your computer and mount the new SSD into the PC. After that, you should boot into the firmware to change from SATA/AHCI to PCIe/NVMe mode.
Bottom Line
Has this post helped you figure out NVMe vs M.2 vs PCIe? If you have any doubt about the comparison, please leave a comment below. Besides, if you have difficulty in migrating computer to new SSD, you can contact us via [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.





User Comments :