When it comes to increasing computer storage space, it is hard for users to decide whether to buy an internal hard drove or an external hard drive. This post focuses on internal vs external hard drive and details the differences between the two kinds of hard drives.
How to expand your computer storage space? Upgrade to a large internal hard drive or connect an external hard drive? What are the differences between an internal hard drive and an external hard drive? Keep reading.
Internal vs External Hard Drive
Every computer ships with a hard drive—that is the internal hard drive. This kind of hard drive is installed within the laptop or the computer host.
External hard drives are not placed inside a laptop or a computer host—they connect to a computer via a USB or FireWire cable. However, take an external hard drive out of the hard drive case and you will discover the internal hard drive has the same internals structure with the hard drive used in the computer.
The usage is the main difference between the internal hard drive and external hard drive. Other differences like performance, reliability, and cost are discussed in the following content.
Internal vs External Hard Drive Speed
Are internal hard drives faster than external hard drives? The answer is going to Yes.
As we know, an external hard drive connects to a computer through a USB cable. Although some of USB interfaces come with faster speeds but the external hard drives involve an interface change, for example, switching from SATA to USB introduces some latency. As to internal hard drives, they are connected directly to the interface on the motherboard and this allows data to be transferred at a faster rate compared to external hard drives that are connected through USB cables.
Aside from the interface factor, the form factor also makes the internal hard drives faster than the external hard drives.
Generally, HDDs adopt standard spin speeds of 5,400 RPM and 7,200 RPM. Both 2.5-inch hard drives and 3.5-inch hard drives support the two RPMs but it is much easier for the latter to have greater spin speeds due to its higher power consumption and physical dimensions.
External hard drives generally are 2.5-inch drives in SATA to USB enclosures, while there are lots of 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch internal hard drives.
Recommended article: 2.5 VS 3.5 HDD: What Are the Differences and Which One Is Better?
Internal vs External Hard Drive Reliability
Are internal hard drives more reliable than external hard drives?
Internal hard drives and external hard drives feature the same mechanism and therefore there should be no reliability difference between the two kinds of hard drives.
However, external hard drives seem to fail frequently than internal hard drives. Why? The reasons are as follows:
First, internal hard drives are placed inside a computer host or a laptop whereas external hard drives are always placed on a desk. So, the latter is more exposed to physical damage like sudden hit or fall.
Second, the point of failure is not actually the external hard drive but the USB to SATA converter connected to the hard drive inside the hard drive case. So, users mistake this as a failure of the external hard drove itself.
Third, due to the portability, users place them in their bags and carry them around but they are always being naked, without protection, which breaks them easier.
Recommended article: External Hard Drive Lifespan: How to Prolong It.
Internal vs External Hard Drive Price
Are internal hard drives more expensive than external hard drives?
With the same brand and specification, some hard drives are more expensive as an internal hard drive than as an external hard drive. However, sometimes the opposite is found to be true.
Things become tricky when comparing the price between internal hard drives and external hard drives.
Pros and Cons of Choosing Internal and External Hard Drives
Let’s see what the pros and cons are if upgrading to a new internal hard drive and adding an external hard drive.
Internal Hard Drive Pros and Cons
Upgrading to a powerful internal hard drive can boost computer performance. Then, internal hard drives are always connected to computers, which means that there is no need to worry about the files not being there when computers start.
However, hard drive installation is required, which might be tricky for some users.
External Hard Drive Pros and Cons
External hard drives are lightweight and portable and you can take it on your business trip. Second, they can be connected to any computer. Third, you do not need to spend time installing the hard drive. Last, using an external hard drive can increase data security.
External hard drives are not just used to expand computer storage. They are also used to add extra protection to computers’ internal hard drives as files stored on internal hard drives can be corrupted by viruses and be stolen by hackers. Click here to see more usages of an external hard drive.
The cons of adding an external hard drive are: 1). There is no computer performance improved; 2). External hard drives are easy to lose.
What to Do If You Choose an Internal Hard Drive
If you decide to choose an internal hard drive, how to upgrade to it? You can try MiniTool Partition Wizard. It is a Windows-based program that is expert in managing disk, recovering lost data, cloning disk, etc. The feature Migrate OS to SDD/HDD can help you upgrade to a new internal hard drive without reinstalling Windows.
The tutorial on how to upgrade to a new internal hard drive is below.
Step 1: Connect the internal hard drive through a connection adapter.
Step 2: Get MiniTool Partition Wizard by clicking the button below.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 3: Install the program and launch it to get its main interface.
Step 4: The original and new internal hard drives should be displayed on the disk map. Click the feature Migrate OS to SSD/HD Wizard from the left panel.
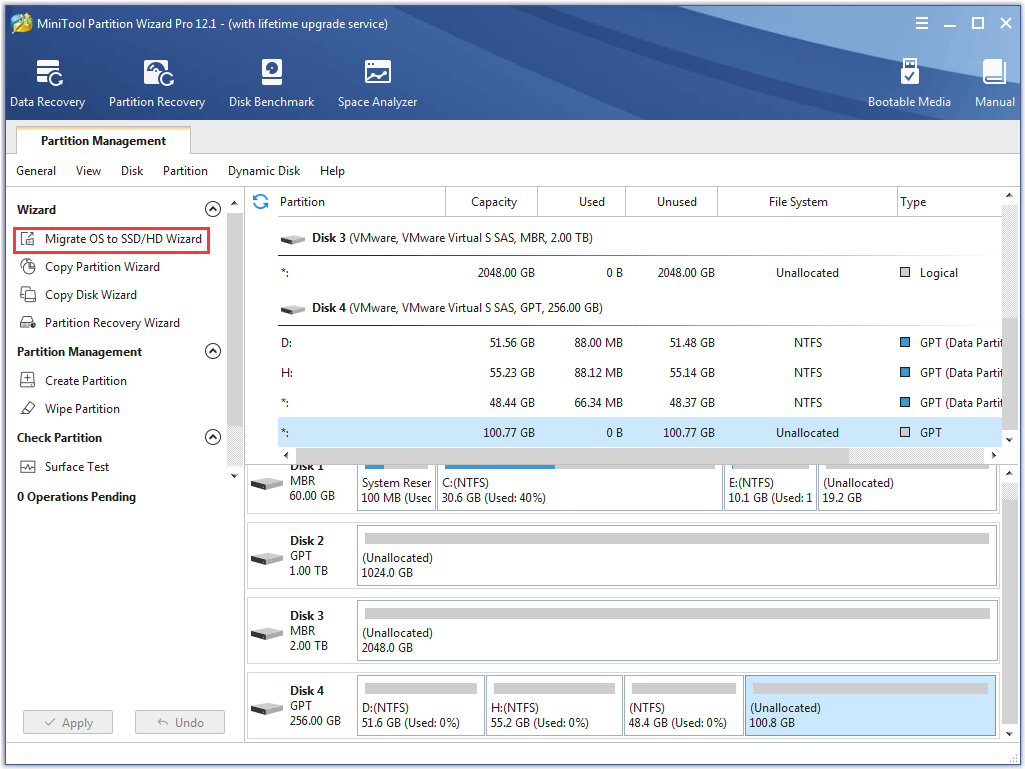
Step 5: Choose a method to migrate the system disk and click the Next button.
- Option A is to copy all partitions on the original internal hard drive to the new internal hard drive.
- Option B is to just copy the system required partitions only.
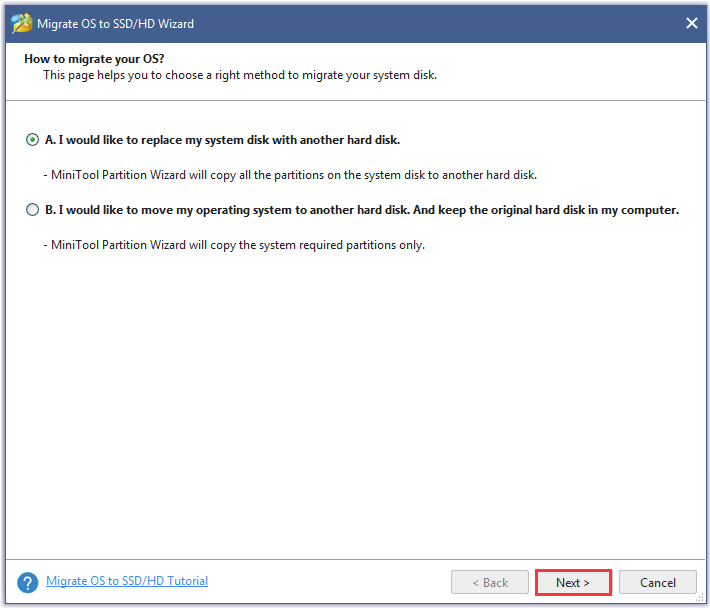
Step 6: Select the new internal hard drive as the target disk and then click the Next button.
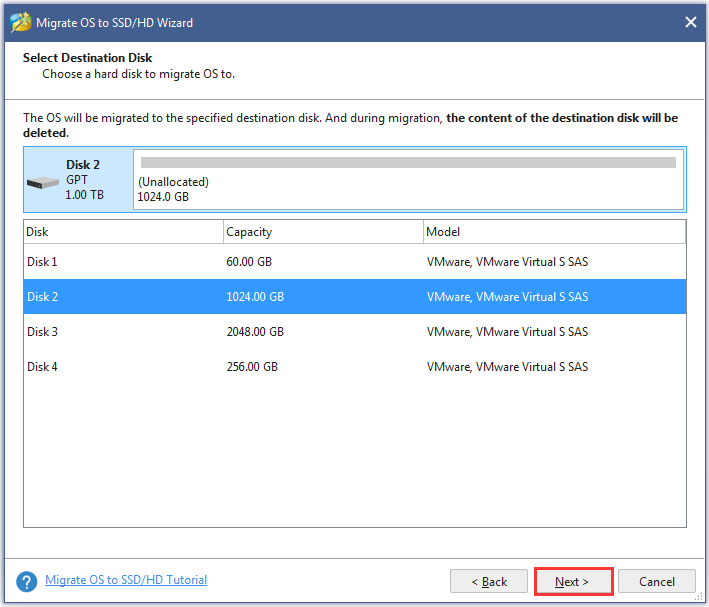
Step 7: Choose a copy option. Then, click the Next button to continue.
- The first option is to automatically make partitions take up the entire new internal hard drive.
- The second option is to copy partitions without resizing to the new internal hard drive.
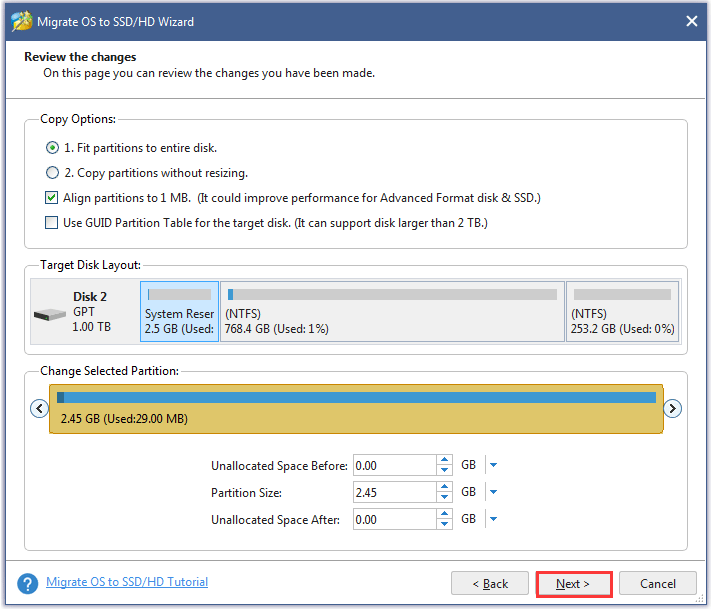
Step 8: Read the note on the following window and then click the Finish button.
Step 9: Click the Apply button on the main interface and then click the Yes button to apply the changes.
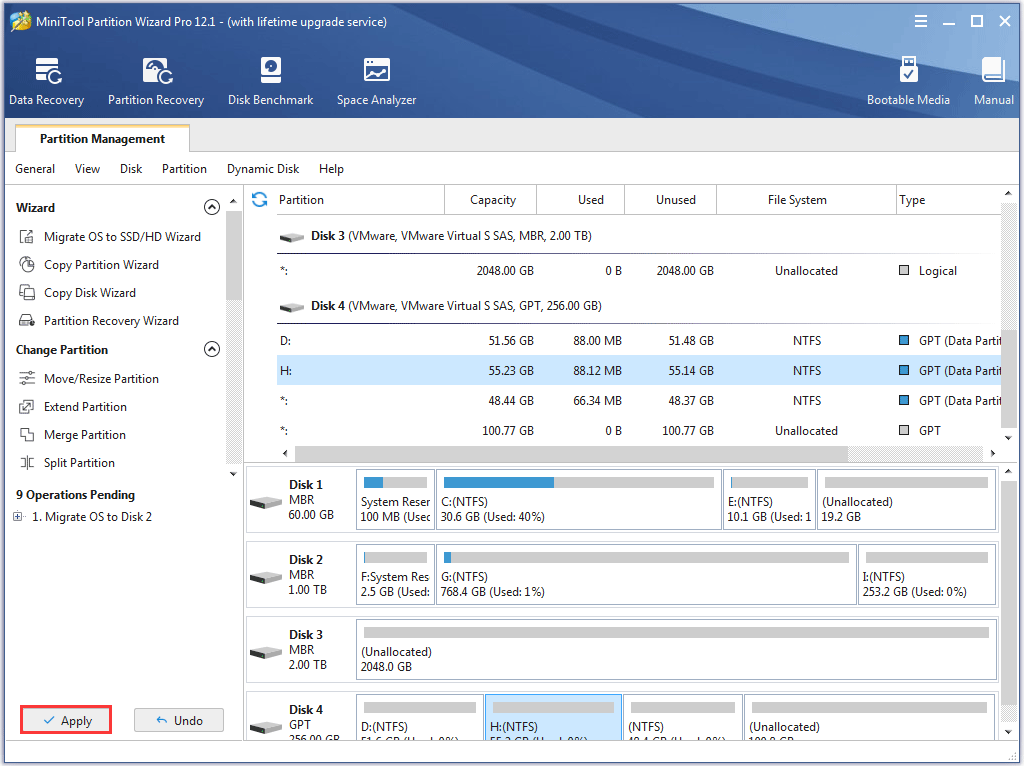
Step 10: Wait for the migrating process comes to an end. Once it ends, enter BIOS and set the new internal hard drive as the first boot order.
Step 11: Disconnect the new internal hard drive and then power off your computer.
Step 12: Replace then original internal hard drive with the new internal hard drive.
Step 13: Turn on your computer and you can enjoy the larger storage space.
What to Do If You Choose an External Hard Drive
Generally, all external hard drives are preformatted to be compatible with Windows systems. So, it is easy to use it: connect it to your computer through a USB cable, it appears on your computer, and you can simply move your files onto it.
If you want to use the drive on other operating systems like MacOS, Android, Linux, you need to reformat it to FAT32.
If your external hard drive exceeds in 32GB, give MiniTool Partition Wizard a try. It can help you format your drive to FAT32 even it is larger than 32GB.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
The process is easy:
- Connect the external hard drive to your computer.
- Highlight the external hard drive on the main interface of MiniTool Partition Wizard.
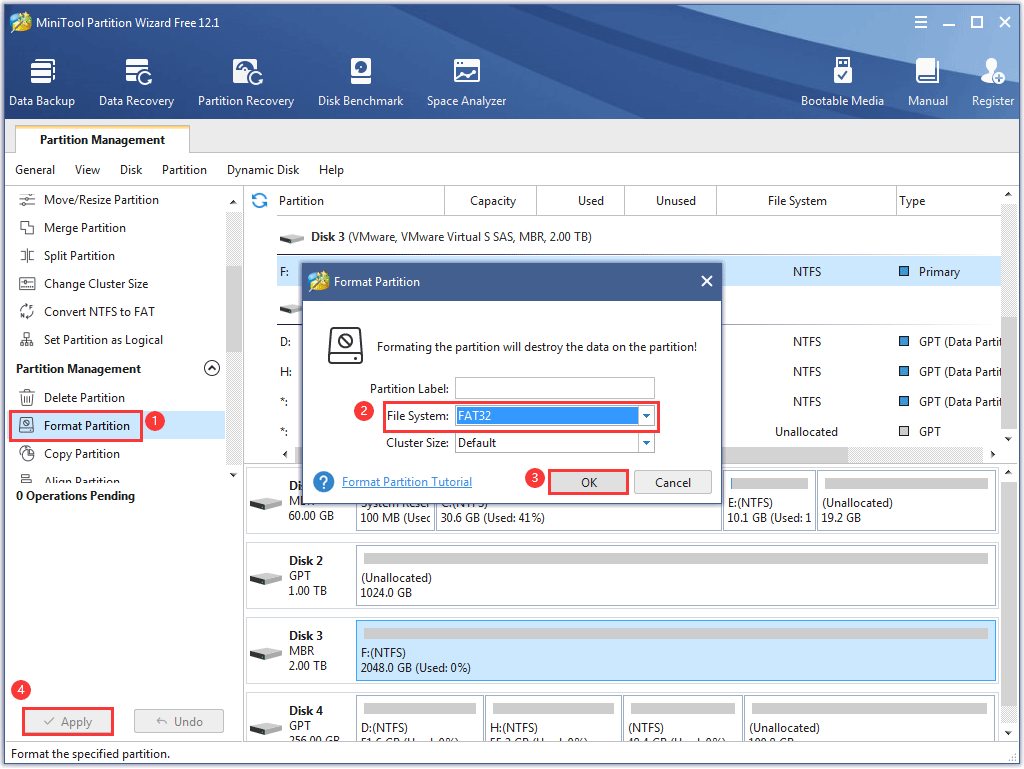
- Click the Format Partition feature.
- Select the FAT32 as the new file system.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the Apply button.
Although using an external hard drive is far easier than upgrading an external hard drive, there are more things you need to pay attention to:
- Keep the external hard drive and surrounding areas free of dust to avoid overheat.
- Keep the area around the external hard drive tidy to allow for maximum airflow.
- Make copies of the data stored on the external hard drive regularly in case of hard drive failure.
Which One Have You Picked?
This post has compared the two kinds from three aspects: performance, reliability, and cost. If you still have some doubts about external hard drive vs internal hard drive, please leave a comment in the following zone.
Which one have you picked? Internal or external hard drive? If you ran into some issues when using MiniTool Partition Wizard, please feel free to connect us via [email protected] and we will reply to you as soon as possible.
Internal vs External Hard drive FAQ
This depends on how the external hard drive manufacturer designed the device.
Generally, an external hard drive is a SATA hard drive, so you can take it out of the case and then mount it on your computer like other drives.
If the external hard drive is not like that, you need to prepare a converter cable to mount it on your computer. However, the shortcoming is that the read and write speed will slow down as your computer has to go through an extra bus every time it reads and writes data.
Moreover, most internal hard drives are affordable. So, it is wise to buy one and upgrade to it.
Leaving an external hard drive plugged in all the time is convenient for manual backup. However, there are also some disadvantages:
- Virus or malware infection: nowadays, viruses and malware easily attack a computer, which means the data stored on the external hard drive will be in such danger if you leave the drive plugged in all the time.
- Hard drive damage if suffering sudden power failures: if your external hard drive will be powered on automatically as your computer starts up, it will be vulnerable to power failures.
There are lots of factors you need to consider when choosing an external hard drive:
- Hard drive type (SSD or HDD);
- Size;
- Compatibility;
- Portability;
- Durability;
- Security.



User Comments :