A Swap partition is very useful when your Linux is running out of memory. Here MiniTool tells you what a Swap partition is and how to create a Swap partition.
What Is Swap Partition
As you know, swap partition is an important part of Linux. When installing Linux system, you may need to add a swap partition to your Linux. So, what is Swap Partition?
In fact, Linux Swap partition refers to the virtual memory partition under Linux. When physical memory of the system is not enough, the Swap partition can release a part of the hard disk space so that the current running programs can use it. The disk space which is released may come from some procedures that are not used for a long time, and the released disk space is temporarily saved to the swap partition.
When running those procedures, it allows to recover data that is saved to memory from a Swap partition. In other words, when the operating system needs data from the disk, Swap partition exchanges a part of data in main memory with a portion of data on the disk. The virtual memory technique breaks the limitation of physical memory in function, and it enables a computer to execute programs and manipulate data larger than the actual physical memory space. What’s more, it can ensure that each process is not affected by other program.
In Swap partition size, if Swap space is too large, disk space will be wasted, and if Swap space is too small, then the system may go wrong. Therefore, it is recommended to be 2 times larger than the physical memory. In Linux, it is limited to be at most 2 GB.
Why to Create Swap Partition
The above content introduce some important information about Swap partition, and now you may ask why to create a swap partition in Linux. Swap partition has three main advantages:
- It can leave some disk space when the computer memory is filled up completely.
- It can move some rarely-needed application and files away from the memory.
- It allows you to hibernate system. If there is no Swap partition, the computer is impossible to hibernate.
- The Swap partition can improve the performance of computer to some degrees.
Due to those merits, Swap partition is really useful and important in Linux. After installing system, you may want to create Linux partition. Here look at an example from forums.linuxmint:
“I just installed Linux mint 11 yesterday to solve my graphics chipset problem. But I forgot to create a swap partition. So my question is how can I create swap partition without reinstalling Linux mint? Also I have 4 GB ram on my laptop and I don’t use hibernation function on my laptop so do I really need swap? The space I reserved for swap partition is 4 GB & it is shown as unusable space in partition s/w. Thanks in advance.”
When encountering such a case, how to create a Swap partition? Don’t worry. Please read on and you can get a very easy way to achieve this aim.
How to Create a Linux Swap Partition
When searching “create Swap partition” in Google, you can find some methods, but it seems that some ways are a little complex. Fortunately, here is a very simple way introduced to you, that is to using a third-party partition and disk management software.
Thereinto, MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition is popular in managing Linux partition and disk for free. And it makes these Linux partitions intuitive on your computers so you can do Linux partition management easily. As a reliable and professional Swap partition manager, it can be used to copy partition, change partition type ID, do surface test, wipe partition and create partition.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Here are the steps about creating a Linux Swap partition.
Firstly you need to free download MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition and install it to your computer. Then launch this application to its main interface to do partition creation.
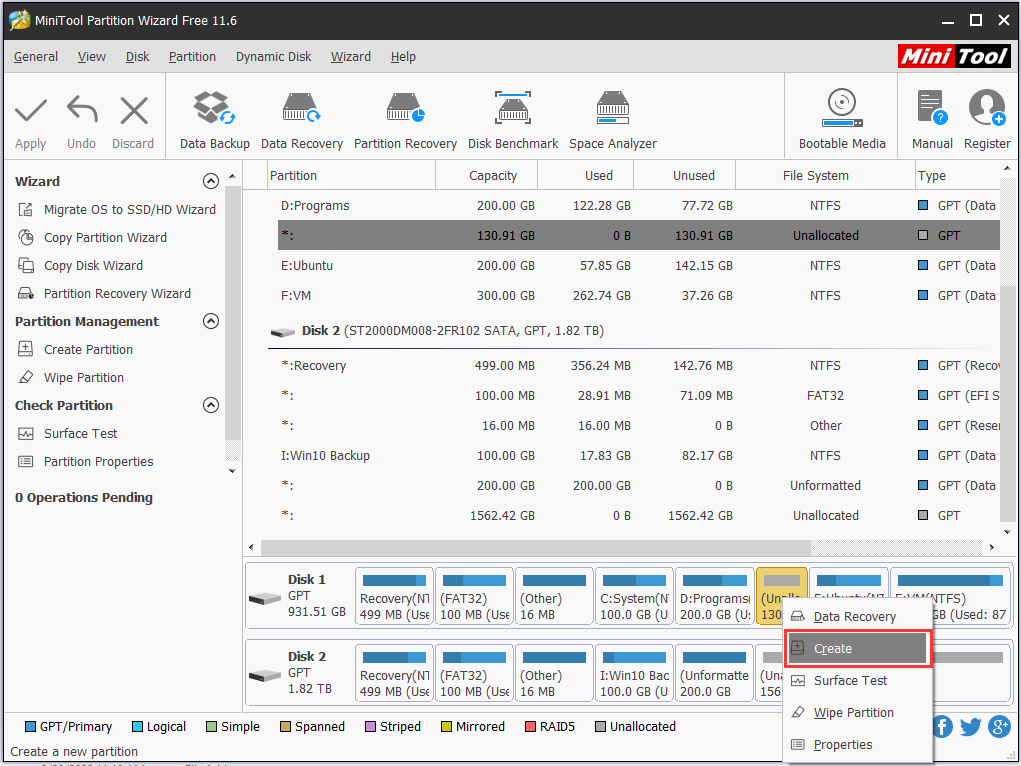
Step 1: Right click the unallocated space and select “Create” or click “Create Partition” from the left “Operations” menu after selecting the target unallocated space.
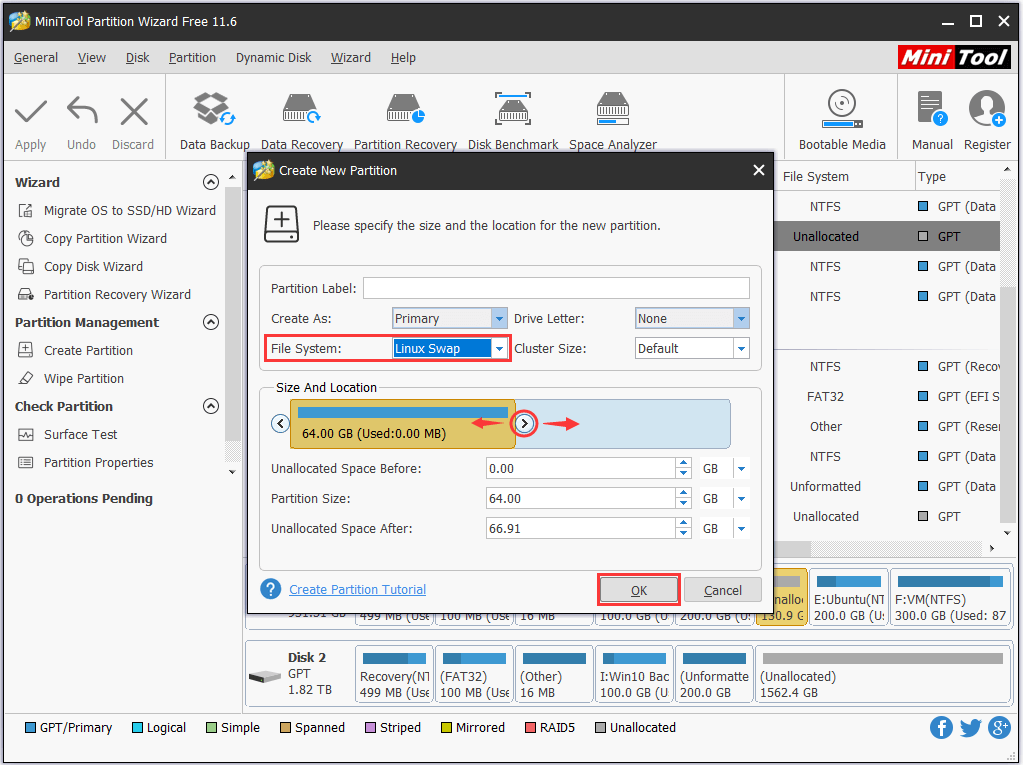
Step 2: Then you can select “Linux Swap” from the “File System” drop-down menu. Here you can set partition logical or primary and also set partition label. Moreover, during the process, you can change partition size. Here please set partition size as 4 GB by dragging the partition bar or by inputting 4096 in the “Partition Size” textbox.
Step 3: At last, click “Apply” to execute all operations.
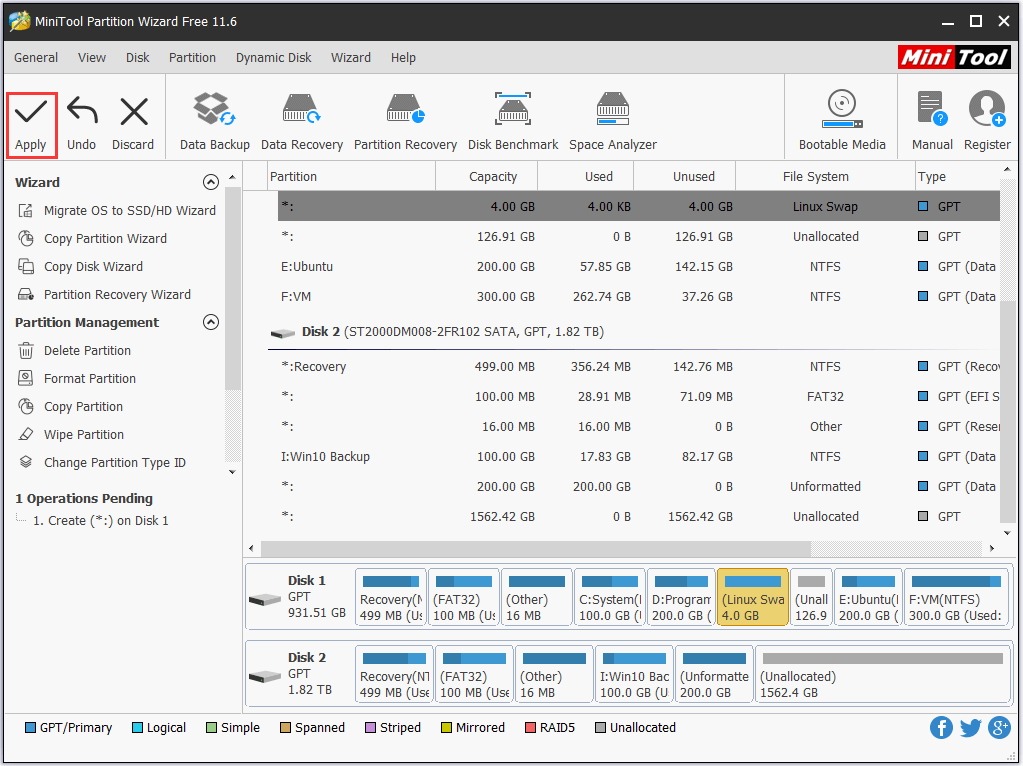
In conclusion, with the assistance of MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition, you can create Swap partition quickly and easily. Just only with three steps, you are able to achieve your aim. Please try this freeware at once.
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
